জেনারেটিভ মডেলগুলি অনেক ধরণের সমস্যা সমাধানে শক্তিশালী। তবে, এগুলি সীমাবদ্ধতার দ্বারা সীমাবদ্ধ যেমন:
- প্রশিক্ষণের পর এগুলো হিমায়িত হয়ে যায়, যার ফলে পুরনো জ্ঞানের সৃষ্টি হয়।
- তারা বাহ্যিক ডেটা জিজ্ঞাসা বা পরিবর্তন করতে পারে না।
ফাংশন কলিং আপনাকে এই সীমাবদ্ধতাগুলির কিছু কাটিয়ে উঠতে সাহায্য করতে পারে। ফাংশন কলিংকে কখনও কখনও টুল ব্যবহার বলা হয় কারণ এটি একটি মডেলকে তার চূড়ান্ত প্রতিক্রিয়া তৈরি করতে API এবং ফাংশনের মতো বহিরাগত সরঞ্জাম ব্যবহার করতে দেয়।
এই নির্দেশিকাটি আপনাকে দেখায় যে আপনি কীভাবে এই পৃষ্ঠার পরবর্তী প্রধান বিভাগে বর্ণিত দৃশ্যের অনুরূপ একটি ফাংশন কল সেটআপ বাস্তবায়ন করতে পারেন। উচ্চ-স্তরে, আপনার অ্যাপে ফাংশন কলিং সেট আপ করার পদক্ষেপগুলি এখানে দেওয়া হল:
ধাপ ১ : এমন একটি ফাংশন লিখুন যা মডেলটিকে তার চূড়ান্ত প্রতিক্রিয়া তৈরি করার জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় তথ্য সরবরাহ করতে পারে (উদাহরণস্বরূপ, ফাংশনটি একটি বহিরাগত API কল করতে পারে)।
ধাপ ২ : একটি ফাংশন ঘোষণা তৈরি করুন যা ফাংশন এবং এর পরামিতিগুলি বর্ণনা করে।
ধাপ ৩ : মডেল ইনিশিয়ালাইজেশনের সময় ফাংশন ডিক্লারেশন প্রদান করুন যাতে মডেল জানতে পারে যে প্রয়োজনে এটি কীভাবে ফাংশনটি ব্যবহার করতে পারে।
ধাপ ৪ : আপনার অ্যাপটি এমনভাবে সেট আপ করুন যাতে মডেলটি আপনার অ্যাপের ফাংশন কল করার জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় তথ্য পাঠাতে পারে।
ধাপ ৫ : ফাংশনের প্রতিক্রিয়াটি মডেলটিতে ফেরত পাঠান যাতে মডেলটি তার চূড়ান্ত প্রতিক্রিয়া তৈরি করতে পারে।
একটি ফাংশন কলিং উদাহরণের সংক্ষিপ্তসার
যখন আপনি মডেলটিকে একটি অনুরোধ পাঠান, তখন আপনি মডেলটিকে "টুল" (যেমন ফাংশন) এর একটি সেটও প্রদান করতে পারেন যা এটি তার চূড়ান্ত প্রতিক্রিয়া তৈরি করতে ব্যবহার করতে পারে। এই ফাংশনগুলি ব্যবহার করতে এবং তাদের কল করতে ("ফাংশন কলিং") করার জন্য, মডেল এবং আপনার অ্যাপকে একে অপরের কাছে তথ্য প্রেরণ করতে হবে, তাই ফাংশন কলিং ব্যবহার করার প্রস্তাবিত উপায় হল মাল্টি-টার্ন চ্যাট ইন্টারফেসের মাধ্যমে।
কল্পনা করুন যে আপনার কাছে এমন একটি অ্যাপ আছে যেখানে একজন ব্যবহারকারী একটি প্রম্পট লিখতে পারেন যেমন: What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? ।
জেমিনি মডেলগুলি হয়তো এই আবহাওয়ার তথ্য জানে না; তবে, কল্পনা করুন যে আপনি একটি বহিরাগত আবহাওয়া পরিষেবা API জানেন যা এটি প্রদান করতে পারে। আপনি জেমিনি মডেলটিকে সেই API এবং এর আবহাওয়ার তথ্যের পথ দেওয়ার জন্য ফাংশন কলিং ব্যবহার করতে পারেন।
প্রথমে, আপনি আপনার অ্যাপে একটি ফাংশন fetchWeather লিখুন যা এই কাল্পনিক বহিরাগত API এর সাথে ইন্টারঅ্যাক্ট করে, যার ইনপুট এবং আউটপুট এই রকম:
| প্যারামিটার | আদর্শ | প্রয়োজনীয় | বিবরণ |
|---|---|---|---|
| ইনপুট | |||
location | বস্তু | হাঁ | আবহাওয়া জানার জন্য শহর এবং তার রাজ্যের নাম। শুধুমাত্র মার্কিন যুক্তরাষ্ট্রের শহরগুলি সমর্থিত। সর্বদা city এবং state একটি নেস্টেড অবজেক্ট হতে হবে। |
date | স্ট্রিং | হাঁ | আবহাওয়ার তথ্য সংগ্রহের তারিখ (সর্বদা YYYY-MM-DD ফর্ম্যাটে থাকতে হবে)। |
| আউটপুট | |||
temperature | পূর্ণসংখ্যা | হাঁ | তাপমাত্রা (ফারেনহাইটে) |
chancePrecipitation | স্ট্রিং | হাঁ | বৃষ্টিপাতের সম্ভাবনা (শতাংশ হিসাবে প্রকাশ করা হয়েছে) |
cloudConditions | স্ট্রিং | হাঁ | মেঘলা অবস্থা ( clear , partlyCloudy , mostlyCloudy , cloudy ) |
মডেলটি শুরু করার সময়, আপনি মডেলটিকে বলবেন যে এই fetchWeather ফাংশনটি বিদ্যমান এবং প্রয়োজনে আগত অনুরোধগুলি প্রক্রিয়া করার জন্য এটি কীভাবে ব্যবহার করা যেতে পারে। এটিকে "ফাংশন ঘোষণা" বলা হয়। মডেলটি সরাসরি ফাংশনটি কল করে না। পরিবর্তে, মডেলটি আগত অনুরোধটি প্রক্রিয়া করার সময়, এটি সিদ্ধান্ত নেয় যে fetchWeather ফাংশনটি অনুরোধের প্রতিক্রিয়া জানাতে সহায়তা করতে পারে কিনা। যদি মডেল সিদ্ধান্ত নেয় যে ফাংশনটি আসলেই কার্যকর হতে পারে, তাহলে মডেলটি স্ট্রাকচার্ড ডেটা তৈরি করে যা আপনার অ্যাপকে ফাংশনটি কল করতে সহায়তা করবে।
আবার আগত অনুরোধটি দেখুন: What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? । মডেলটি সম্ভবত সিদ্ধান্ত নেবে যে fetchWeather ফাংশনটি প্রতিক্রিয়া তৈরি করতে সাহায্য করতে পারে। মডেলটি fetchWeather এর জন্য কোন ইনপুট প্যারামিটারগুলি প্রয়োজন তা দেখবে এবং তারপর ফাংশনের জন্য কাঠামোগত ইনপুট ডেটা তৈরি করবে যা মোটামুটি এইরকম দেখাচ্ছে:
{
functionName: fetchWeather,
location: {
city: Boston,
state: Massachusetts // the model can infer the state from the prompt
},
date: 2024-10-17
}
মডেলটি এই স্ট্রাকচার্ড ইনপুট ডেটা আপনার অ্যাপে পাঠায় যাতে আপনার অ্যাপটি fetchWeather ফাংশনটি কল করতে পারে। যখন আপনার অ্যাপ API থেকে আবহাওয়ার পরিস্থিতি ফেরত পায়, তখন এটি মডেলটিতে তথ্য প্রেরণ করে। এই আবহাওয়ার তথ্য মডেলটিকে তার চূড়ান্ত প্রক্রিয়াকরণ সম্পূর্ণ করতে এবং What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? এর প্রাথমিক অনুরোধের প্রতিক্রিয়া তৈরি করতে দেয়।
মডেলটি একটি চূড়ান্ত প্রাকৃতিক-ভাষা প্রতিক্রিয়া প্রদান করতে পারে যেমন: On October 17, 2024, in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
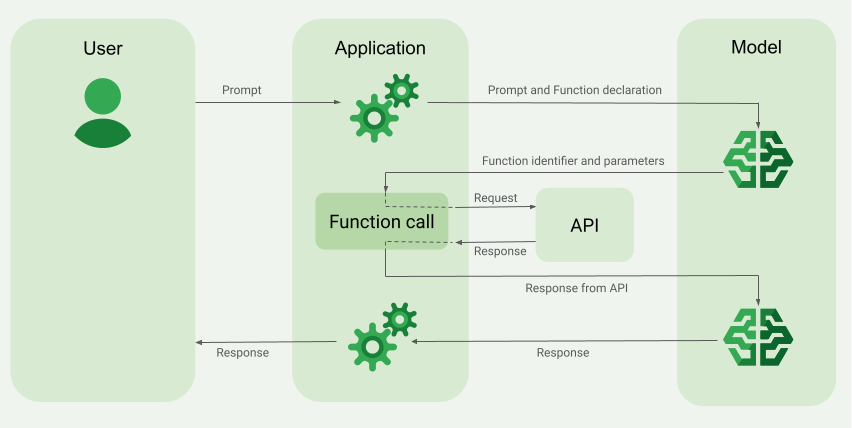
ফাংশন কলিং বাস্তবায়ন করুন
এই নির্দেশিকার নিম্নলিখিত ধাপগুলি আপনাকে দেখায় যে কীভাবে একটি ফাংশন কল সেটআপ বাস্তবায়ন করতে হয় যা ফাংশন কলিংয়ের উদাহরণের সংক্ষিপ্তসারে বর্ণিত ওয়ার্কফ্লোের অনুরূপ (এই পৃষ্ঠার উপরের অংশটি দেখুন)।
শুরু করার আগে
এই পৃষ্ঠায় প্রোভাইডার-নির্দিষ্ট কন্টেন্ট এবং কোড দেখতে আপনার জেমিনি API প্রোভাইডারে ক্লিক করুন। |
যদি আপনি ইতিমধ্যেই না করে থাকেন, তাহলে শুরু করার নির্দেশিকাটি সম্পূর্ণ করুন, যেখানে বর্ণনা করা হয়েছে কিভাবে আপনার Firebase প্রকল্প সেট আপ করবেন, আপনার অ্যাপটি Firebase-এর সাথে সংযুক্ত করবেন, SDK যোগ করবেন, আপনার নির্বাচিত Gemini API প্রদানকারীর জন্য ব্যাকএন্ড পরিষেবা শুরু করবেন এবং একটি GenerativeModel ইনস্ট্যান্স তৈরি করবেন।
ধাপ ১ : ফাংশনটি লিখুন
কল্পনা করুন যে আপনার কাছে এমন একটি অ্যাপ আছে যেখানে একজন ব্যবহারকারী একটি প্রম্পট লিখতে পারেন যেমন: What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? । জেমিনি মডেলগুলি এই আবহাওয়ার তথ্য নাও জানতে পারে; তবে, কল্পনা করুন যে আপনি একটি বহিরাগত আবহাওয়া পরিষেবা API সম্পর্কে জানেন যা এটি প্রদান করতে পারে। এই নির্দেশিকার দৃশ্যপট এই কাল্পনিক বহিরাগত API এর উপর নির্ভর করে।
আপনার অ্যাপে এমন একটি ফাংশন লিখুন যা কাল্পনিক বহিরাগত API এর সাথে ইন্টারঅ্যাক্ট করবে এবং মডেলটিকে তার চূড়ান্ত অনুরোধ তৈরি করার জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় তথ্য সরবরাহ করবে। এই আবহাওয়ার উদাহরণে, এটি একটি fetchWeather ফাংশন হবে যা এই কাল্পনিক বহিরাগত API তে কল করবে।
সুইফট
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
func fetchWeather(city: String, state: String, date: String) -> JSONObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return [
"temperature": .number(38),
"chancePrecipitation": .string("56%"),
"cloudConditions": .string("partlyCloudy"),
]
}
Kotlin
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
data class Location(val city: String, val state: String)
suspend fun fetchWeather(location: Location, date: String): JsonObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return JsonObject(mapOf(
"temperature" to JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation" to JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions" to JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")
))
}
Java
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
public JsonObject fetchWeather(Location location, String date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new JsonObject(Map.of(
"temperature", JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation", JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions", JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")));
}
Web
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
async function fetchWeather({ location, date }) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return {
temperature: 38,
chancePrecipitation: "56%",
cloudConditions: "partlyCloudy",
};
}
Dart
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
Future<Map<String, Object?>> fetchWeather(
Location location, String date
) async {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
final apiResponse = {
'temperature': 38,
'chancePrecipitation': '56%',
'cloudConditions': 'partlyCloudy',
};
return apiResponse;
}
ঐক্য
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object> FetchWeather(
string city, string state, string date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object>() {
{"temperature", 38},
{"chancePrecipitation", "56%"},
{"cloudConditions", "partlyCloudy"},
};
}
ধাপ ২ : একটি ফাংশন ঘোষণা তৈরি করুন
মডেলটিকে পরবর্তীতে যে ফাংশন ডিক্লারেশনটি প্রদান করবেন তা তৈরি করুন (এই নির্দেশিকার পরবর্তী ধাপ)।
আপনার ঘোষণাপত্রে, ফাংশন এবং এর পরামিতিগুলির বর্ণনায় যতটা সম্ভব বিস্তারিত অন্তর্ভুক্ত করুন।
মডেলটি ফাংশন ঘোষণার তথ্য ব্যবহার করে কোন ফাংশনটি নির্বাচন করতে হবে এবং ফাংশনে প্রকৃত কলের জন্য প্যারামিটার মান কীভাবে প্রদান করতে হবে তা নির্ধারণ করে। মডেলটি কীভাবে ফাংশনগুলির মধ্যে একটি বেছে নিতে পারে, সেইসাথে আপনি কীভাবে সেই পছন্দটি নিয়ন্ত্রণ করতে পারেন তার জন্য এই পৃষ্ঠায় পরে অতিরিক্ত আচরণ এবং বিকল্পগুলি দেখুন।
আপনার দেওয়া স্কিমা সম্পর্কে নিম্নলিখিত বিষয়গুলি লক্ষ্য করুন:
আপনাকে অবশ্যই OpenAPI স্কিমার সাথে সামঞ্জস্যপূর্ণ স্কিমা ফর্ম্যাটে ফাংশন ঘোষণা প্রদান করতে হবে। Vertex AI OpenAPI স্কিমার সীমিত সমর্থন প্রদান করে।
নিম্নলিখিত বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি সমর্থিত:
type,nullable,required,format,description,properties,items,enum।নিম্নলিখিত বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলি সমর্থিত নয় :
default,optional,maximum,oneOf.
ডিফল্টরূপে, Firebase AI Logic SDK-এর জন্য, সমস্ত ক্ষেত্র প্রয়োজনীয় বলে বিবেচিত হবে যদি না আপনি একটি
optionalPropertiesঅ্যারেতে ঐচ্ছিক হিসাবে নির্দিষ্ট করেন। এই ঐচ্ছিক ক্ষেত্রগুলির জন্য, মডেলটি ক্ষেত্রগুলি পূরণ করতে পারে বা সেগুলি এড়িয়ে যেতে পারে। মনে রাখবেন যে আপনি যদি তাদের সার্ভার SDK বা তাদের API সরাসরি ব্যবহার করেন তবে এটি দুটি Gemini API প্রদানকারীর ডিফল্ট আচরণের বিপরীত।
নাম এবং বর্ণনার টিপস সহ ফাংশন ঘোষণা সম্পর্কিত সেরা অনুশীলনের জন্য, দেখুনজেমিনি ডেভেলপার এপিআই ডকুমেন্টেশনের সেরা অনুশীলন ।
এখানে আপনি কিভাবে একটি ফাংশন ঘোষণা লিখতে পারেন:
সুইফট
let fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: [
"location": .object(
properties: [
"city": .string(description: "The city of the location."),
"state": .string(description: "The US state of the location."),
],
description: """
The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the
USA are supported.
"""
),
"date": .string(
description: """
The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.
"""
),
]
)
Kotlin
val fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
mapOf(
"location" to Schema.obj(
mapOf(
"city" to Schema.string("The city of the location."),
"state" to Schema.string("The US state of the location."),
),
description = "The name of the city and its state for which " +
"to get the weather. Only cities in the " +
"USA are supported."
),
"date" to Schema.string("The date for which to get the weather." +
" Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
),
),
)
Java
FunctionDeclaration fetchWeatherTool = new FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
Map.of("location",
Schema.obj(Map.of(
"city", Schema.str("The city of the location."),
"state", Schema.str("The US state of the location."))),
"date",
Schema.str("The date for which to get the weather. " +
"Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.")),
Collections.emptyList());
Web
const fetchWeatherTool: FunctionDeclarationsTool = {
functionDeclarations: [
{
name: "fetchWeather",
description:
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date",
parameters: Schema.object({
properties: {
location: Schema.object({
description:
"The name of the city and its state for which to get " +
"the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.",
properties: {
city: Schema.string({
description: "The city of the location."
}),
state: Schema.string({
description: "The US state of the location."
}),
},
}),
date: Schema.string({
description:
"The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the" +
" format: YYYY-MM-DD.",
}),
},
}),
},
],
};
Dart
final fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
'fetchWeather',
'Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.',
parameters: {
'location': Schema.object(
description:
'The name of the city and its state for which to get'
'the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.',
properties: {
'city': Schema.string(
description: 'The city of the location.'
),
'state': Schema.string(
description: 'The US state of the location.'
),
},
),
'date': Schema.string(
description:
'The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.'
),
},
);
ঐক্য
var fetchWeatherTool = new Tool(new FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "location", Schema.Object(
properties: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "city", Schema.String(description: "The city of the location.") },
{ "state", Schema.String(description: "The US state of the location.")}
},
description: "The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported."
) },
{ "date", Schema.String(
description: "The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
)}
}
));
ধাপ ৩ : মডেল ইনিশিয়ালাইজেশনের সময় ফাংশন ঘোষণা প্রদান করুন
অনুরোধের সাথে আপনি সর্বাধিক ১২৮টি ফাংশন ঘোষণা প্রদান করতে পারবেন। মডেলটি কীভাবে ফাংশনগুলির মধ্যে একটি বেছে নিতে পারে, সেইসাথে আপনি কীভাবে সেই পছন্দটি নিয়ন্ত্রণ করতে পারেন ( ফাংশন কলিং মোড সেট করতে toolConfig ব্যবহার করে) তার জন্য এই পৃষ্ঠায় পরে অতিরিক্ত আচরণ এবং বিকল্পগুলি দেখুন।
সুইফট
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool])]
)
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools = listOf(Tool.functionDeclarations(listOf(fetchWeatherTool)))
)
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(
FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash",
null,
null,
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
List.of(Tool.functionDeclarations(List.of(fetchWeatherTool)))));
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const firebaseAI = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(firebaseAI, {
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: fetchWeatherTool
});
Dart
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
_functionCallModel = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'gemini-2.5-flash',
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [
Tool.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool]),
],
);
ঐক্য
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = FirebaseAI.DefaultInstance.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: new Tool[] { fetchWeatherTool }
);
মডেল কীভাবে নির্বাচন করবেন তা শিখুনআপনার ব্যবহারের ক্ষেত্রে এবং অ্যাপের জন্য উপযুক্ত।
ধাপ ৪ : বাহ্যিক API চালু করার জন্য ফাংশনটি কল করুন
যদি মডেলটি সিদ্ধান্ত নেয় যে fetchWeather ফাংশনটি প্রকৃতপক্ষে একটি চূড়ান্ত প্রতিক্রিয়া তৈরি করতে সাহায্য করতে পারে, তাহলে আপনার অ্যাপটিকে মডেল দ্বারা প্রদত্ত স্ট্রাকচার্ড ইনপুট ডেটা ব্যবহার করে সেই ফাংশনে প্রকৃত কল করতে হবে।
যেহেতু মডেল এবং অ্যাপের মধ্যে তথ্য বারবার আদান-প্রদান করতে হয়, তাই ফাংশন কলিং ব্যবহারের প্রস্তাবিত উপায় হল মাল্টি-টার্ন চ্যাট ইন্টারফেসের মাধ্যমে।
নিচের কোড স্নিপেটটি দেখায় যে কীভাবে আপনার অ্যাপকে বলা হয়েছে যে মডেলটি fetchWeather ফাংশন ব্যবহার করতে চায়। এটি আরও দেখায় যে মডেলটি ফাংশন কলের জন্য (এবং এর অন্তর্নিহিত বহিরাগত API) প্রয়োজনীয় ইনপুট প্যারামিটার মান সরবরাহ করেছে।
এই উদাহরণে, ইনকামিং রিকোয়েস্টে What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? প্রম্পটটি ছিল। এই প্রম্পট থেকে, মডেলটি fetchWeather ফাংশনের (অর্থাৎ, city , state এবং date ) প্রয়োজনীয় ইনপুট প্যারামিটারগুলি অনুমান করেছে।
সুইফট
let chat = model.startChat()
let prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let response = try await chat.sendMessage(prompt)
var functionResponses = [FunctionResponsePart]()
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
for functionCall in response.functionCalls {
if functionCall.name == "fetchWeather" {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
guard case let .object(location) = functionCall.args["location"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(city) = location["city"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(state) = location["state"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(date) = functionCall.args["date"] else { fatalError() }
functionResponses.append(FunctionResponsePart(
name: functionCall.name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: fetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
))
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
Kotlin
val prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
val chat = model.startChat()
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
val result = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
val functionCalls = result.functionCalls
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
val fetchWeatherCall = functionCalls.find { it.name == "fetchWeather" }
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
val functionResponse = fetchWeatherCall?.let {
// Alternatively, if your `Location` class is marked as @Serializable, you can use
// val location = Json.decodeFromJsonElement<Location>(it.args["location"]!!)
val location = Location(
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["city"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content,
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["state"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
)
val date = it.args["date"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
fetchWeather(location, date)
}
Java
String prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
ChatFutures chatFutures = model.startChat();
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response =
chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("user", List.of(new TextPart(prompt))));
ListenableFuture<JsonObject> handleFunctionCallFuture = Futures.transform(response, result -> {
for (FunctionCallPart functionCall : result.getFunctionCalls()) {
if (functionCall.getName().equals("fetchWeather")) {
Map<String, JsonElement> args = functionCall.getArgs();
JsonObject locationJsonObject =
JsonElementKt.getJsonObject(args.get("location"));
String city =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("city")));
String state =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("state")));
Location location = new Location(city, state);
String date = JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
args.get("date")));
return fetchWeather(location, date);
}
}
return null;
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
const chat = model.startChat();
const prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let result = await chat.sendMessage(prompt);
const functionCalls = result.response.functionCalls();
let functionCall;
let functionResult;
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.length > 0) {
for (const call of functionCalls) {
if (call.name === "fetchWeather") {
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
functionResult = await fetchWeather(call.args);
functionCall = call;
}
}
}
Dart
final chat = _functionCallModel.startChat();
const prompt = 'What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?';
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.sendMessage(Content.text(prompt));
final functionCalls = response.functionCalls.toList();
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.isNotEmpty) {
for (final functionCall in functionCalls) {
if (functionCall.name == 'fetchWeather') {
Map<String, dynamic> location =
functionCall.args['location']! as Map<String, dynamic>;
var date = functionCall.args['date']! as String;
var city = location['city'] as String;
var state = location['state'] as String;
final functionResult =
await fetchWeather(Location(city, state), date);
// Send the response to the model so that it can use the result to
// generate text for the user.
response = await functionCallChat.sendMessage(
Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult),
);
}
}
} else {
throw UnimplementedError(
'Function not declared to the model: ${functionCall.name}',
);
}
ঐক্য
var chat = model.StartChat();
var prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.SendMessageAsync(prompt);
var functionResponses = new List<ModelContent>();
foreach (var functionCall in response.FunctionCalls) {
if (functionCall.Name == "fetchWeather") {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
var city = functionCall.Args["city"] as string;
var state = functionCall.Args["state"] as string;
var date = functionCall.Args["date"] as string;
functionResponses.Add(ModelContent.FunctionResponse(
name: functionCall.Name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: FetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
));
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
ধাপ ৫ : চূড়ান্ত প্রতিক্রিয়া তৈরি করতে মডেলটিকে ফাংশনের আউটপুট প্রদান করুন।
fetchWeather ফাংশনটি আবহাওয়ার তথ্য ফেরত দেওয়ার পরে, আপনার অ্যাপটিকে এটি মডেলের কাছে ফেরত পাঠাতে হবে।
তারপর, মডেলটি তার চূড়ান্ত প্রক্রিয়াকরণ সম্পাদন করে এবং একটি চূড়ান্ত প্রাকৃতিক-ভাষা প্রতিক্রিয়া তৈরি করে যেমন: On October 17, 2024 in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
সুইফট
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
let finalResponse = try await chat.sendMessage(
[ModelContent(role: "function", parts: functionResponses)]
)
// Log the text response.
print(finalResponse.text ?? "No text in response.")
Kotlin
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
val finalResponse = chat.sendMessage(content("function") {
part(FunctionResponsePart("fetchWeather", functionResponse!!))
})
// Log the text response.
println(finalResponse.text ?: "No text in response")
Java
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> modelResponseFuture = Futures.transformAsync(
handleFunctionCallFuture,
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
functionCallResult -> chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("function",
List.of(new FunctionResponsePart(
"fetchWeather", functionCallResult)))),
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Futures.addCallback(modelResponseFuture, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
if (result.getText() != null) {
// Log the text response.
System.out.println(result.getText());
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
// handle error
}
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
result = await chat.sendMessage([
{
functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name, // "fetchWeather"
response: functionResult,
},
},
]);
console.log(result.response.text());
Dart
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
response = await chat
.sendMessage(Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult));
ঐক্য
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
var finalResponse = await chat.SendMessageAsync(functionResponses);
// Log the text response.
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(finalResponse.Text ?? "No text in response.");
অতিরিক্ত আচরণ এবং বিকল্পগুলি
ফাংশন কলিংয়ের জন্য এখানে কিছু অতিরিক্ত আচরণ দেওয়া হল যা আপনার কোড এবং আপনার নিয়ন্ত্রণে থাকা বিকল্পগুলিতে অন্তর্ভুক্ত করতে হবে।
মডেলটি আবার একটি ফাংশন অথবা অন্য কোনও ফাংশন কল করতে বলতে পারে।
যদি একটি ফাংশন কল থেকে প্রাপ্ত প্রতিক্রিয়া মডেলটির চূড়ান্ত প্রতিক্রিয়া তৈরি করতে অপর্যাপ্ত হয়, তাহলে মডেলটি একটি অতিরিক্ত ফাংশন কল চাইতে পারে, অথবা সম্পূর্ণ ভিন্ন ফাংশনে কল চাইতে পারে। পরবর্তীটি কেবল তখনই ঘটতে পারে যদি আপনি আপনার ফাংশন ঘোষণার তালিকার মডেলটিকে একাধিক ফাংশন প্রদান করেন।
আপনার অ্যাপটিকে এমনভাবে মানিয়ে নিতে হবে যে মডেলটি অতিরিক্ত ফাংশন কল চাইতে পারে।
মডেলটি একই সময়ে একাধিক ফাংশন কল করতে বলতে পারে।
তুমি তোমার ফাংশন ঘোষণার তালিকা থেকে ১২৮টি পর্যন্ত ফাংশন মডেলটিকে প্রদান করতে পারো। এই কারণে, মডেলটি সিদ্ধান্ত নিতে পারে যে তার চূড়ান্ত প্রতিক্রিয়া তৈরি করতে সাহায্য করার জন্য একাধিক ফাংশনের প্রয়োজন। এবং এটি একই সময়ে এই ফাংশনগুলির কিছু কল করার সিদ্ধান্ত নিতে পারে - এটিকে প্যারালাল ফাংশন কলিং বলা হয়।
আপনার অ্যাপটিকে এমনভাবে মানিয়ে নিতে হবে যে মডেলটি একই সময়ে একাধিক ফাংশন চালানোর জন্য অনুরোধ করতে পারে এবং আপনার অ্যাপটিকে ফাংশন থেকে সমস্ত প্রতিক্রিয়া মডেলে ফিরিয়ে আনতে হবে।
মডেলটি কীভাবে এবং কীভাবে ফাংশন কল করতে বলবে তা আপনি নিয়ন্ত্রণ করতে পারেন।
মডেলটি কীভাবে এবং প্রদত্ত ফাংশন ঘোষণাগুলি ব্যবহার করবে কিনা সে সম্পর্কে আপনি কিছু সীমাবদ্ধতা রাখতে পারেন। এটিকে ফাংশন কলিং মোড সেট করা বলা হয়। এখানে কিছু উদাহরণ দেওয়া হল:
মডেলটিকে তাৎক্ষণিক প্রাকৃতিক ভাষা প্রতিক্রিয়া এবং একটি ফাংশন কলের মধ্যে একটি বেছে নেওয়ার অনুমতি দেওয়ার পরিবর্তে, আপনি এটিকে সর্বদা ফাংশন কল ব্যবহার করতে বাধ্য করতে পারেন। এটিকে বলা হয় জোরপূর্বক ফাংশন কলিং ।
যদি আপনি একাধিক ফাংশন ঘোষণা প্রদান করেন, তাহলে আপনি মডেলটিকে শুধুমাত্র প্রদত্ত ফাংশনগুলির একটি উপসেট ব্যবহার করার মধ্যে সীমাবদ্ধ রাখতে পারেন।
আপনি প্রম্পট এবং ফাংশন ঘোষণার সাথে একটি টুল কনফিগারেশন ( toolConfig ) যোগ করে এই সীমাবদ্ধতাগুলি (অথবা মোডগুলি) বাস্তবায়ন করতে পারেন। টুল কনফিগারেশনে, আপনি নিম্নলিখিত মোডগুলির মধ্যে একটি নির্দিষ্ট করতে পারেন। সবচেয়ে কার্যকর মোড হল ANY ।
| মোড | বিবরণ |
|---|---|
AUTO | ডিফল্ট মডেল আচরণ। মডেলটি সিদ্ধান্ত নেয় যে ফাংশন কল ব্যবহার করা হবে নাকি প্রাকৃতিক ভাষা প্রতিক্রিয়া ব্যবহার করা হবে। |
ANY | মডেলটিকে অবশ্যই ফাংশন কল ("ফোর্সড ফাংশন কলিং") ব্যবহার করতে হবে। মডেলটিকে ফাংশনের একটি উপসেটে সীমাবদ্ধ রাখতে, allowedFunctionNames এ অনুমোদিত ফাংশনের নামগুলি নির্দিষ্ট করুন। |
NONE | মডেলটি অবশ্যই ফাংশন কল ব্যবহার করবে না। এই আচরণটি কোনও সম্পর্কিত ফাংশন ঘোষণা ছাড়াই একটি মডেল অনুরোধের সমতুল্য। |
তুমি আর কি করতে পারো?
অন্যান্য ক্ষমতা চেষ্টা করে দেখুন
- বহু-পালা কথোপকথন (চ্যাট) তৈরি করুন।
- শুধুমাত্র টেক্সট প্রম্পট থেকে টেক্সট তৈরি করুন।
- ছবি , পিডিএফ , ভিডিও এবং অডিওর মতো বিভিন্ন ধরণের ফাইল ব্যবহার করে প্রম্পট করে টেক্সট তৈরি করুন।
কন্টেন্ট তৈরি কীভাবে নিয়ন্ত্রণ করতে হয় তা শিখুন
- সর্বোত্তম অনুশীলন, কৌশল এবং উদাহরণ প্রম্পট সহ দ্রুত নকশা বুঝুন ।
- তাপমাত্রা এবং সর্বোচ্চ আউটপুট টোকেন ( জেমিনির জন্য) অথবা আকৃতির অনুপাত এবং ব্যক্তি প্রজন্ম ( ইমেজেনের জন্য) এর মতো মডেল প্যারামিটারগুলি কনফিগার করুন ।
- ক্ষতিকারক বলে বিবেচিত হতে পারে এমন প্রতিক্রিয়া পাওয়ার সম্ভাবনা সামঞ্জস্য করতে নিরাপত্তা সেটিংস ব্যবহার করুন ।
সমর্থিত মডেলগুলি সম্পর্কে আরও জানুন
বিভিন্ন ব্যবহারের ক্ষেত্রে উপলব্ধ মডেল এবং তাদের কোটা এবং মূল্য সম্পর্কে জানুন।Firebase AI Logic এর সাথে আপনার অভিজ্ঞতা সম্পর্কে মতামত দিন।

