تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية هو أداة تتيح للنموذج إنشاء رموز Python البرمجية وتشغيلها. يمكن للنموذج أن يتعلّم بشكل متكرّر من نتائج تنفيذ الرمز إلى أن يصل إلى الناتج النهائي.
يمكنك استخدام ميزة "تنفيذ الرمز" لإنشاء ميزات تستفيد من الاستدلال المستند إلى الرمز وتنشئ ناتجًا نصيًا. على سبيل المثال، يمكنك استخدام ميزة "تنفيذ الرمز" لحل المعادلات أو معالجة النصوص. يمكنك أيضًا استخدام المكتبات المضمّنة في بيئة تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي لإجراء مهام أكثر تخصصًا.
وكما هو الحال مع جميع الأدوات التي تقدّمها للنموذج، يقرّر النموذج متى يستخدم ميزة "تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي".
مقارنة بين تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي واستدعاء الدالة
تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية واستدعاء الدوال هما ميزتان متشابهتان. بشكل عام، ننصحك باستخدام تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي إذا كان بإمكان النموذج التعامل مع حالة الاستخدام. كما أنّ تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية أسهل استخدامًا لأنّ ما عليك سوى تفعيله.
في ما يلي بعض الاختلافات الإضافية بين تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية واستدعاء الدالة:
| تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية | استدعاء الدالة |
|---|---|
| استخدِم ميزة "تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي" إذا كنت تريد أن يكتب النموذج رمز Python ويشغّله نيابةً عنك ويعرض النتيجة. | استخدِم ميزة "استدعاء الدوال" إذا كانت لديك دوال خاصة بك تريد تشغيلها محليًا. |
| تتيح ميزة "تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية" للنموذج تشغيل الرموز البرمجية في الخلفية لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات في بيئة ثابتة ومعزولة. | تتيح لك ميزة "استدعاء الدوال" تنفيذ الدوال التي يطلبها النموذج في أي بيئة تريدها. |
| يتم حلّ تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي في طلب واحد. على الرغم من أنّه يمكنك اختياريًا استخدام تنفيذ الرمز مع ميزة المحادثة، إلا أنّ ذلك ليس شرطًا. | تتطلّب ميزة "استدعاء الدوال" طلبًا إضافيًا لإعادة إرسال الناتج من كل عملية استدعاء دالة. وبالتالي، عليك استخدام ميزة المحادثة. |
النماذج المتوافقة
gemini-3-pro-previewgemini-2.5-progemini-2.5-flashgemini-2.5-flash-lite-
gemini-2.0-flash-001(والاسم المستعارgemini-2.0-flashالذي يتم تعديله تلقائيًا) gemini-2.0-flash-live-preview-04-09
استخدام تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية
يمكنك استخدام ميزة تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية مع كلّ من الإدخال النصي فقط والإدخال المتعدّد الوسائط، ولكن ستكون الاستجابة دائمًا نصًا أو تعليمات برمجية فقط.
قبل البدء
|
انقر على مزوّد Gemini API لعرض المحتوى والرمز الخاصين بالمزوّد على هذه الصفحة. |
إذا لم يسبق لك إجراء ذلك، أكمل دليل بدء الاستخدام الذي يوضّح كيفية إعداد مشروعك على Firebase وربط تطبيقك بمنصة Firebase وإضافة حزمة تطوير البرامج (SDK) وتهيئة خدمة الخلفية لمقدّم خدمة Gemini API الذي اخترته وإنشاء مثيل GenerativeModel.
لاختبار طلباتك وتكرارها، ننصحك باستخدام Google AI Studio.
تفعيل تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية
|
قبل تجربة هذا النموذج، أكمل القسم
قبل البدء من هذا الدليل
لإعداد مشروعك وتطبيقك. في هذا القسم، ستنقر أيضًا على زر لمقدّم الخدمة الذي اخترته Gemini API حتى يظهر لك المحتوى الخاص بمقدّم الخدمة في هذه الصفحة. |
عند إنشاء مثيل GenerativeModel، قدِّم CodeExecution كأداة يمكن للنموذج استخدامها لإنشاء الرد. يتيح ذلك للنموذج إنشاء رموز Python البرمجية وتشغيلها.
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
let ai = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI())
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = ai.generativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [.codeExecution()]
)
let prompt = """
What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers?
Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.
"""
let response = try await model.generateContent(prompt)
guard let candidate = response.candidates.first else {
print("No candidates in response.")
return
}
for part in candidate.content.parts {
if let textPart = part as? TextPart {
print("Text = \(textPart.text)")
} else if let executableCode = part as? ExecutableCodePart {
print("Code = \(executableCode.code), Language = \(executableCode.language)")
} else if let executionResult = part as? CodeExecutionResultPart {
print("Outcome = \(executionResult.outcome), Result = \(executionResult.output ?? "no output")")
}
}
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools = listOf(Tool.codeExecution())
)
val prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
val response = model.generateContent(prompt)
response.candidates.first().content.parts.forEach {
if(it is TextPart) {
println("Text = ${it.text}")
}
if(it is ExecutableCodePart) {
println("Code = ${it.code}, Language = ${it.language}")
}
if(it is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
println("Outcome = ${it.outcome}, Result = ${it.output}")
}
}
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
null,
null,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
List.of(Tool.codeExecution()));
// Use the GenerativeModelFutures Java compatibility layer which offers
// support for ListenableFuture and Publisher APIs
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
String text = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText(text)
.build();
ListenableFuture response = model.generateContent(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse response) {
// Access the first candidate's content parts
List parts = response.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts();
for (Part part : parts) {
if (part instanceof TextPart) {
TextPart textPart = (TextPart) part;
System.out.println("Text = " + textPart.getText());
} else if (part instanceof ExecutableCodePart) {
ExecutableCodePart codePart = (ExecutableCodePart) part;
System.out.println("Code = " + codePart.getCode() + ", Language = " + codePart.getLanguage());
} else if (part instanceof CodeExecutionResultPart) {
CodeExecutionResultPart resultPart = (CodeExecutionResultPart) part;
System.out.println("Outcome = " + resultPart.getOutcome() + ", Result = " + resultPart.getOutput());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const ai = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(
ai,
{
model: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }]
}
);
const prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
const result = await model.generateContent(prompt);
const response = await result.response;
const parts = response.candidates?.[0].content.parts;
if (parts) {
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(`Text: ${part.text}`);
} else if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(
`Code: ${part.executableCode.code}, Language: ${part.executableCode.language}`
);
} else if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(
`Outcome: ${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}, Result: ${part.codeExecutionResult.output}`
);
}
});
}
Dart
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
final model = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'GEMINI_MODEL_NAME',
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [
Tool.codeExecution(),
],
);
const prompt = 'What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? '
'Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.';
final response = await model.generateContent([Content.text(prompt)]);
final buffer = StringBuffer();
for (final part in response.candidates.first.content.parts) {
if (part is TextPart) {
buffer.writeln(part.text);
} else if (part is ExecutableCodePart) {
buffer.writeln('Executable Code:');
buffer.writeln('Language: ${part.language}');
buffer.writeln('Code:');
buffer.writeln(part.code);
} else if (part is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
buffer.writeln('Code Execution Result:');
buffer.writeln('Outcome: ${part.outcome}');
buffer.writeln('Output:');
buffer.writeln(part.output);
}
}
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
var ai = FirebaseAI.GetInstance(FirebaseAI.Backend.GoogleAI());
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = ai.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: new Tool[] { new Tool(new CodeExecution()) }
);
var prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
var response = await model.GenerateContentAsync(prompt);
foreach (var part in response.Candidates.First().Content.Parts) {
if (part is ModelContent.TextPart tp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Text = {tp.Text}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.ExecutableCodePart esp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Code = {esp.Code}, Language = {esp.Language}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.CodeExecutionResultPart cerp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Outcome = {cerp.Outcome}, Output = {cerp.Output}");
}
}
تعرَّف على كيفية اختيار نموذج مناسبَين لحالة الاستخدام والتطبيق.
استخدام ميزة "تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي" في المحادثة
يمكنك أيضًا استخدام تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية كجزء من محادثة:
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
let ai = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI())
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = ai.generativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [.codeExecution()]
)
let prompt = """
What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers?
Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.
"""
let chat = model.startChat()
let response = try await chat.sendMessage(prompt)
guard let candidate = response.candidates.first else {
print("No candidates in response.")
return
}
for part in candidate.content.parts {
if let textPart = part as? TextPart {
print("Text = \(textPart.text)")
} else if let executableCode = part as? ExecutableCodePart {
print("Code = \(executableCode.code), Language = \(executableCode.language)")
} else if let executionResult = part as? CodeExecutionResultPart {
print("Outcome = \(executionResult.outcome), Result = \(executionResult.output ?? "no output")")
}
}
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools = listOf(Tool.codeExecution())
)
val prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
val chat = model.startChat()
val response = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
response.candidates.first().content.parts.forEach {
if(it is TextPart) {
println("Text = ${it.text}")
}
if(it is ExecutableCodePart) {
println("Code = ${it.code}, Language = ${it.language}")
}
if(it is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
println("Outcome = ${it.outcome}, Result = ${it.output}")
}
}
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
null,
null,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
List.of(Tool.codeExecution()));
// Use the GenerativeModelFutures Java compatibility layer which offers
// support for ListenableFuture and Publisher APIs
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
String text = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText(text)
.build();
ChatFutures chat = model.startChat();
ListenableFuture response = chat.sendMessage(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse response) {
// Access the first candidate's content parts
List parts = response.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts();
for (Part part : parts) {
if (part instanceof TextPart) {
TextPart textPart = (TextPart) part;
System.out.println("Text = " + textPart.getText());
} else if (part instanceof ExecutableCodePart) {
ExecutableCodePart codePart = (ExecutableCodePart) part;
System.out.println("Code = " + codePart.getCode() + ", Language = " + codePart.getLanguage());
} else if (part instanceof CodeExecutionResultPart) {
CodeExecutionResultPart resultPart = (CodeExecutionResultPart) part;
System.out.println("Outcome = " + resultPart.getOutcome() + ", Result = " + resultPart.getOutput());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const ai = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(
ai,
{
model: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }]
}
);
const prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
const chat = model.startChat()
const result = await chat.sendMessage(prompt);
const parts = result.response.candidates?.[0].content.parts;
if (parts) {
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(`Text: ${part.text}`);
} else if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(
`Code: ${part.executableCode.code}, Language: ${part.executableCode.language}`
);
} else if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(
`Outcome: ${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}, Result: ${part.codeExecutionResult.output}`
);
}
});
}
Dart
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
final model = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'GEMINI_MODEL_NAME',
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [
Tool.codeExecution(),
],
);
final codeExecutionChat = await model.startChat();
const prompt = 'What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? '
'Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.';
final response = await codeExecutionChat.sendMessage(Content.text(prompt));
final buffer = StringBuffer();
for (final part in response.candidates.first.content.parts) {
if (part is TextPart) {
buffer.writeln(part.text);
} else if (part is ExecutableCodePart) {
buffer.writeln('Executable Code:');
buffer.writeln('Language: ${part.language}');
buffer.writeln('Code:');
buffer.writeln(part.code);
} else if (part is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
buffer.writeln('Code Execution Result:');
buffer.writeln('Outcome: ${part.outcome}');
buffer.writeln('Output:');
buffer.writeln(part.output);
}
}
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
var ai = FirebaseAI.GetInstance(FirebaseAI.Backend.GoogleAI());
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = ai.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: new Tool[] { new Tool(new CodeExecution()) }
);
var prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
var chat = model.StartChat();
var response = await chat.SendMessageAsync(prompt);
foreach (var part in response.Candidates.First().Content.Parts) {
if (part is ModelContent.TextPart tp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Text = {tp.Text}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.ExecutableCodePart esp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Code = {esp.Code}, Language = {esp.Language}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.CodeExecutionResultPart cerp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Outcome = {cerp.Outcome}, Output = {cerp.Output}");
}
}
تعرَّف على كيفية اختيار نموذج مناسبَين لحالة الاستخدام والتطبيق.
الأسعار
لا يتم تحصيل أي رسوم إضافية مقابل تفعيل تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية وتوفيرها كأداة للنموذج. إذا قرر النموذج استخدام ميزة تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية، سيتم تحصيل الرسوم منك وفقًا للسعر الحالي لرموز الإدخال والإخراج استنادًا إلى نموذج Gemini الذي تستخدمه.
يوضّح الرسم البياني التالي نموذج الفوترة لتنفيذ الرمز:
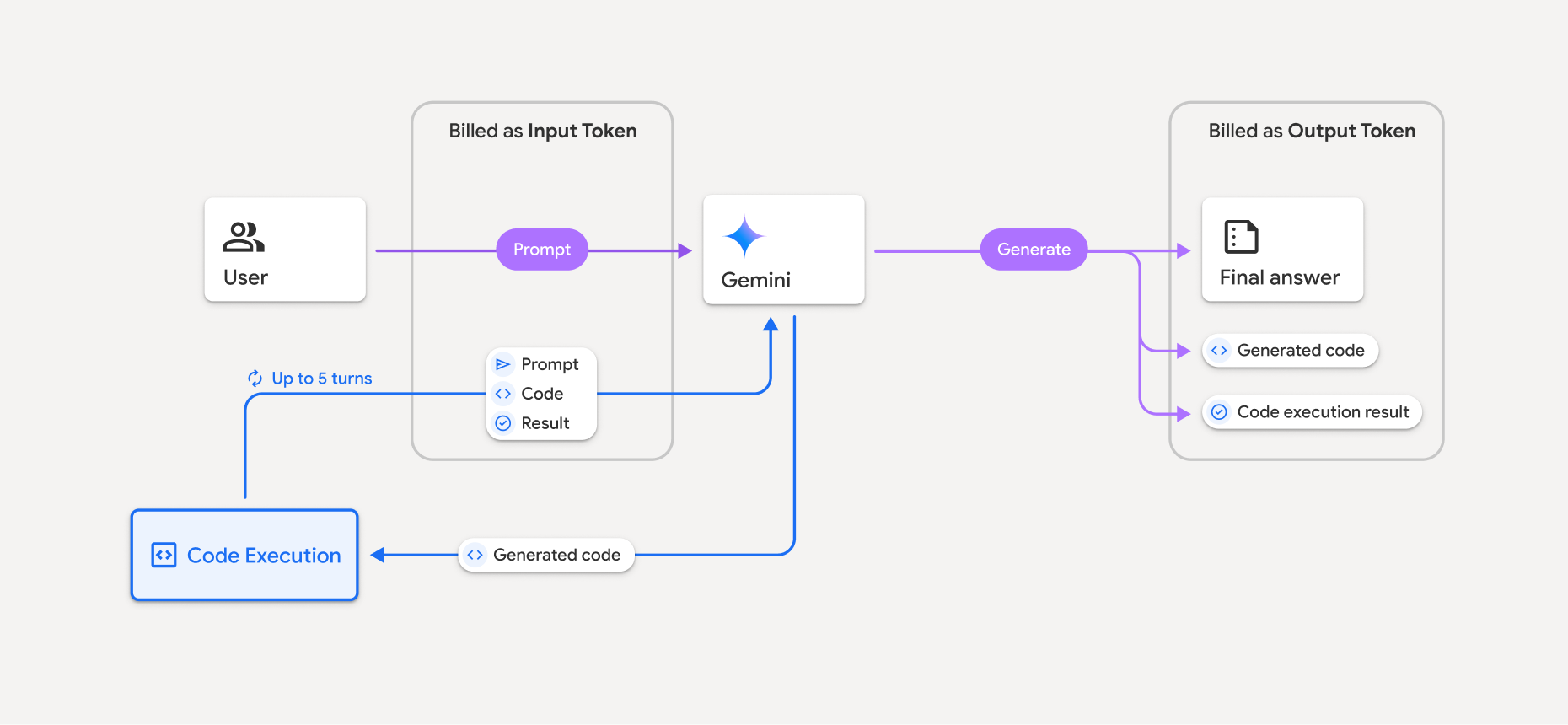
في ما يلي ملخّص لطريقة احتساب تكلفة الرموز المميزة عندما يستخدم النموذج تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي:
تتم محاسبتك على الطلب الأصلي مرة واحدة. يتم تصنيف الرموز المميزة الخاصة به على أنّها رموز مميزة وسيطة، ويتم تحصيل الرسوم منها باعتبارها رموزًا مميزة للإدخال.
يتم تحصيل رسوم مقابل الرمز البرمجي الذي تم إنشاؤه ونتيجة الرمز البرمجي الذي تم تنفيذه على النحو التالي:
عند استخدامها أثناء تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي، يتم تصنيفها على أنّها رموز وسيطة يتم تحصيل رسومها كرموز إدخال.
عندما يتم تضمينها كجزء من الرد النهائي، يتم تحصيل الرسوم منها باعتبارها رموزًا مميزة للناتج.
يتم تحصيل رسوم الملخّص النهائي في الردّ الأخير على أنّه رموز مميّزة للناتج.
يتضمّن Gemini API عدد الرموز المميزة الوسيطة في الردّ من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات، ما يتيح لك معرفة سبب تحصيل رسوم منك مقابل الرموز المميزة للإدخال التي تتجاوز طلبك الأولي.
يُرجى العِلم أنّ الرمز الذي يتم إنشاؤه يمكن أن يتضمّن نصًا ومخرجات متعدّدة الوسائط، مثل الصور.
القيود وأفضل الممارسات
يمكن للنموذج إنشاء رموز Python وتنفيذها فقط. ولا يمكنه عرض عناصر أخرى، مثل ملفات الوسائط.
يمكن أن يستغرق تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي 30 ثانية كحدّ أقصى قبل انتهاء المهلة.
في بعض الحالات، يمكن أن يؤدي تفعيل تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية إلى تراجع في مجالات أخرى من ناتج النموذج (على سبيل المثال، كتابة قصة).
لا تتيح أداة تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية استخدام معرّفات الموارد الموحّدة للملفات كمدخلات أو مخرجات. ومع ذلك، تتيح أداة تنفيذ الرموز البرمجية إدخال الملفات وإخراج الرسومات البيانية كبايتات مضمّنة. باستخدام إمكانات الإدخال والإخراج هذه، يمكنك تحميل ملفات CSV وملفات نصية، وطرح أسئلة حول الملفات، وإنشاء رسومات بيانية باستخدام Matplotlib كجزء من نتيجة تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي. أنواع MIME المتوافقة مع وحدات البايت المضمّنة هي
.cppو.csvو.javaو.jpegو.jsو.pngو.pyو.tsو.xml.
المكتبات المتوافقة
تتضمّن بيئة تنفيذ الرمز البرمجي المكتبات التالية. لا يمكنك تثبيت مكتباتك الخاصة.
تقديم ملاحظات حول تجربتك مع Firebase AI Logic
