1. Before you begin
In this codelab, you'll learn to use Genkit for integrating generative AI into your app. Genkit is an open source framework that helps you build, deploy, and monitor production-ready AI-powered apps.
Genkit is designed for app developers, to help you easily integrate powerful AI capabilities into your apps with familiar patterns and paradigms. It's built by the Firebase team, leveraging our experience in building tools used by millions of developers worldwide.
Prerequisites
- Familiarity with Firestore, Node.js, and TypeScript.
What you'll learn
- How to build smarter apps with Firestore's advanced vector similarity search capabilities.
- How to practically implement generative AI in your apps using Genkit.
- Get your solution ready for deployment and integration.
What you'll need
- A browser of your choice, such as Google Chrome
- A development environment with a code editor and terminal
- A Google Account for the creation and management of your Firebase project
2. Review the web app and cloud services used
In this section, you'll review the web app that you'll build with this codelab, as well learn about the cloud services that you'll use.
Web app
In this codelab, you'll work in the codebase of an app called Compass — a vacation planning app. Users can pick a destination, look through activities at the destination, and create an itinerary for their trip.
In this codelab, you'll implement two new features that are intended to improve user engagement with the app's homepage. Both features are powered by generative AI:
- The app currently displays a static list of destinations. You'll change it to be dynamic!
- You'll implement an auto-populated itinerary to hopefully increase stickiness.

Services used
In this codelab, you'll use many Firebase and Cloud services and features, and most of the starter code for them is provided for you. The following table contains the services that you'll use and the reasons for using them.
Service | Reason for use |
You use Genkit to bring generative AI into a Node.js / Next.js application. | |
You store data in Cloud Firestore, which is then used for vector similarity search. | |
You use foundational models from Vertex AI (like Gemini) to power your AI features. | |
You can optionally use the new streamlined Firebase App Hosting to serve your dynamic Next.js web app (connected to a GitHub repo). |
3. Set up your development environment
Verify your Node.js version
- In your terminal, verify that you have Node.js version 20.0.0 or higher installed:
node -v - If you don't have Node.js version 20.0.0 or higher, download the latest LTS version and install it.
Get the source code for the codelab
If you have a GitHub account:
- Create a new repository using our template from github.com/FirebaseExtended/codelab-ai-genkit-rag
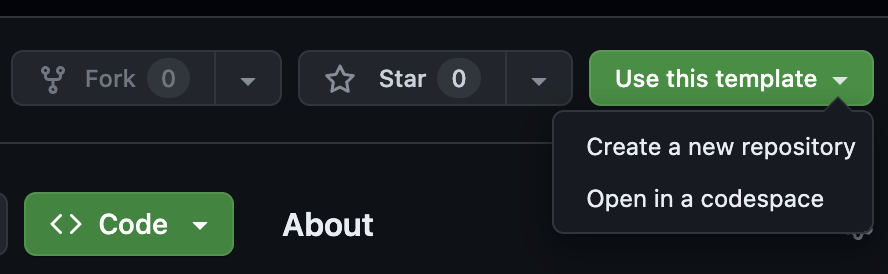
- Create a local clone of the codelab's GitHub repository you just created:
git clone https://github.com/<your-github-handle>/codelab-ai-genkit-rag
If you don't have git installed or prefer to not create a new repo:
Download the GitHub repository as a zip file.
Review the folder structure
On your local machine, find the cloned repository and review the folder structure:
Folder | Description |
| Helper command line tool to quickly pre-populate your Firestore collection |
*everything else | Next.js web app code |
The root folder includes a README.md file that offers a quick start to run the web app, using streamlined instructions. However, if you're a first-time learner, you should complete this codelab (instead of the quickstart) because the codelab contains the most comprehensive set of instructions.
If you're unsure of whether you correctly applied code as instructed throughout this codelab, you can find the solution code in the end git branch.
Install the Firebase CLI
- Verify that you have the Firebase CLI installed and that it's version 13.6 or higher:
firebase --version - If you have the Firebase CLI installed, but it's not version 13.6 or higher, update it:
npm update -g firebase-tools - If you don't have the Firebase CLI installed, install it:
npm install -g firebase-tools
If you're unable to update or install the Firebase CLI because of permission errors, see the npm documentation or use another installation option.
Log into Firebase
- In your terminal, log in to Firebase:
firebase login - In your terminal, depending on whether you want Firebase to collect data, enter
YorN. (either option works for this codelab) - In your browser, select your Google Account and click Allow.
Install Google Cloud's gcloud CLI
- Install the gcloud CLI.
- In your terminal, log into Google Cloud:
gcloud auth login
4. Set up your Firebase project
In this section, you'll set up a Firebase project and register a Firebase Web App in it. You'll also enable a few services that are used by the sample web app later in this codelab.
All of the steps in this section are performed in the Firebase console.
Create a Firebase project
- Sign into the Firebase console using the same Google Account you used in the previous step.
- Click the button to create a new project, and then enter a project name (for example,
Compass Codelab).
- Click Continue.
- If prompted, review and accept the Firebase terms, and then click Continue.
- (Optional) Enable AI assistance in the Firebase console (called "Gemini in Firebase").
- For this codelab, you do not need Google Analytics, so toggle off the Google Analytics option.
- Click Create project, wait for your project to provision, and then click Continue.
Add a web app to your Firebase project
- Navigate to the Project Overview screen in your Firebase project, and then click
 Web.
Web.
- In the App nickname text box, enter a memorable app nickname, such as
My Compass Codelab App. You can leave the check box for setting up Firebase Hosting unchecked, because you will be optionally setting up a hosting service in the last step of this codelab.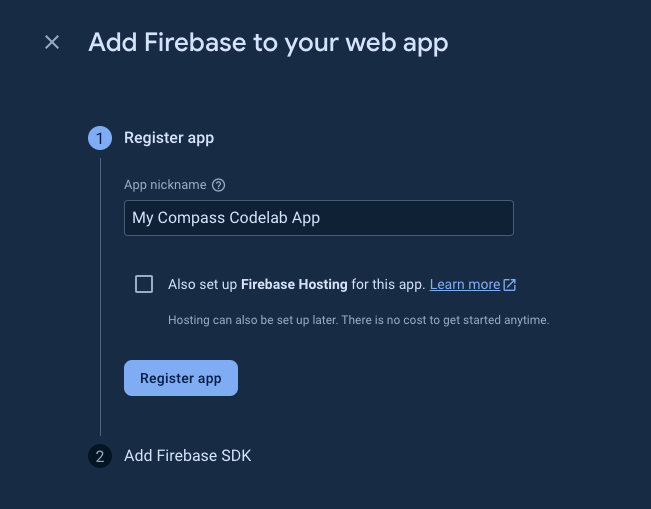
- Click Register app > Continue to console.
Great! You have now registered a web app in your new Firebase project.
Upgrade your Firebase pricing plan
To use Genkit and Vertex AI (and their underlying cloud services), your Firebase project needs to be on the pay-as-you go (Blaze) pricing plan, which means it's linked to a Cloud Billing account.
- A Cloud Billing account requires a payment method, like a credit card.
- If you're new to Firebase and Google Cloud, check if you're eligible for a $300 credit and a Free Trial Cloud Billing account.
- If you're doing this codelab as part of an event, ask your organizer if there are any Cloud credits available.
Learn more about pricing for Vertex AI.
To upgrade your project to the Blaze plan, follow these steps:
- In the Firebase console, select to upgrade your plan.
- Select the Blaze plan. Follow the on-screen instructions to link a Cloud Billing account to your project.
If you needed to create a Cloud Billing account as part of this upgrade, you might need to navigate back to the upgrade flow in the Firebase console to complete the upgrade.
Set up Cloud Firestore
- In the left-panel of the Firebase console, expand Build and then select Firestore database.
- Click Create database.
- Choose Standard edition and click Next.
- Leave the Database ID set to
(default). - Select a location for your database, then click Next.
For a real app, you want to choose a location that's close to your users. - Click Start in test mode. Read the disclaimer about the security rules.
Do not distribute or expose an app publicly without adding Security Rules for your database. - Click Create.
Enable Vertex AI
Use the gcloud CLI to set up Vertex AI. For all the commands on this page, make sure to replace YOUR_PROJECT_ID with the ID of your Firebase project.
- In your terminal, set the default project for the Google Cloud SDK:
gcloud config set project YOUR_PROJECT_ID - If you see a warning message saying "WARNING: Your active project does not match the quota project in your local Application Default Credentials file. This might result in unexpected quota issues.", then run the following command to set the quota project:
gcloud auth application-default set-quota-project YOUR_PROJECT_ID - Enable the Vertex AI service in your project:
gcloud services enable aiplatform.googleapis.com
5. Set up the web app
To run the web app, you'll need to run commands in your terminal and add code within your code editor. For all the commands on this page, make sure to replace YOUR_PROJECT_ID with the ID of your Firebase project.
Configure the Firebase CLI to target your project
- In your terminal, navigate to the root directory of your codelab project.
- To make the Firebase CLI execute all commands against your Firebase project, run the following command:
firebase use YOUR_PROJECT_ID
Import sample data into Firestore
So that you can get started quickly, this codelab provides you with pre-generated sample data for Firestore.
- To allow the local codebase to run code that would normally use a service account, run the following command in your terminal:
gcloud auth application-default login - To import the sample Firestore data, run the following commands:
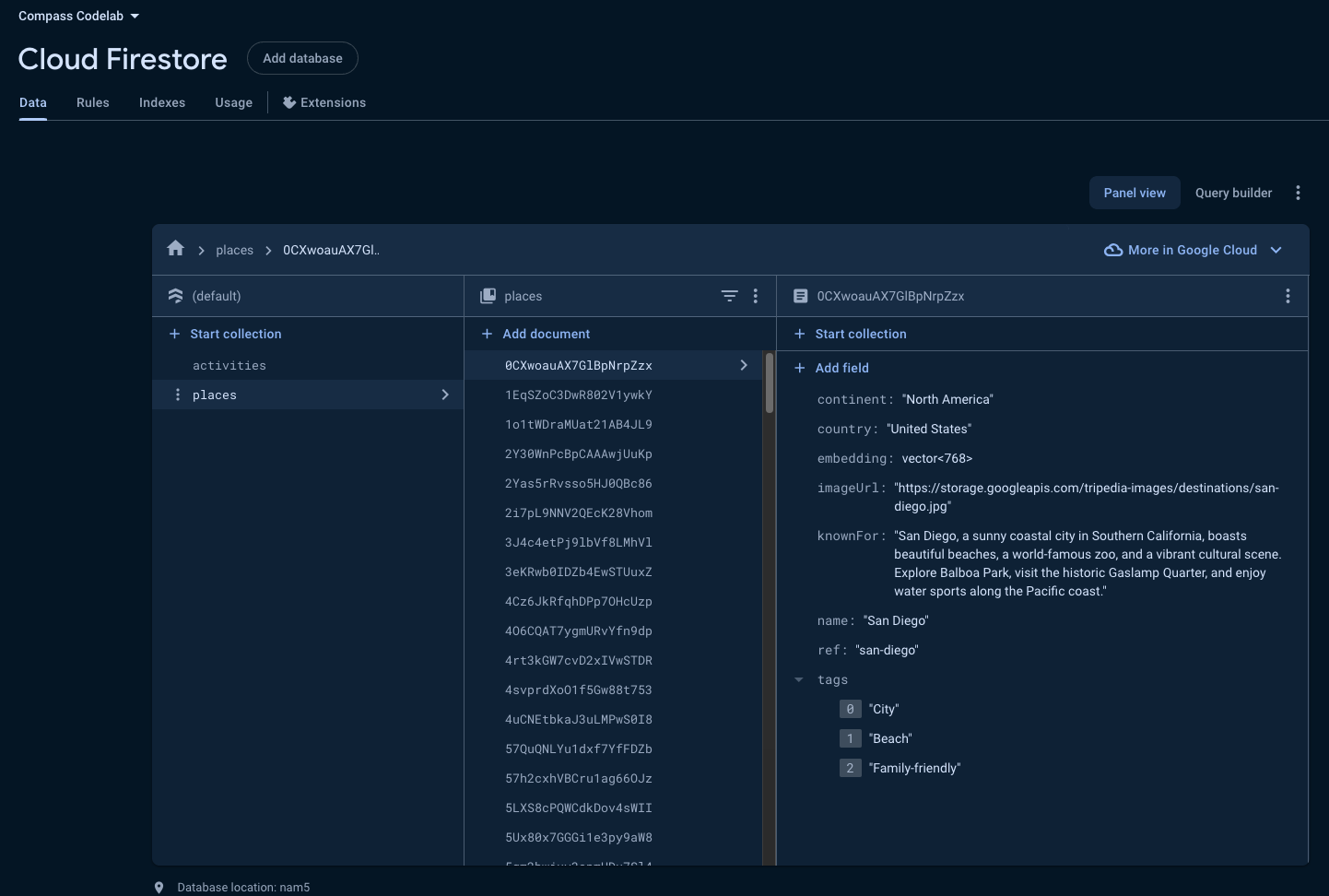
cd load-firestore-data npm ci node index.js YOUR_PROJECT_ID cd .. - Verify that the data was successfully added to your database by going to the Firestore section of your Firebase project in the Firebase console.You should see the imported data schema and its contents displayed.
Connect your web app to your Firebase project
Your web app's codebase needs to be associated with the correct Firebase project to utilize its services, such as the database. To accomplish this, you need to add your Firebase configuration to your app's codebase. This configuration includes essential values like your project ID, your app's API key and app ID, as well as other values that enable your app to interact with Firebase.
- Obtain your app's Firebase configuration:
- In the Firebase console, navigate to your Firebase project.
- In the left-side panel, click the gear icon next to Project Overview and select Project settings.
- In the "Your apps" card, select your web app.
- Under the "SDK setup and configuration" section, select the Config option.
- Copy the snippet. It begins with
const firebaseConfig ....
- Add your Firebase configuration to your web app's codebase:
- In your code editor, open the
src/lib/genkit/genkit.config.tsfile. - Replace the relevant section with the code that you copied.
- Save the file.
- In your code editor, open the
Preview the web app in your browser
- In your terminal, install dependencies and then run the web app:
npm install npm run dev:next - In your browser, navigate to the locally hosted Hosting URL to view the web app. For example, in most cases, the URL is http://localhost:3000/ or something similar.
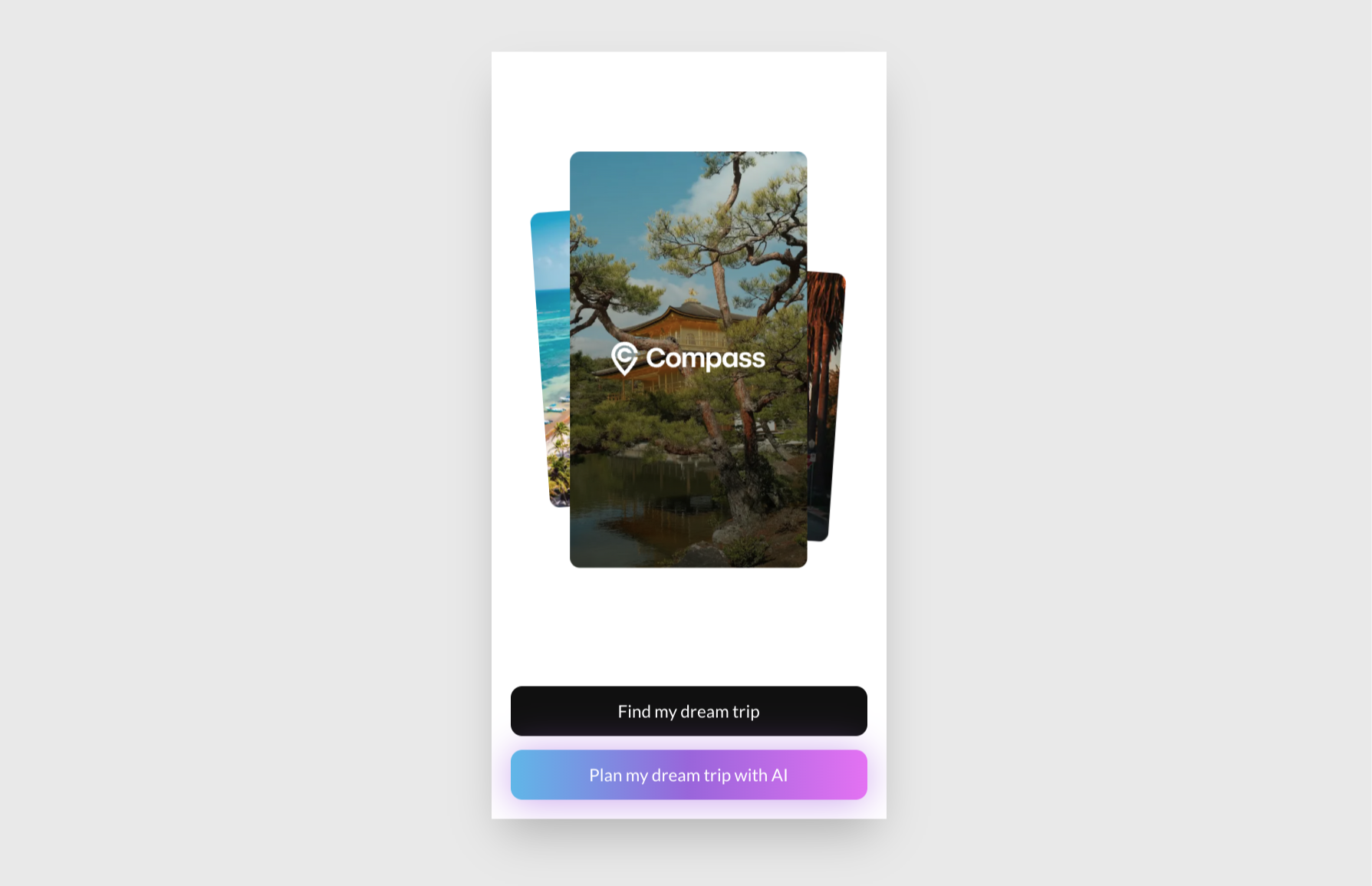
Compass is a Next.js app using React Server Components, and this is the homepage.
Click Find my dream trip. You can see it displaying some hard-coded data for some fixed destinations:
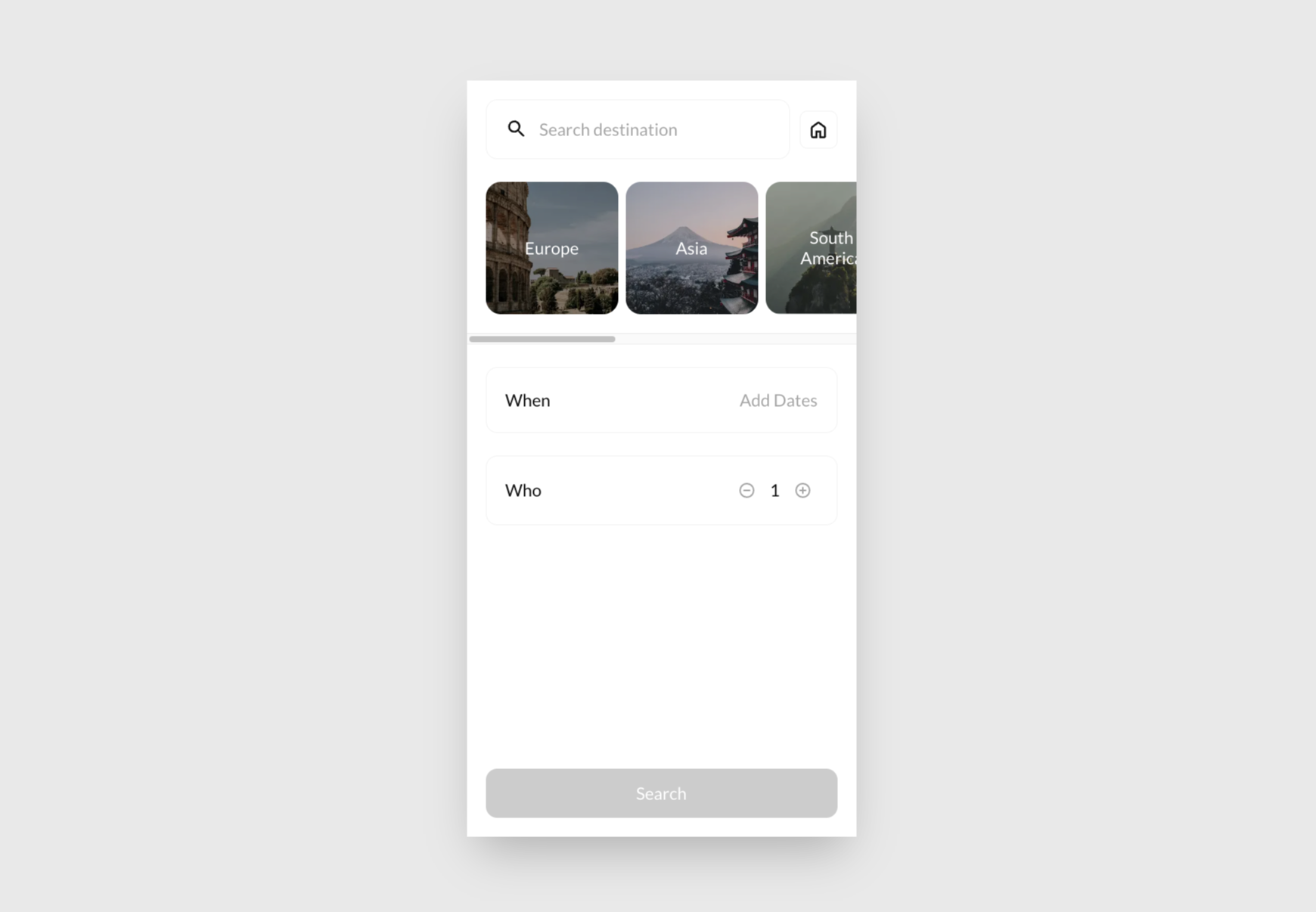
Feel free to explore. When you're ready to continue, click the  home button (in the top-right corner).
home button (in the top-right corner).
6. Dive into generative AI with Genkit
Now you're ready to leverage the power of generative AI in your application! This section of the codelab will guide you through implementing a feature that suggests destinations based on user-provided inspiration. You'll use Genkit and Google Cloud's Vertex AI as the provider for the generative model (you will be using Gemini).
Genkit can store trace and flow state (which allows you to inspect the result of executing Genkit flows). In this codelab, you'll be using Firestore to store these traces.
As a final step in this codelab, you'll deploy your Genkit app to Firebase App Hosting.
Connect your Genkit app to your Firebase project
We already connected Genkit to your project by editing src/lib/genkit/genkit.config.ts in the previous step.
Launch the Genkit Developer UI
Genkit comes with a web-based UI that lets you to interact with LLMs, Genkit flows, retrievers, and other AI components.
In your terminal, run:
npm run dev:genkit
In your browser, navigate to the locally hosted Genkit URL. In most cases, it's http://localhost:4000/.
Interact with Gemini
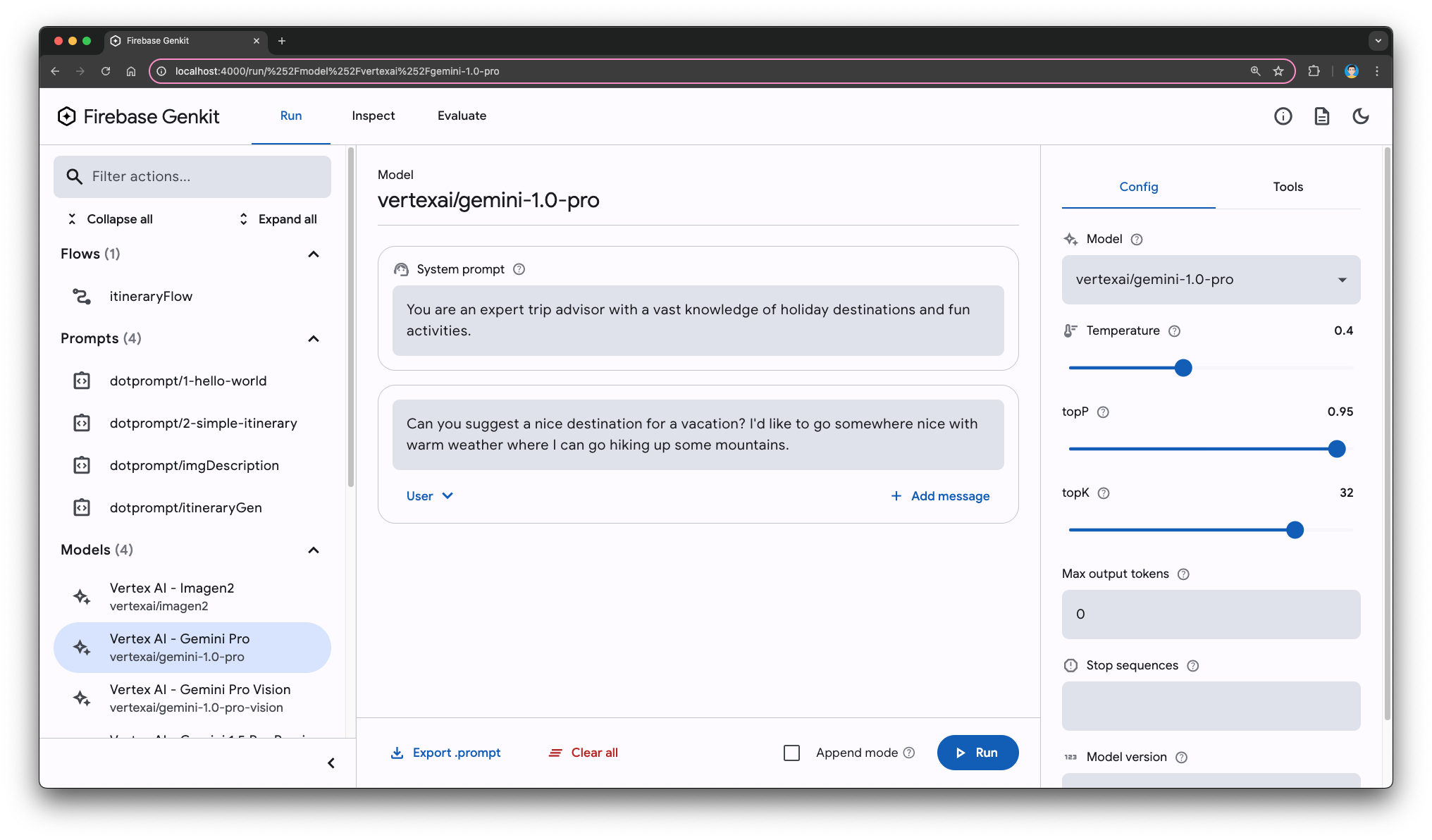
You can now use Genkit's Developer UI to interact with any of the supported models or any of the other AI components, such as the prompts, retrievers, and Genkit flows.
For example, try asking Gemini to suggest a holiday vacation. Note how you can use system instructions to steer the behaviour of the model based on your specific needs. This also works for models that don't natively support system instructions.
Manage prompts
Genkit introduces Dotprompt, a plugin and text format designed to streamline the creation and management of your generative AI prompts. The core idea behind Dotprompt is treating prompts as code, allowing you to write, maintain, and version control them alongside your application code.
To use Dotprompt, start with a hello-world:
- In your code editor, open the
prompts/1-hello-world.promptfile. - In the Genkit Developer UI, open
prompts/1-hello-world. - Use any language name or code that you're familiar with, or leave it as an empty string.
- Click Run.
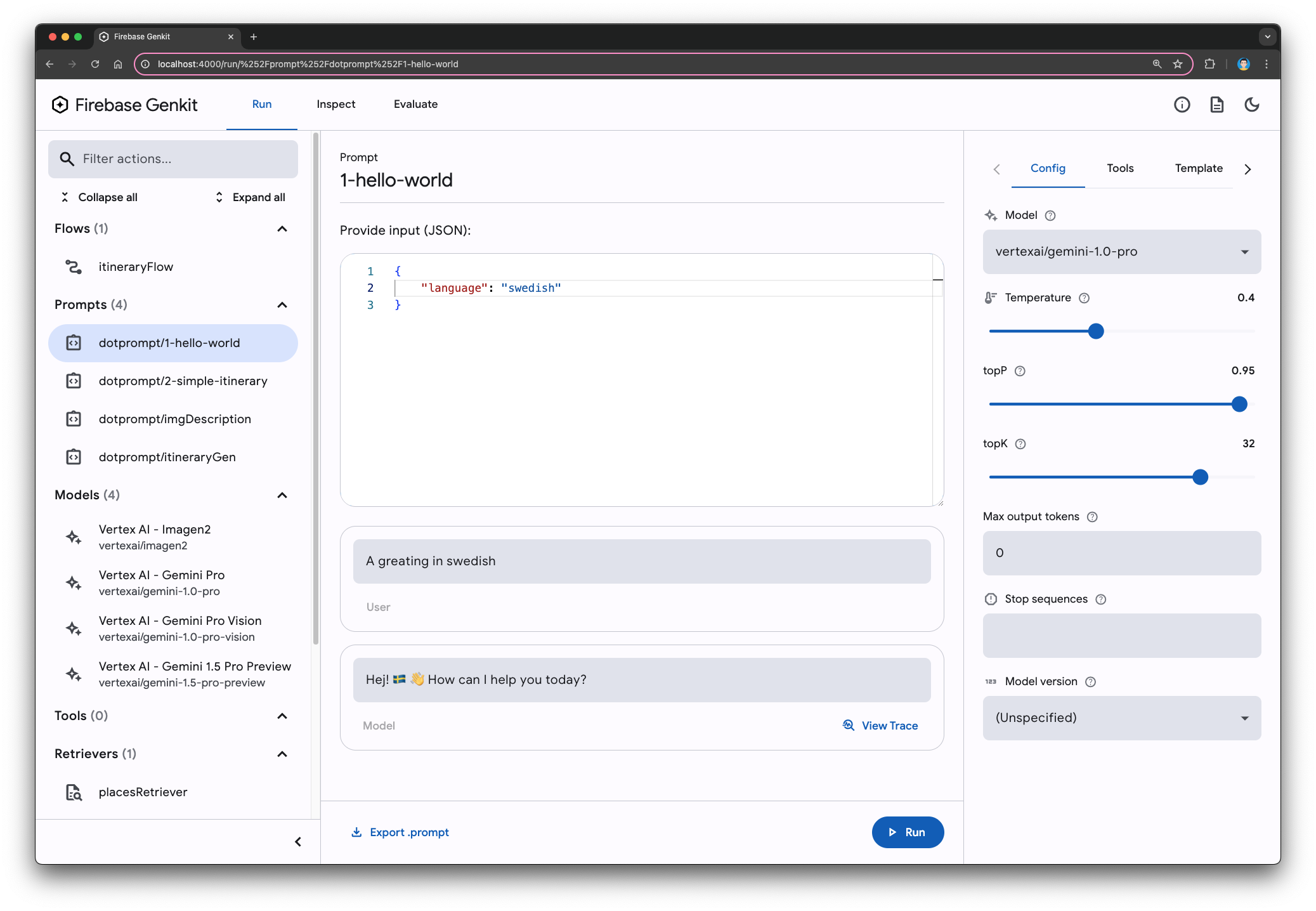
- Try a few different values. Large language models are good at understanding abbreviated, misspelled, or incomplete prompts in simple queries like this one.
Enrich your output with structured data
Beyond generating plain text, Genkit empowers you to structure your output for enhanced presentation and integration within your app's UI. By defining a schema, you can instruct the LLM to produce structured data that aligns with your desired format.
Exploring output schemas
You can also specify the output schema of an LLM call.
- In your code editor, examine the prompt file:
- Open the
prompts/2-simple-itinerary.promptfile. - Examine the defined input and output schemas.
- Open the
- Interact with the UI:
- In the Genkit Developer UI, navigate to the
prompts/2-simple-itinerarysection. - Provide input by populating the
placeandinterestsfields with sample data:{ "interests": [ "Museums" ], "place": "Paris" } - Click Run.
- In the Genkit Developer UI, navigate to the
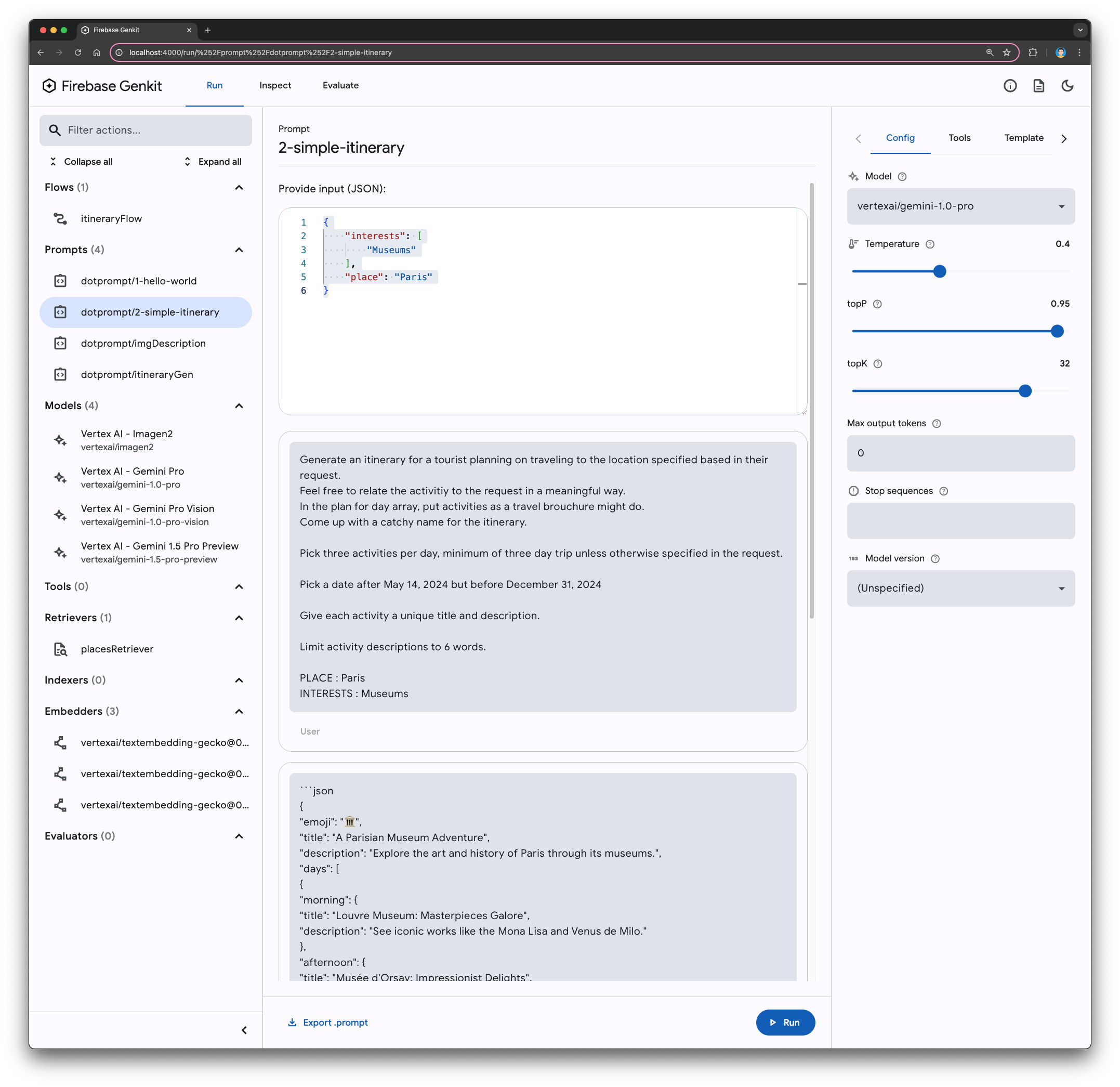
Understanding schema-driven output
Notice how the generated output conforms to the defined schema. By specifying the desired structure, you've instructed the LLM to produce data that's easily parsed and integrated into your application. Genkit automatically validates the output against the schema, ensuring data integrity.
Moreover, you can configure Genkit to retry or attempt to repair the output if it doesn't match the schema.
Key advantages of output schemas
- Simplified integration: Easily incorporate structured data into your app's UI elements.
- Data validation: Ensure the accuracy and consistency of generated output.
- Error handling: Implement mechanisms to address schema mismatches.
Leveraging output schemas elevates your Genkit experience, enabling you to create tailored, structured data for richer and more dynamic user experiences.
Utilize multimodal input
Imagine your app suggesting personalized vacation destinations based on images your users find inspiring. Genkit, combined with a multimodal generative model, empowers you to bring this vision to life.
- In your code editor, examine the prompt file:
- Open the
prompts/imgDescription.promptfile. - Note the inclusion of
{{media url=this}}, which is a Handlebars syntax element that facilitates incorporating images into your prompt.
- Open the
- Interact with the UI:
- In the Genkit Developer UI, open the
prompts/imgDescriptionprompt. - Input an Image URL in the
imageUrlsfield by pasting a URL of an image. For example, you can use a thumbnail image from Wikipedia showcasing the Eiffel Tower:{ "imageUrls": [ "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4b/La_Tour_Eiffel_vue_de_la_Tour_Saint-Jacques%2C_Paris_ao%C3%BBt_2014_%282%29.jpg/556px-La_Tour_Eiffel_vue_de_la_Tour_Saint-Jacques%2C_Paris_ao%C3%BBt_2014_%282%29.jpg" ] } - Click Run.
- In the Genkit Developer UI, open the

7. Implement retrieval with vector similarity search
While generating creative content with AI models is impressive, practical applications often require grounding the output in a specific context.
In the case of this codelab, you have a database of destinations (places and activities) and aim to ensure that the Gemini model's generated suggestions exclusively reference entries within this database.
To bridge the gap between unstructured queries and relevant content, you'll harness the power of vector similarity search on generated embeddings.
Understanding embeddings and vector similarity
- Vectors: Vectors are numerical representations of data points, often used to model complex information like text or images. Each dimension in a vector corresponds to a specific feature of the data.
- Embedding Models: These specialized AI models transform input data, such as text, into high-dimensional vectors. The fascinating aspect is that similar inputs are mapped to vectors that are close to each other in this high-dimensional space.
- Vector Similarity Search: This technique leverages the proximity of embedding vectors to identify relevant data points. Given an input query, it finds entries in the database with similar embedding vectors, indicating semantic relatedness.
Understanding how the retrieval process works
- Embedding the query: Your user's input (for example, "romantic dinner in Paris") is passed through an embedding model, generating a query vector.
- Database embeddings: Ideally, you've pre-processed your database of destinations, creating embedding vectors for each entry.
- Similarity calculation: The query vector is compared to each embedding vector in the database using a similarity metric (for example, cosine similarity).
- Retrieval: The most similar entries from the database, based on their proximity to the query vector, are retrieved as relevant suggestions.
By incorporating this retrieval mechanism into your application, you leverage the Gemini model to generate suggestions that are not only creative but also firmly rooted in your specific dataset. This approach ensures that the generated output remains contextually relevant and aligned with the information available in your database.
Enable vector similarity search in Firestore
In a previous step of this codelab, you populated your Firestore database with sample places and activities. Each place entry includes a knownFor text field describing its notable attributes, along with a corresponding embedding field containing the vector representation of this description.

To leverage the power of vector similarity search on these embeddings, you'll need to create a Firestore index. This index enables efficient retrieval of places based on the similarity of their embedding vectors to a given query.
- Create the index, making sure to replace
YOUR_PROJECT_IDwith your project's ID.- For macOS / Linux
gcloud firestore indexes composite create \ --project=YOUR_PROJECT_ID \ --collection-group=places \ --query-scope=COLLECTION \ --field-config field-path=embedding,vector-config='{"dimension":"768","flat":"{}"}'- For Windows (PowerShell)
gcloud firestore indexes composite create ` --project=YOUR_PROJECT_ID ` --collection-group=places ` --query-scope=COLLECTION ` --field-config="field-path=embedding,vector-config={'dimension':'768','flat':'{}'}" - In the Genkit Developer UI, open the
retrievers/placesRetriever. - Click Run. Observe the scaffolded object with placeholder text, indicating where you'll implement the retriever logic.
- In your code editor, open the
src/lib/genkit/placesRetriever.tsfile. - Scroll all the way down and replace the placeholder
placesRetrieverwith the following:export const placesRetriever = defineFirestoreRetriever(ai, { name: 'placesRetriever', firestore, collection: 'places', contentField: 'knownFor', vectorField: 'embedding', embedder: vertexAI.embedder('text-embedding-005', {outputDimensionality: 768}), distanceMeasure: 'COSINE', });
Test the retriever
- In the Genkit Developer UI, open the
retrievers/placesRetrieverretriever. - Provide the following Query:
{ "content": [ { "text": "UNESCO" } ] } - You can also provide Options. For example, here's how to specify how many documents the retriever should return:
{ "limit": 4 } - Click Run.

You can do additional filtering on the data beyond similarity by adding where clauses to the Options.
8. Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) with Genkit
In previous sections, you've built individual prompts capable of handling text, JSON, and images, generating vacation destinations and other engaging content for your users. You've also implemented a prompt that retrieves relevant destinations from your Firestore database. Now, it's time to orchestrate these components into a cohesive retrieval augmented generation (RAG) flow.
This section introduces an important Genkit concept called flows. Flows are strongly typed, streamable functions that can be invoked both locally and remotely, with full observability. You can manage and invoke flows both from Genkit's CLI and the Genkit Developer UI.
- In your code editor, examine the itinerary prompt:
- Open the
prompts/itineraryGen.promptfile. - Note how the prompt has been expanded to accept additional inputs, specifically the activities data sourced from the retriever.
- Open the
- In the Genkit Developer UI, view a Genkit flow in the
src/lib/genkit/itineraryFlow.tsfile.
Tip: To streamline debugging, consider breaking down lengthy flows into smaller, manageable steps. - Enhance the flow by integrating an "image description" step:
- Locate the
TODO: 2comment (around line 81). This marks the spot where you'll enhance your flow. - Replace the empty
imgDescriptionplaceholder with theai.run('imgDescription', ...)block that generates a description fromtripDetails.imageUrls.
- Locate the
- Test the flow:
- Navigate to the
flows/itineraryFlow. - Use the following input to test successful execution of
itineraryFlowwith your newly added step:{ "request": "Sightseeing in Paris", "imageUrls": [ "https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4b/La_Tour_Eiffel_vue_de_la_Tour_Saint-Jacques%2C_Paris_ao%C3%BBt_2014_%282%29.jpg/556px-La_Tour_Eiffel_vue_de_la_Tour_Saint-Jacques%2C_Paris_ao%C3%BBt_2014_%282%29.jpg" ] } - Click Run.
- Observe the generated output, which should incorporate the image description into the itinerary suggestion.

- Navigate to the
- If you encounter any errors or unexpected behaviors, click View trace to see details. You can also use this tab to review the history of executions from the Trace Store.

RAG for your web application
- Make sure the web app is still running by visiting http://localhost:3000/ in your browser.
- If the web app is no longer running, run these commands in your terminal:
npm install npm run dev - Check out the Dream Your Vacation web app page (http://localhost:3000/gemini).
- View its source code (
src/app/gemini/page.tsx) for a Next.js integration example.
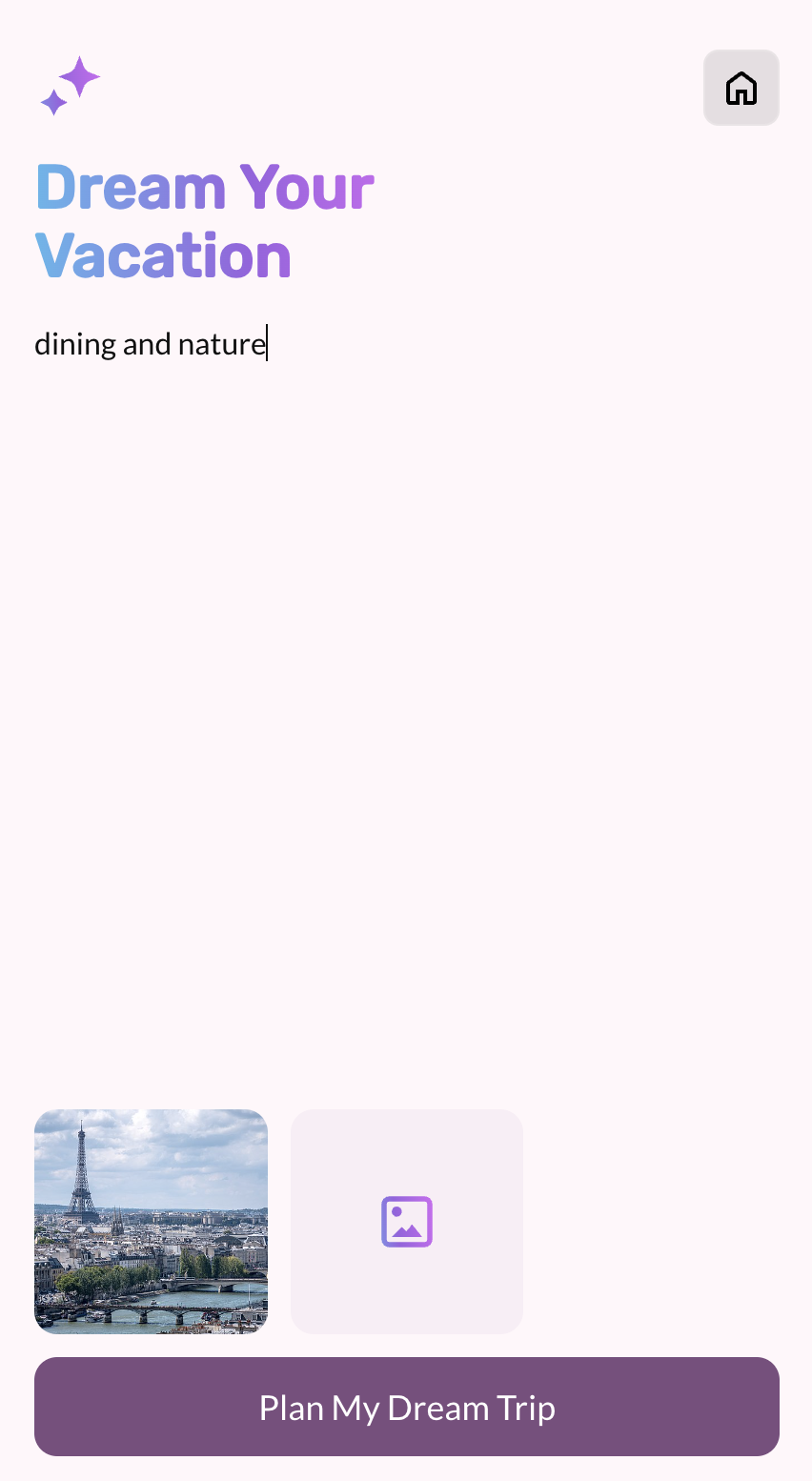
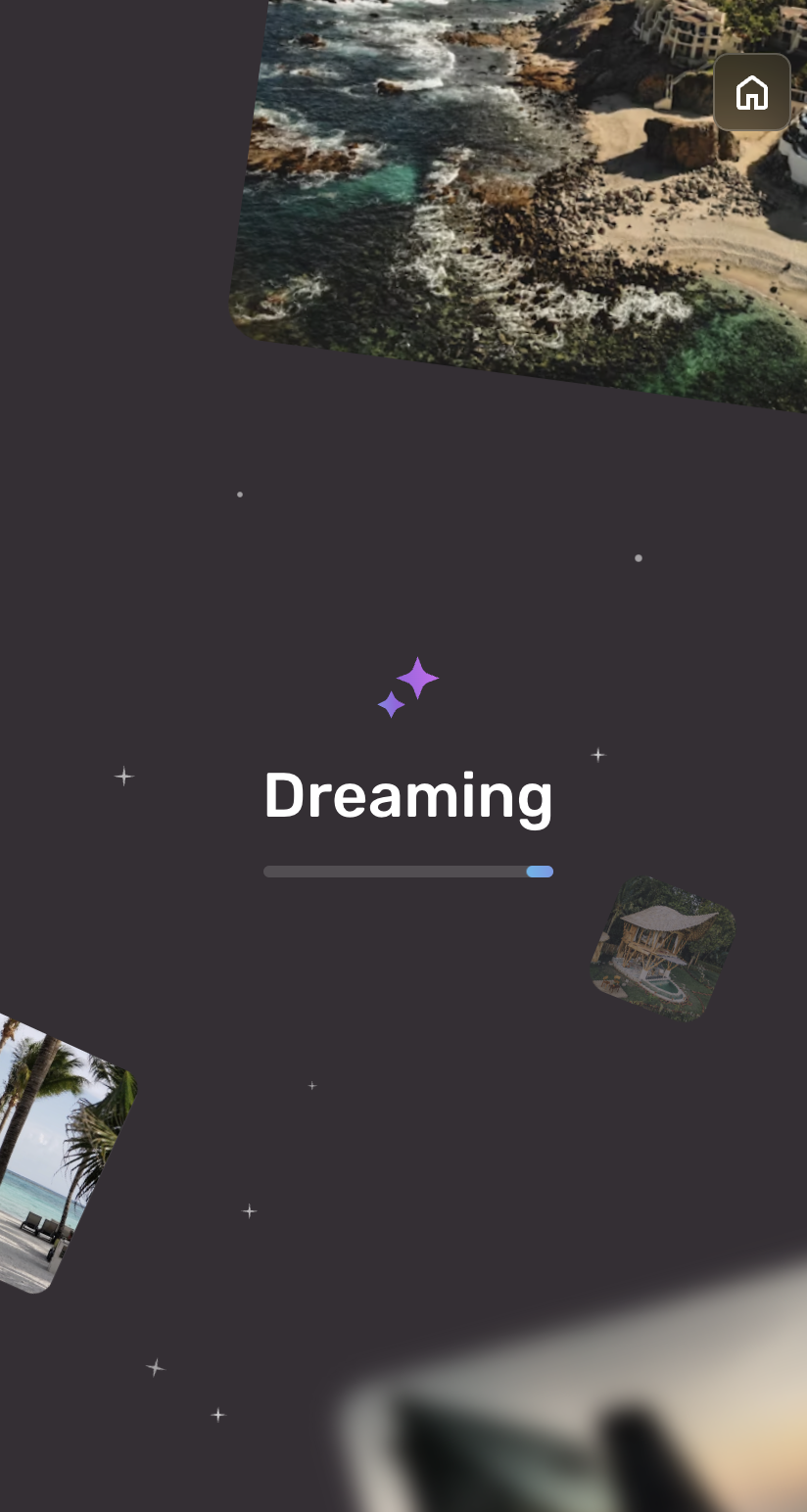

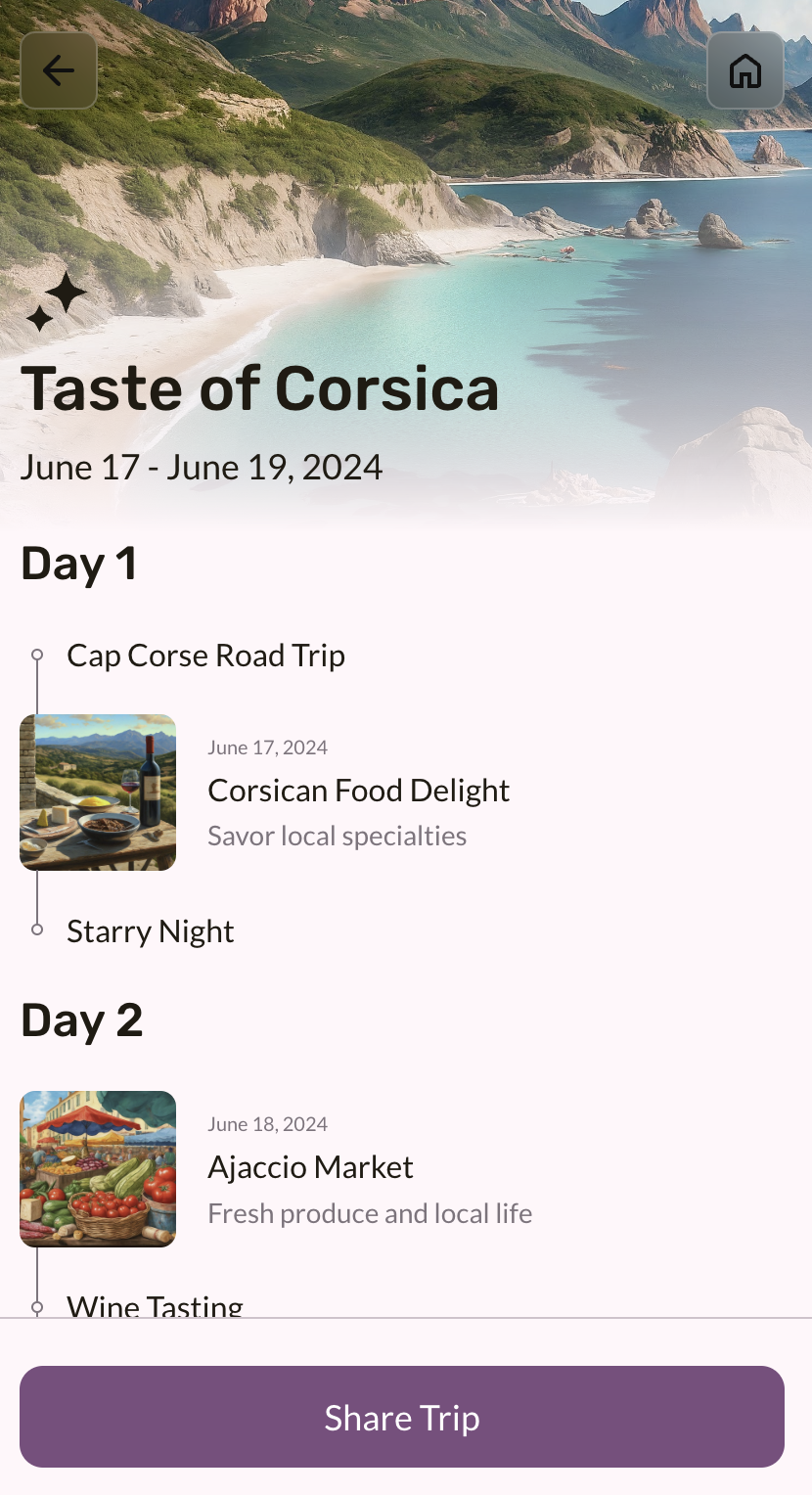
9. Deploy your application with Firebase App Hosting
The final step in this journey is deploying your web app. You'll leverage Firebase App Hosting, a framework-aware hosting solution designed to simplify the deployment of Next.js and Angular apps to a serverless backend.
- Commit your changes to your local git repository and then push to GitHub.
- In the Firebase console, navigate to App Hosting within your Firebase project.
- Click Get started > Connect to GitHub.
- Select your GitHub account and Repository. Click Next.
- In Deployment setting > Root directory, keep the default value. To use automatic rollouts, enable the Automatic rollouts on option.
- For the Live branch, select the main branch of your GitHub repo. Click Next.
- Enter an ID for your backend (for example,
compass). - When asked whether to Create or associate a Firebase web app, choose Select an existing Firebase web app, and pick the app you created in an earlier step in this codelab.
- Click Finish and Deploy.
Monitoring deployment status
The deployment process will take a few minutes. You can track the progress in the App Hosting section of the Firebase console.
Grant permissions to your service account
In order for your Node.js backend to access Vertex AI resources, you need to assign the aiplatform.user role to your app's service account:
gcloud projects add-iam-policy-binding YOUR_PROJECT_ID \
--member "serviceAccount:firebase-app-hosting-compute@YOUR_PROJECT_ID.iam.gserviceaccount.com" \
--role "roles/aiplatform.user"
Once completed, your web app will be accessible to users.
Automatic redeployment
Firebase App Hosting streamlines future updates. Whenever you push changes to the main branch of your GitHub repository, Firebase App Hosting will automatically rebuild and redeploy your app, ensuring your users always experience the latest version.
10. Conclusion
Congratulations on completing this comprehensive codelab!
You've successfully harnessed the power of Genkit, Firestore, and Vertex AI to create a sophisticated "flow" that generates personalized vacation recommendations based on user preferences and inspiration, all while grounding the suggestions in your application's data.
Throughout this journey, you've gained hands-on experience with essential software engineering patterns crucial for building robust generative AI applications. These patterns include:
- Prompt management: Organizing and maintaining prompts as code for better collaboration and version control.
- Multimodal content: Integrating diverse data types, such as images and text, to enhance AI interactions.
- Input/Output Schemas: Structuring data for seamless integration and validation in your application.
- Vector Stores: Leveraging vector embeddings for efficient similarity search and retrieval of relevant information.
- Data Retrieval: Implementing mechanisms to fetch and incorporate data from databases into AI-generated content.
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG): Combining retrieval techniques with generative AI for contextually relevant and accurate outputs.
- Flow Instrumentation: Building and orchestrating complex AI workflows for seamless and observable execution.
By mastering these concepts and applying them within the Firebase ecosystem, you're well-equipped to embark on your own genAI adventures. Explore the vast possibilities, create innovative applications, and continue pushing the boundaries of what's achievable with generative AI.
Exploring alternative deployment options
Genkit offers a variety of deployment options to suit your specific needs, including:
- Cloud Functions for Firebase
- Cloud Run
- Next.js
- Any Node.js environment
- Genkit also supports Go
Just choose the one that's best for you by running the following command inside your (package.json) node folder:
npx genkit start
Next steps
- Experiment with prompts and take advantage of the large context windows in Google AI Studio or Vertex AI Studio.
- Learn more about AI retrieval augmented generation (RAG) search.
- Check out the official docs for Genkit.
- Learn more about similarity search capabilities in Firestore and Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL.
- Go deeper into genAI flows with function calling.
