1. Overview
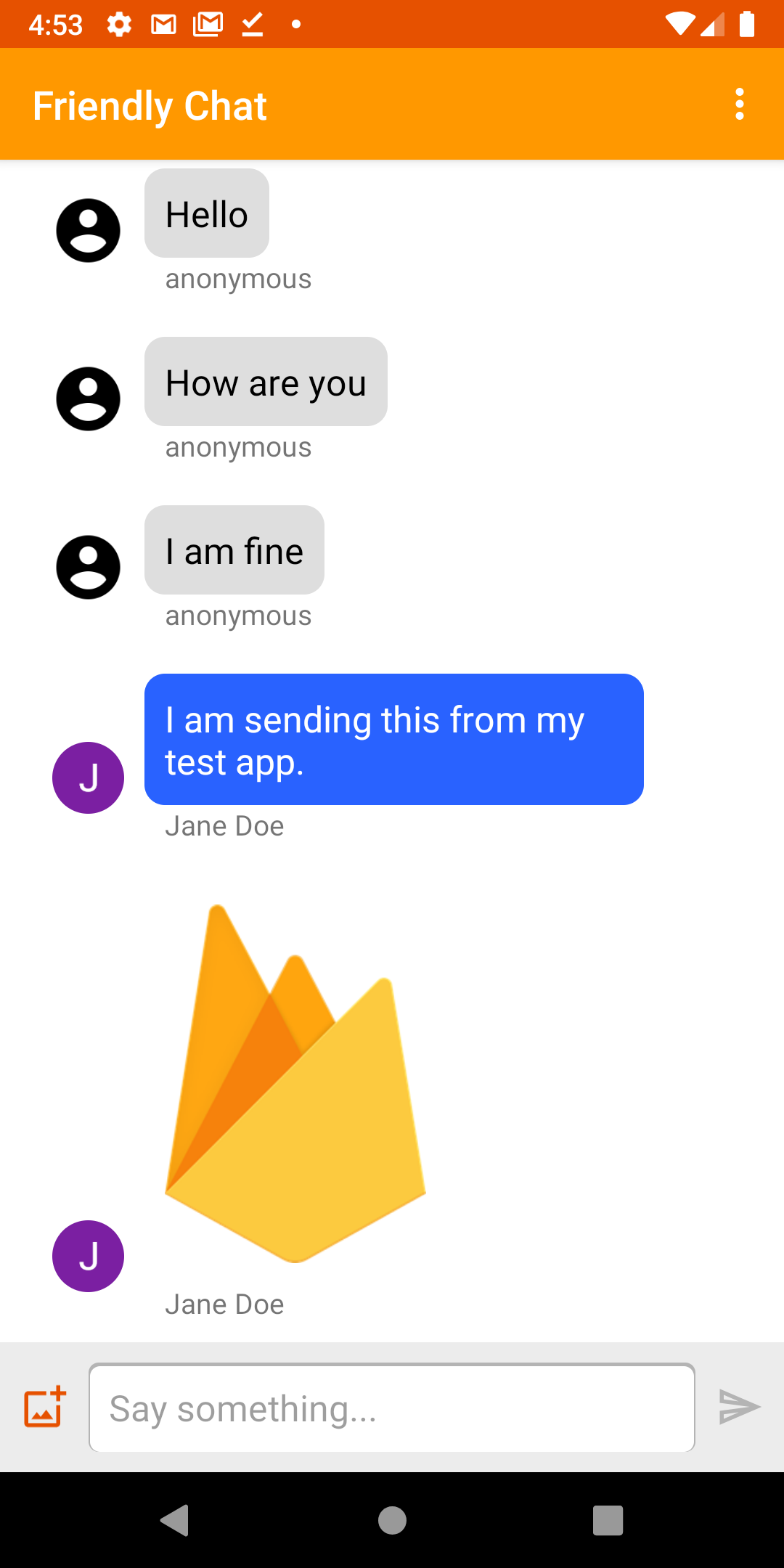
Image: Working Friendly Chat app.
Welcome to the Friendly Chat codelab. In this codelab, you'll learn how to use the Firebase platform to create a chat app on Android.
What you'll learn
- How to use Firebase Authentication to allow users to sign in.
- How to sync data using the Firebase Realtime Database.
- How to store binary files in Cloud Storage for Firebase.
- How to use the Firebase Local Emulator Suite to develop an Android app with Firebase.
What you'll need
- Latest Android Studio version.
- An Android Emulator with Android 5.0+.
- Node.js version 10 or higher (to use the Emulator Suite).
- Java 8 or higher. To install Java use these instructions; to check your version, run
java -version. - Familiarity with the Kotlin programming language.
2. Get the sample code
Clone the repository
Clone the GitHub repository from the command line:
$ git clone https://github.com/firebase/codelab-friendlychat-android
Import into Android Studio
In Android Studio, select File > Open, then select the build-android-start directory (  ) from the directory where you downloaded the sample code.
) from the directory where you downloaded the sample code.
You should now have the build-android-start project open in Android Studio. If you see a warning about a google-services.json file missing, don't worry. It will be added in a later step.
Check dependencies
In this codelab all of the dependencies you will need have already been added for you, but it's important to understand how to add the Firebase SDK to your app:
build.gradle.kts
plugins {
id("com.android.application") version "8.0.0" apply false
id("com.android.library") version "8.0.0" apply false
id("org.jetbrains.kotlin.android") version "1.8.20" apply false
// The google-services plugin is required to parse the google-services.json file
id("com.google.gms.google-services") version "4.3.15" apply false
}
app/build.gradle.kts
plugins {
id("com.android.application")
id("kotlin-android")
id("com.google.gms.google-services")
}
android {
// ...
}
dependencies {
// ...
// Google Sign In SDK
implementation("com.google.android.gms:play-services-auth:20.5.0")
// Firebase SDK
implementation(platform("com.google.firebase:firebase-bom:32.0.0"))
implementation("com.google.firebase:firebase-database-ktx")
implementation("com.google.firebase:firebase-storage-ktx")
implementation("com.google.firebase:firebase-auth-ktx")
// Firebase UI Library
implementation("com.firebaseui:firebase-ui-auth:8.0.2")
implementation("com.firebaseui:firebase-ui-database:8.0.2")
}
3. Install the Firebase CLI
In this codelab you'll use the Firebase Emulator Suite to locally emulate Firebase Auth, the Realtime Database and Cloud Storage. This provides a safe, fast, and no-cost local development environment to build your app.
Install the Firebase CLI
First you will need to install the Firebase CLI. If you are using macOS or Linux, you can run the following cURL command:
curl -sL https://firebase.tools | bash
If you are using Windows, read the installation instructions to get a standalone binary or to install via npm.
Once you've installed the CLI, running firebase --version should report a version of 9.0.0 or higher:
$ firebase --version 9.0.0
Log In
Run firebase login to connect the CLI to your Google account. This will open a new browser window to complete the login process. Make sure to choose the same account you used when creating your Firebase project earlier.
4. Connect to the Firebase Emulator Suite
Start the emulators
In your terminal, run the following command from the root of your local codelab-friendlychat-android directory:
firebase emulators:start --project=demo-friendlychat-android
You should see some logs like this. The port values were defined in the firebase.json file, which was included in the cloned sample code.
$ firebase emulators:start --project=demo-friendlychat-android
i emulators: Starting emulators: auth, database, storage
i emulators: Detected demo project ID "demo-friendlychat-android", emulated services will use a demo configuration and attempts to access non-emulated services for this project will fail.
i database: Database Emulator logging to database-debug.log
i ui: Emulator UI logging to ui-debug.log
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ ✔ All emulators ready! It is now safe to connect your app. │
│ i View Emulator UI at http://localhost:4000 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
┌────────────────┬────────────────┬────────────────────────────────┐
│ Emulator │ Host:Port │ View in Emulator UI │
├────────────────┼────────────────┼────────────────────────────────┤
│ Authentication │ localhost:9099 │ http://localhost:4000/auth │
├────────────────┼────────────────┼────────────────────────────────┤
│ Database │ localhost:9000 │ http://localhost:4000/database │
├────────────────┼────────────────┼────────────────────────────────┤
│ Storage │ localhost:9199 │ http://localhost:4000/storage │
└────────────────┴────────────────┴────────────────────────────────┘
Emulator Hub running at localhost:4400
Other reserved ports: 4500
Issues? Report them at https://github.com/firebase/firebase-tools/issues and attach the *-debug.log files.
Navigate to http://localhost:4000 in your web browser to view the Firebase Emulator Suite UI:
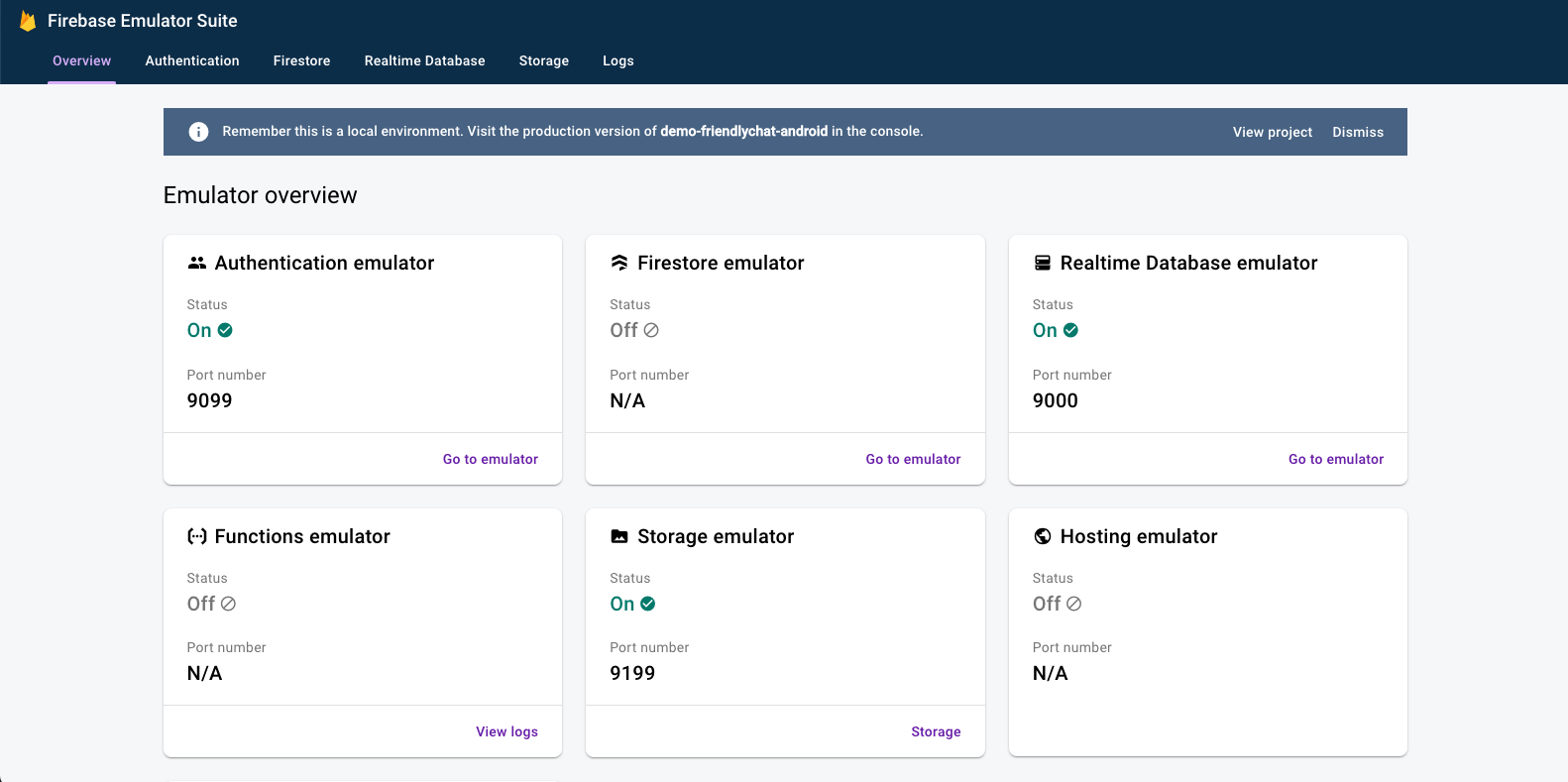
Leave the emulators:start command running for the rest of the codelab.
Connect your app
In Android Studio, open MainActivity.kt, then add the following code inside the onCreate method:
// When running in debug mode, connect to the Firebase Emulator Suite.
// "10.0.2.2" is a special IP address which allows the Android Emulator
// to connect to "localhost" on the host computer. The port values (9xxx)
// must match the values defined in the firebase.json file.
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Firebase.database.useEmulator("10.0.2.2", 9000)
Firebase.auth.useEmulator("10.0.2.2", 9099)
Firebase.storage.useEmulator("10.0.2.2", 9199)
}
5. Run the starter app
Add google-services.json
In order for your Android app to connect to Firebase, you must add a google-services.json file inside the app folder of your Android project. For the purposes of this codelab, we've provided a mock JSON file which will allow you to connect to the Firebase Emulator Suite.
Copy the mock-google-services.json file into the build-android-start/app folder as google-services.json:
cp mock-google-services.json build-android-start/app/google-services.json
In the final step of this codelab, you'll learn how to create a real Firebase project and Firebase Android App so that you can replace this mock JSON file with your own configuration.
Run the app
Now that you've imported the project into Android Studio and added a Firebase configuration JSON file, you're ready to run the app for the first time.
- Start your Android Emulator.
- In Android Studio, click Run (
 ) in the toolbar.
) in the toolbar.
The app should launch on your Android Emulator. At this point, you should see an empty message list, and sending and receiving messages will not work. In the next step of this codelab, you'll authenticate users so that they can use Friendly Chat.
6. Enable Authentication
This app will use Firebase Realtime Database to store all chat messages. Before we add data, though, we should make sure that the app is secure and that only authenticated users can post messages. In this step, we will enable Firebase Authentication and configure Realtime Database Security Rules.
Add basic sign-in functionality
Next we'll add some basic Firebase Authentication code to the app to detect users and implement a sign-in screen.
Check for current user
First add the following instance variable to the MainActivity.kt class:
MainActivity.kt
// Firebase instance variables
private lateinit var auth: FirebaseAuth
Now let's modify MainActivity to send the user to the sign-in screen whenever they open the app and are unauthenticated. Add the following to the onCreate() method after the binding is attached to the view:
MainActivity.kt
// Initialize Firebase Auth and check if the user is signed in
auth = Firebase.auth
if (auth.currentUser == null) {
// Not signed in, launch the Sign In activity
startActivity(Intent(this, SignInActivity::class.java))
finish()
return
}
We also want to check if the user is signed in during onStart():
MainActivity.kt
public override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
// Check if user is signed in.
if (auth.currentUser == null) {
// Not signed in, launch the Sign In activity
startActivity(Intent(this, SignInActivity::class.java))
finish()
return
}
}
Then implement the getUserPhotoUrl() and getUserName() methods to return the appropriate information about the currently authenticated Firebase user:
MainActivity.kt
private fun getPhotoUrl(): String? {
val user = auth.currentUser
return user?.photoUrl?.toString()
}
private fun getUserName(): String? {
val user = auth.currentUser
return if (user != null) {
user.displayName
} else ANONYMOUS
}
Then implement the signOut() method to handle the sign out button:
MainActivity.kt
private fun signOut() {
AuthUI.getInstance().signOut()
startActivity(Intent(this, SignInActivity::class.java))
finish()
}
Now we have all of the logic in place to send the user to the sign-in screen when necessary. Next we need to implement the sign-in screen to properly authenticate users.
Implement the Sign-In screen
Open the file SignInActivity.kt. Here a simple Sign-In button is used to initiate authentication. In this section, you will use FirebaseUI to implement the logic for sign in.
Add an Auth instance variable in the SignInActivity class under the // Firebase instance variables comment:
SignInActivity.kt
// Firebase instance variables
private lateinit var auth: FirebaseAuth
Then, edit the onCreate() method to initialize Firebase in the same way you did in MainActivity:
SignInActivity.kt
// Initialize FirebaseAuth
auth = Firebase.auth
Add an ActivityResultLauncher field to SignInActivity:
SignInActivity.kt
// ADD THIS
private val signIn: ActivityResultLauncher<Intent> =
registerForActivityResult(FirebaseAuthUIActivityResultContract(), this::onSignInResult)
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
// ...
}
Next, edit the onStart() method to kick off the FirebaseUI sign in flow:
SignInActivity.kt
public override fun onStart() {
super.onStart()
// If there is no signed in user, launch FirebaseUI
// Otherwise head to MainActivity
if (Firebase.auth.currentUser == null) {
// Sign in with FirebaseUI, see docs for more details:
// https://firebase.google.com/docs/auth/android/firebaseui
val signInIntent = AuthUI.getInstance()
.createSignInIntentBuilder()
.setLogo(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
.setAvailableProviders(listOf(
AuthUI.IdpConfig.EmailBuilder().build(),
AuthUI.IdpConfig.GoogleBuilder().build(),
))
.build()
signIn.launch(signInIntent)
} else {
goToMainActivity()
}
}
Next, implement the onSignInResult method to handle the sign in result. If the result of the signin was successful, continue to MainActivity:
SignInActivity.kt
private fun onSignInResult(result: FirebaseAuthUIAuthenticationResult) {
if (result.resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
Log.d(TAG, "Sign in successful!")
goToMainActivity()
} else {
Toast.makeText(
this,
"There was an error signing in",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
val response = result.idpResponse
if (response == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Sign in canceled")
} else {
Log.w(TAG, "Sign in error", response.error)
}
}
}
That's it! You've implemented authentication with FirebaseUI in just a few method calls and without needing to manage any server-side configuration.
Test your work
Run the app on your Android Emulator. You should be immediately sent to the sign-in screen. Tap the Sign in with email button, then create an account. If everything is implemented correctly, you should be sent to the messaging screen.
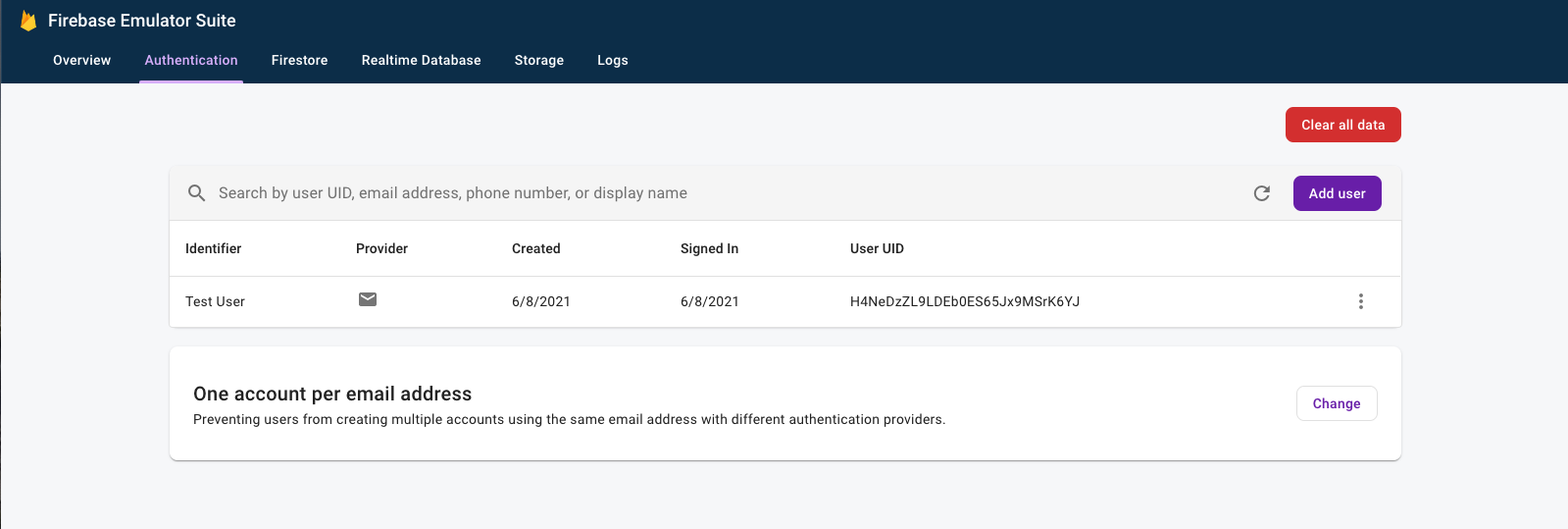
After signing in, open the Firebase Emulator Suite UI in your browser, then click the Authentication tab to see this first signed-in user account.
7. Read messages
In this step, we will add functionality to read and display messages stored in Realtime Database.
Import sample messages
- In the Firebase Emulator Suite UI, select the Realtime Database tab.
- Drag and drop the
initial_messages.jsonfile from your local copy of the codelab repository into the data viewer.
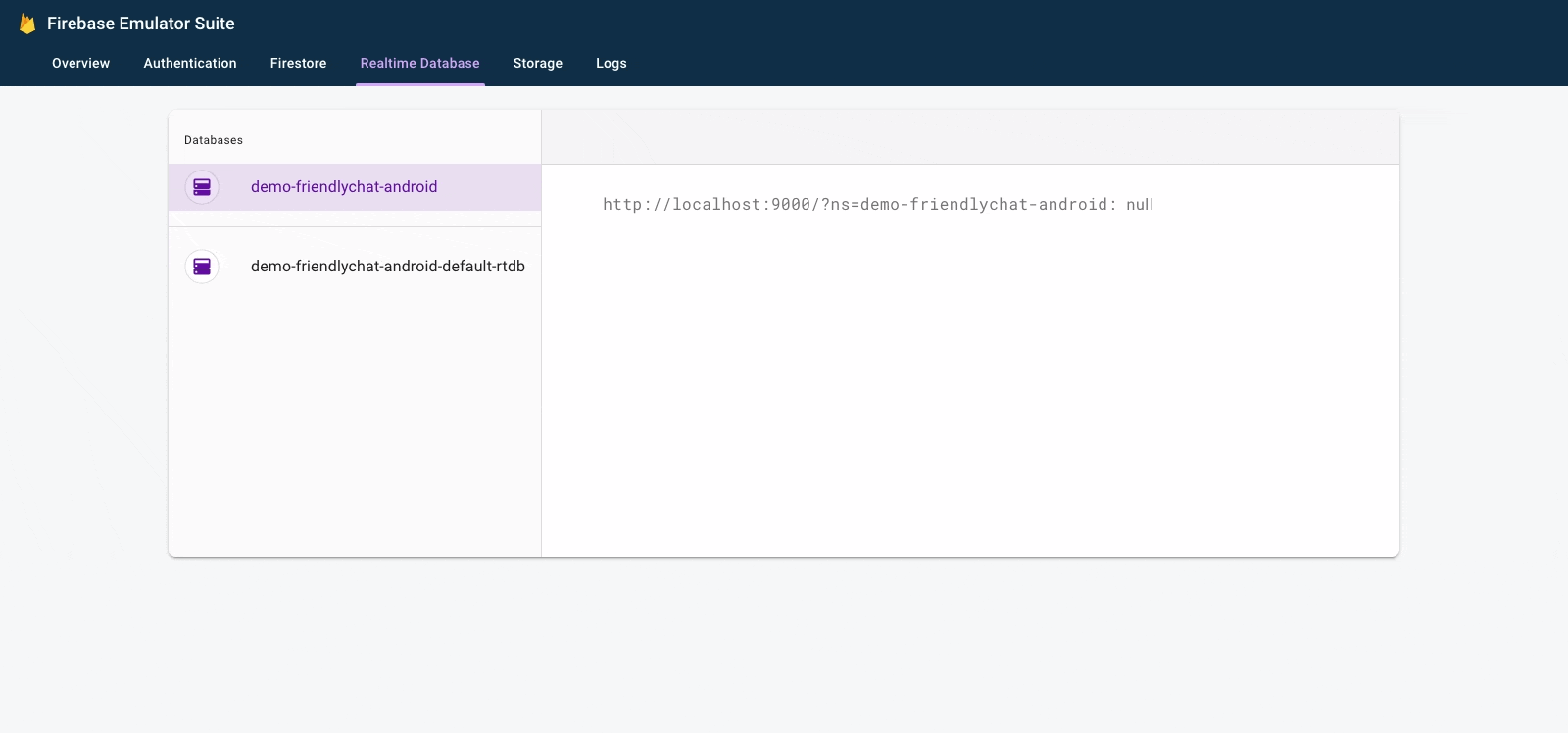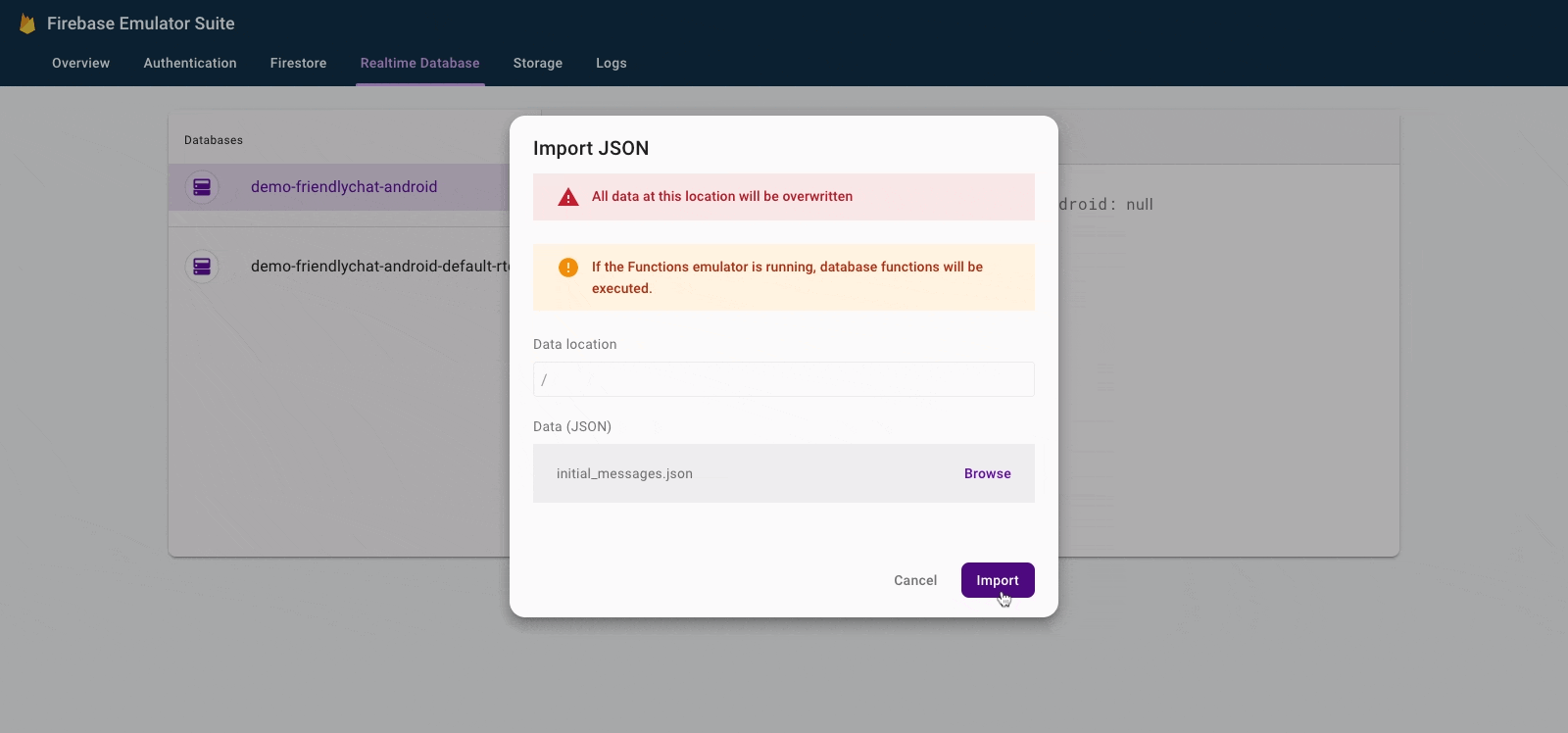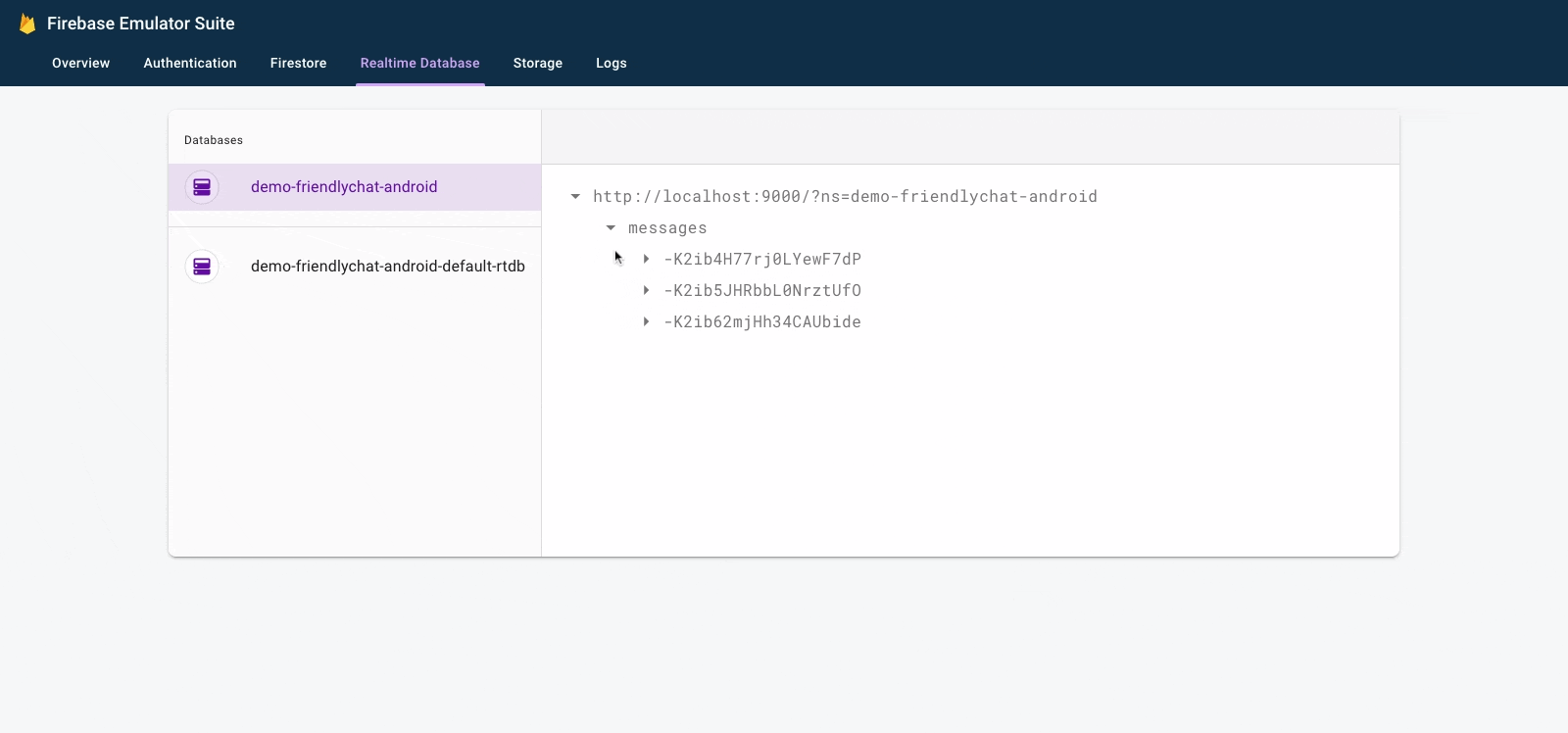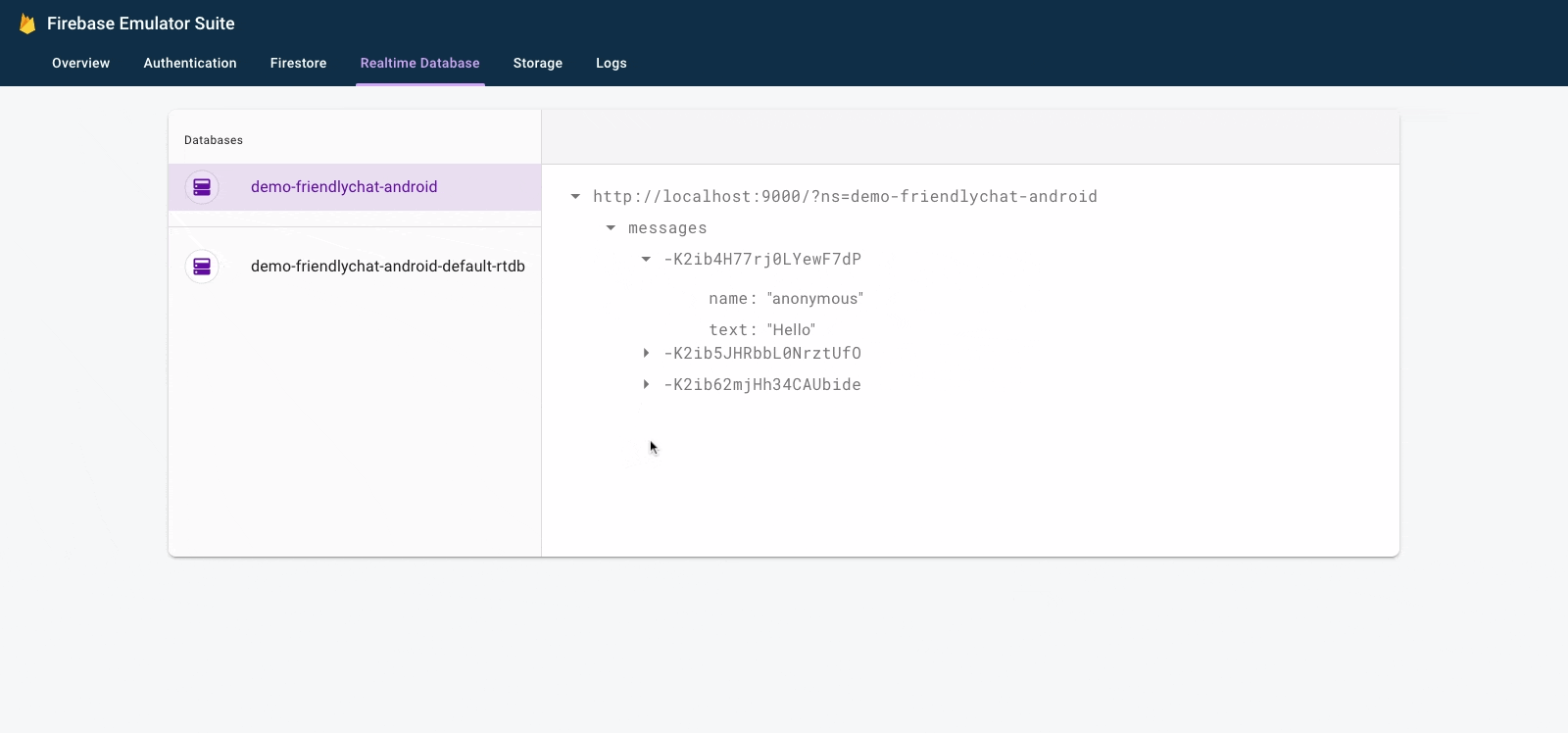
You should now have a few messages under the messages node of the database.
Read data
Synchronize messages
In this section we add code that synchronizes newly added messages to the app UI by:
- Initializing the Firebase Realtime Database and adding a listener to handle changes made to the data.
- Updating the
RecyclerViewadapter so new messages will be shown. - Adding the Database instance variables with your other Firebase instance variables in the
MainActivityclass:
MainActivity.kt
// Firebase instance variables
// ...
private lateinit var db: FirebaseDatabase
private lateinit var adapter: FriendlyMessageAdapter
Modify your MainActivity's onCreate() method under the comment // Initialize Realtime Database and FirebaseRecyclerAdapter with the code defined below. This code adds all existing messages from Realtime Database and then listens for new child entries under the messages path in your Firebase Realtime Database. It adds a new element to the UI for each message:
MainActivity.kt
// Initialize Realtime Database
db = Firebase.database
val messagesRef = db.reference.child(MESSAGES_CHILD)
// The FirebaseRecyclerAdapter class and options come from the FirebaseUI library
// See: https://github.com/firebase/FirebaseUI-Android
val options = FirebaseRecyclerOptions.Builder<FriendlyMessage>()
.setQuery(messagesRef, FriendlyMessage::class.java)
.build()
adapter = FriendlyMessageAdapter(options, getUserName())
binding.progressBar.visibility = ProgressBar.INVISIBLE
manager = LinearLayoutManager(this)
manager.stackFromEnd = true
binding.messageRecyclerView.layoutManager = manager
binding.messageRecyclerView.adapter = adapter
// Scroll down when a new message arrives
// See MyScrollToBottomObserver for details
adapter.registerAdapterDataObserver(
MyScrollToBottomObserver(binding.messageRecyclerView, adapter, manager)
)
Next in the FriendlyMessageAdapter.kt class implement the bind() method within the inner class MessageViewHolder():
FriendlyMessageAdapter.kt
inner class MessageViewHolder(private val binding: MessageBinding) : ViewHolder(binding.root) {
fun bind(item: FriendlyMessage) {
binding.messageTextView.text = item.text
setTextColor(item.name, binding.messageTextView)
binding.messengerTextView.text = if (item.name == null) ANONYMOUS else item.name
if (item.photoUrl != null) {
loadImageIntoView(binding.messengerImageView, item.photoUrl!!)
} else {
binding.messengerImageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.ic_account_circle_black_36dp)
}
}
...
}
We also need to display messages that are images, so also implement the bind() method within the inner class ImageMessageViewHolder():
FriendlyMessageAdapter.kt
inner class ImageMessageViewHolder(private val binding: ImageMessageBinding) :
ViewHolder(binding.root) {
fun bind(item: FriendlyMessage) {
loadImageIntoView(binding.messageImageView, item.imageUrl!!)
binding.messengerTextView.text = if (item.name == null) ANONYMOUS else item.name
if (item.photoUrl != null) {
loadImageIntoView(binding.messengerImageView, item.photoUrl!!)
} else {
binding.messengerImageView.setImageResource(R.drawable.ic_account_circle_black_36dp)
}
}
}
Finally, back in MainActivity, start and stop listening for updates from Firebase Realtime Database. Update the onPause() and onResume() methods in MainActivity as shown below:
MainActivity.kt
public override fun onPause() {
adapter.stopListening()
super.onPause()
}
public override fun onResume() {
super.onResume()
adapter.startListening()
}
Test syncing messages
- Click Run (
 ).
). - In the Emulator Suite UI, return to the Realtime Database tab, then manually add a new message. Confirm that the message shows up in your Android app:
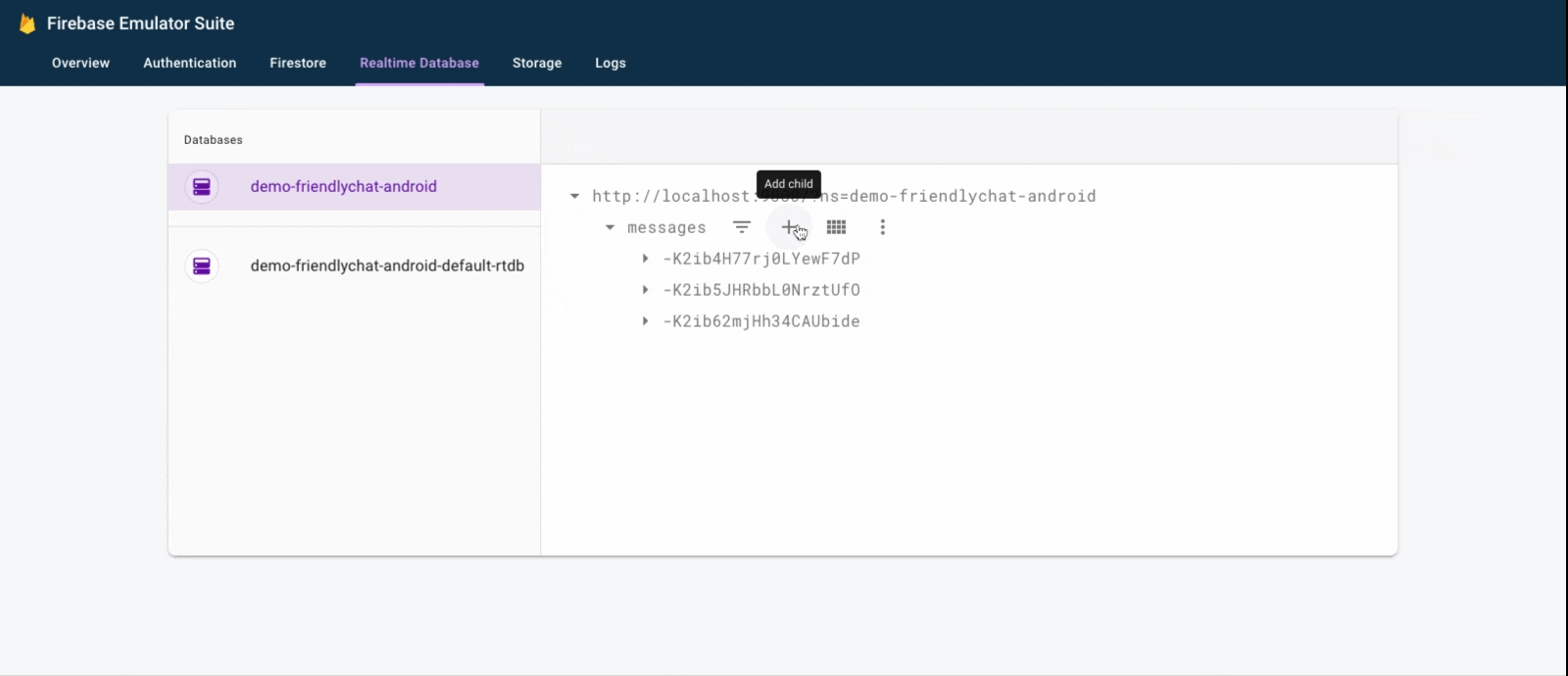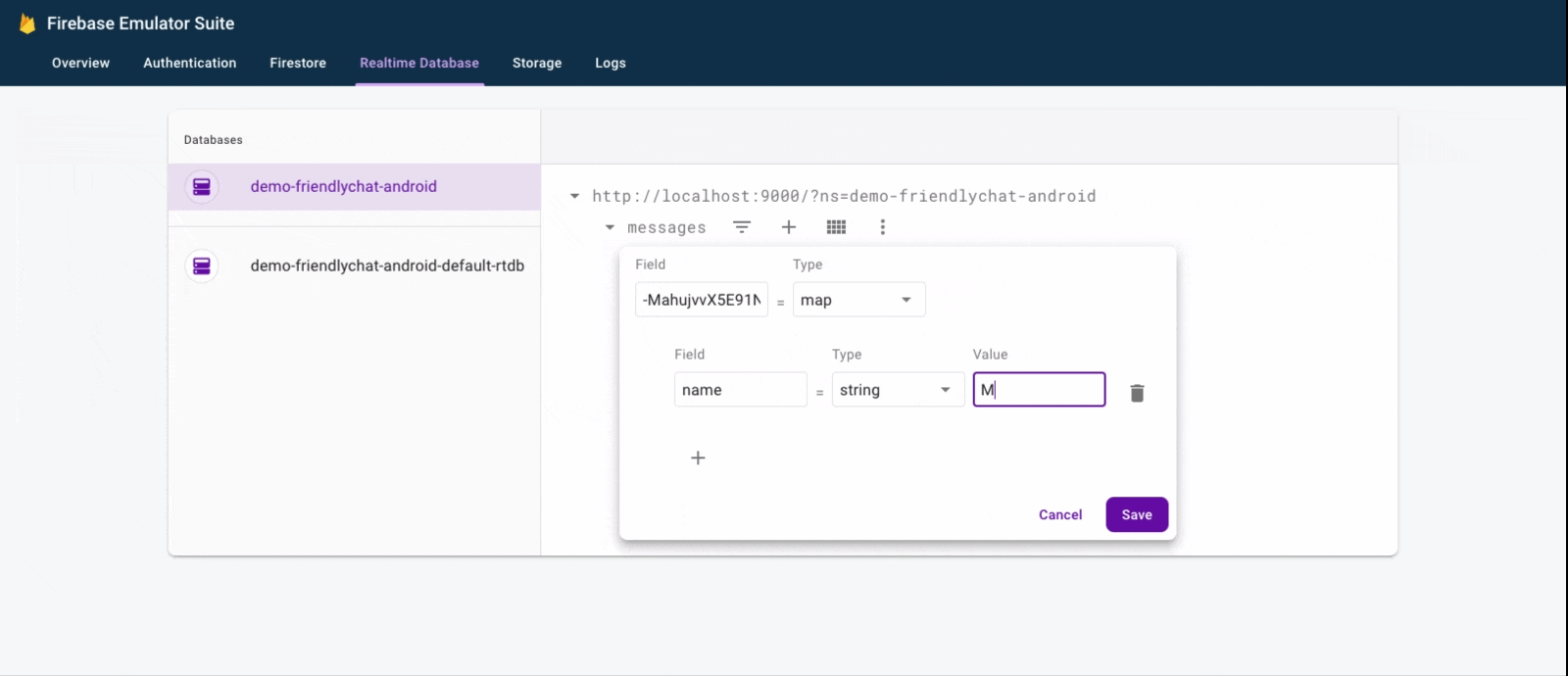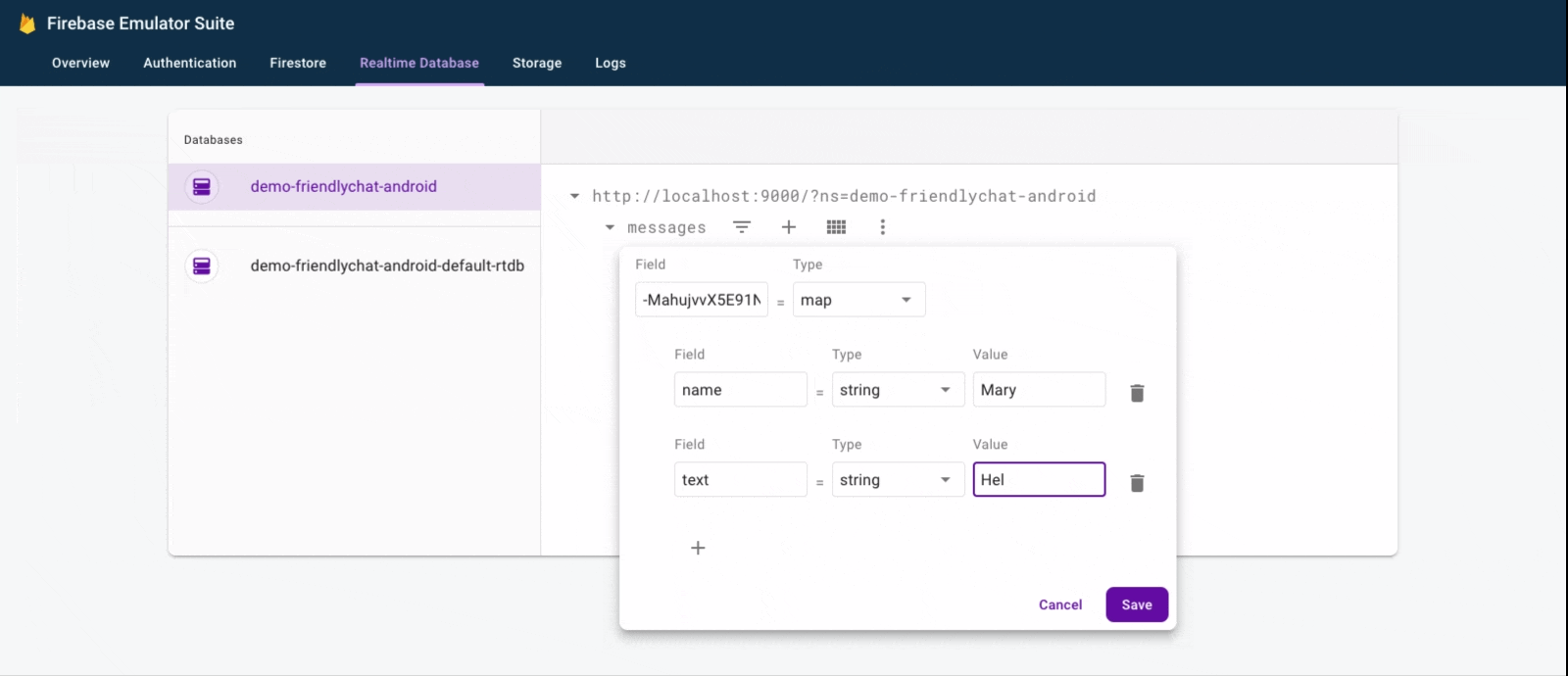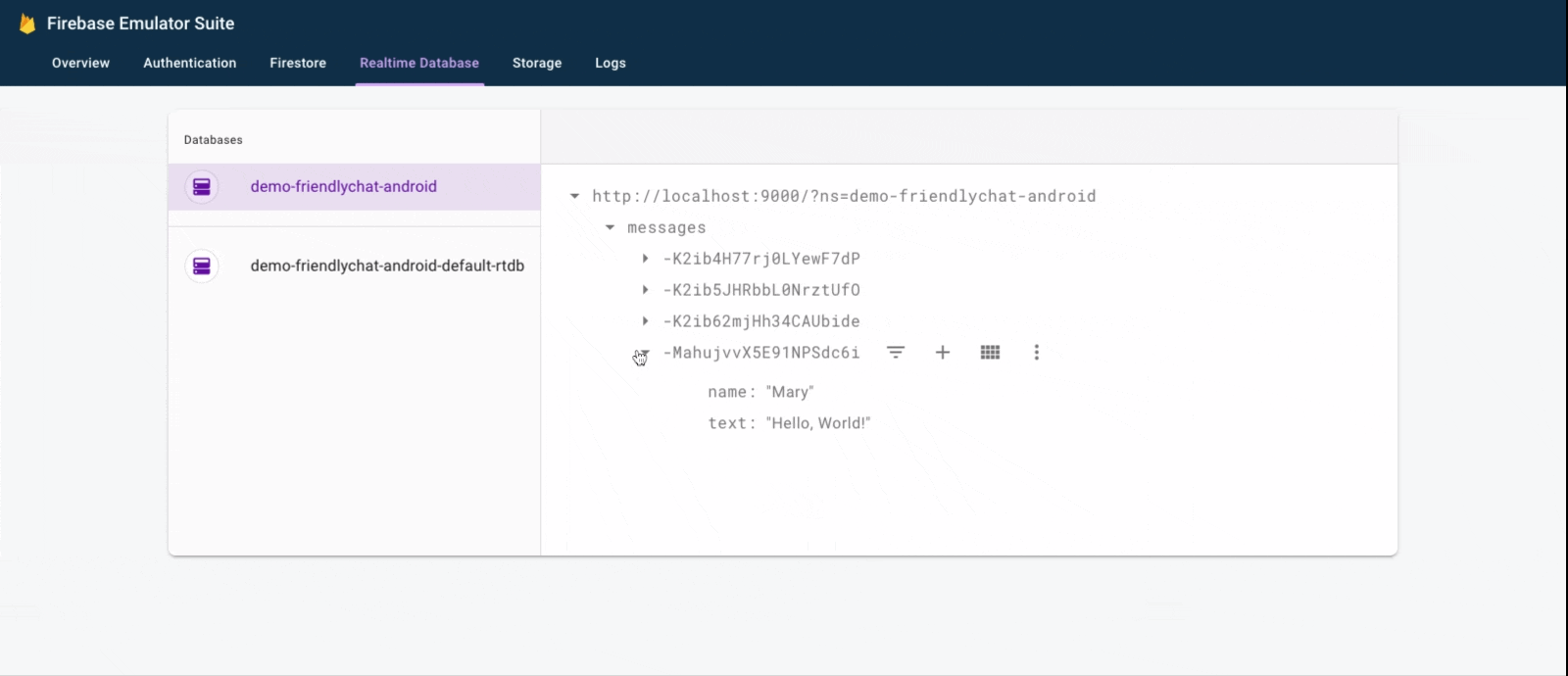
Congratulations, you just added a realtime database to your app!
8. Send Messages
Implement text message sending
In this section, you will add the ability for app users to send text messages. The code snippet below listens for click events on the send button, creates a new FriendlyMessage object with the contents of the message field, and pushes the message to the database. The push() method adds an automatically generated ID to the pushed object's path. These IDs are sequential which ensures that the new messages will be added to the end of the list.
Update the click listener of the send button in the onCreate() method in the MainActivity class. This code is at the bottom of the onCreate() method already. Update the onClick() body to match the code below:
MainActivity.kt
// Disable the send button when there's no text in the input field
// See MyButtonObserver for details
binding.messageEditText.addTextChangedListener(MyButtonObserver(binding.sendButton))
// When the send button is clicked, send a text message
binding.sendButton.setOnClickListener {
val friendlyMessage = FriendlyMessage(
binding.messageEditText.text.toString(),
getUserName(),
getPhotoUrl(),
null /* no image */
)
db.reference.child(MESSAGES_CHILD).push().setValue(friendlyMessage)
binding.messageEditText.setText("")
}
Implement image message sending
In this section, you will add the ability for app users to send image messages. Creating an image message is done with these steps:
- Select image
- Handle image selection
- Write temporary image message to the Realtime Database
- Begin to upload selected image
- Update image message URL to that of the uploaded image, once upload is complete
Select Image
To add images this codelab uses Cloud Storage for Firebase. Cloud Storage is a good place to store the binary data of your app.
Handle image selection and write temp message
Once the user has selected an image, the image selection Intent is launched. This is already implemented in the code at the end of the onCreate() method. When finished it calls the MainActivity's onImageSelected() method. Using the code snippet below, you will write a message with a temporary image url to the database indicating the image is being uploaded.
MainActivity.kt
private fun onImageSelected(uri: Uri) {
Log.d(TAG, "Uri: $uri")
val user = auth.currentUser
val tempMessage = FriendlyMessage(null, getUserName(), getPhotoUrl(), LOADING_IMAGE_URL)
db.reference
.child(MESSAGES_CHILD)
.push()
.setValue(
tempMessage,
DatabaseReference.CompletionListener { databaseError, databaseReference ->
if (databaseError != null) {
Log.w(
TAG, "Unable to write message to database.",
databaseError.toException()
)
return@CompletionListener
}
// Build a StorageReference and then upload the file
val key = databaseReference.key
val storageReference = Firebase.storage
.getReference(user!!.uid)
.child(key!!)
.child(uri.lastPathSegment!!)
putImageInStorage(storageReference, uri, key)
})
}
Upload image and update message
Add the method putImageInStorage() to MainActivity. It is called in onImageSelected() to initiate the upload of the selected image. Once the upload is complete you will update the message to use the appropriate image.
MainActivity.kt
private fun putImageInStorage(storageReference: StorageReference, uri: Uri, key: String?) {
// First upload the image to Cloud Storage
storageReference.putFile(uri)
.addOnSuccessListener(
this
) { taskSnapshot -> // After the image loads, get a public downloadUrl for the image
// and add it to the message.
taskSnapshot.metadata!!.reference!!.downloadUrl
.addOnSuccessListener { uri ->
val friendlyMessage =
FriendlyMessage(null, getUserName(), getPhotoUrl(), uri.toString())
db.reference
.child(MESSAGES_CHILD)
.child(key!!)
.setValue(friendlyMessage)
}
}
.addOnFailureListener(this) { e ->
Log.w(
TAG,
"Image upload task was unsuccessful.",
e
)
}
}
Test sending messages
- In Android Studio, click the
 Run button.
Run button. - In your Android Emulator, enter a message, then tap the send button. The new message should be visible in the app UI and in the Firebase Emulator Suite UI.
- In the Android Emulator, tap the "+" image to select an image from your device. The new message should be visible first with a placeholder image, and then with the selected image once the image upload is complete. The new message should also be visible in the Emulator Suite UI, specifically as an object in the Realtime Database tab and as a blob in the Storage tab.
9. Congratulations!
You just built a real-time chat application using Firebase!
What you learned
- Firebase Authentication
- Firebase Realtime Database
- Cloud Storage for Firebase
Next, try using what you learned in this codelab to add Firebase to your own Android app! To learn more about Firebase, visit firebase.google.com.
If you want to learn how to set up a real Firebase project and use real Firebase resources (instead of a demo project and only emulated resources), continue to the next step.
Note: Even after you set up a real Firebase project and especially when you get started building a real app, we recommend using the Firebase Local Emulator Suite for development and testing.
10. Optional: Create and set up a Firebase project
In this step, you'll create a real Firebase project and a Firebase Android App to use with this codelab. You'll also add your app-specific Firebase configuration to your app. And finally, you'll set up real Firebase resources to use with your app.
Create a Firebase project
- In your browser, go to the Firebase console.
- Select Add project.
- Select or enter a project name. You can use any name you want.
- You do not need Google Analytics for this codelab, so you can skip enabling it for your project.
- Click Create Project. When your project is ready, click Continue.
Add Firebase to your Android project
Before you begin this step, get the SHA1 hash of your app. Run the following command from your local build-android-start directory to determine the SHA1 of your debug key:
./gradlew signingReport Store: /Users/<username>/.android/debug.keystore Alias: AndroidDebugKey MD5: A5:88:41:04:8F:06:59:6A:AE:33:76:87:AA:AD:19:23 SHA1: A7:89:F5:06:A8:07:A1:22:EC:90:6A:A6:EA:C3:D4:8B:3A:30:AB:18 SHA-256: 05:A2:2A:35:EE:F2:51:23:72:4D:72:67:A5:6A:8A:58:22:2C:00:A6:AB:F6:45:D5:A1:82:D8:90:A4:69:C8:FE Valid until: Wednesday, August 10, 2044
You should see some output like the above. The important line is the SHA1 hash. If you're unable to find your SHA1 hash, see this page for more information.
Go back to the Firebase console, and follow these steps to register your Android project with your Firebase project:
- From the overview screen of your new project, click the Android icon to launch the setup workflow:
- On the next screen, enter
com.google.firebase.codelab.friendlychatas the package name for your app. - Click Register App, then click Download google-services.json to download your Firebase configuration file.
- Copy the
google-services.jsonfile into theappdirectory of your Android project. - Skip the next steps shown in the console's setup workflow (they've already been done for you in the
build-android-startproject). - Make sure that all dependencies are available to your app by syncing your project with Gradle files. From the Android Studio toolbar, select File > Sync Project with Gradle Files. You may also need to run Build/Clean Project and Build/Rebuild Project for the config changes to take place.
Configure Firebase Authentication
Before your app can access the Firebase Authentication APIs on behalf of your users, you need to enable Firebase Authentication and the sign-in providers you want to use in your app.
- In the Firebase console, select Authentication from the left-side navigation panel.
- Select the Sign-in method tab.
- Click Email/Password, then toggle the switch to enabled (blue).
- Click Google, then toggle the switch to enabled (blue) and set a project support email.
If you get errors later in this codelab with the message "CONFIGURATION_NOT_FOUND", come back to this step and double check your work.
Configure Realtime Database
The app in this codelab stores chat messages in Firebase Realtime Database. In this section, we'll create a database and configure its security via a JSON configuration language called Firebase Security Rules.
- In the Firebase console, select Realtime Database from the left-side navigation panel.
- Click Create Database to create a new Realtime Database instance. When prompted, select the
us-central1region, then click Next. - When prompted about security rules, choose locked mode, then click Enable.
- Once the database instance has been created, select the Rules tab, then update the rules configuration with the following:
{ "rules": { "messages": { ".read": "auth.uid != null", ".write": "auth.uid != null" } } }
For more information on how Security Rules work (including documentation on the "auth" variable), see the Realtime Database security documentation.
Configure Cloud Storage for Firebase
- In the Firebase console, select Storage from the left-side navigation panel.
- Click Get Started to enable Cloud Storage for your project.
- Follow the steps in the dialog to set up your bucket, using the suggested defaults.
Connect to Firebase resources
In an earlier step of this codelab, you added the following to MainActivity.kt. This conditional block connected your Android project to the Firebase Emulator Suite.
// REMOVE OR DISABLE THIS
if (BuildConfig.DEBUG) {
Firebase.database.useEmulator("10.0.2.2", 9000)
Firebase.auth.useEmulator("10.0.2.2", 9099)
Firebase.storage.useEmulator("10.0.2.2", 9199)
}
If you want to connect your app to your new real Firebase project and its real Firebase resources, you can either remove this block or run your app in release mode so that BuildConfig.DEBUG is false.
