اجرای کد ابزاری است که مدل را قادر میسازد کد پایتون را تولید و اجرا کند. مدل میتواند به صورت تکراری از نتایج اجرای کد یاد بگیرد تا زمانی که به خروجی نهایی برسد.
شما میتوانید از اجرای کد برای ساخت ویژگیهایی استفاده کنید که از استدلال مبتنی بر کد بهره میبرند و خروجی متنی تولید میکنند. به عنوان مثال، میتوانید از اجرای کد برای حل معادلات یا پردازش متن استفاده کنید. همچنین میتوانید از کتابخانههای موجود در محیط اجرای کد برای انجام وظایف تخصصیتر استفاده کنید.
درست مانند تمام ابزارهایی که در اختیار مدل قرار میدهید، مدل تصمیم میگیرد چه زمانی از اجرای کد استفاده کند.
مقایسه اجرای کد در مقابل فراخوانی تابع
اجرای کد و فراخوانی تابع ویژگیهای مشابهی هستند. به طور کلی، اگر مدل بتواند مورد استفاده شما را مدیریت کند، باید ترجیح دهید از اجرای کد استفاده کنید. اجرای کد همچنین سادهتر است زیرا فقط آن را فعال میکنید.
در اینجا چند تفاوت دیگر بین اجرای کد و فراخوانی تابع آورده شده است:
| اجرای کد | فراخوانی تابع |
|---|---|
| اگر میخواهید مدل کد پایتون را برای شما بنویسد و اجرا کند و نتیجه را برگرداند، از اجرای کد استفاده کنید. | اگر از قبل توابع خودتان را دارید که میخواهید به صورت محلی اجرا کنید، از فراخوانی تابع استفاده کنید. |
| اجرای کد به مدل اجازه میدهد تا کد را در بکاند API در یک محیط ثابت و ایزوله اجرا کند. | فراخوانی تابع به شما امکان میدهد توابعی را که مدل درخواست میکند، در هر محیطی که میخواهید اجرا کنید. |
| اجرای کد در یک درخواست واحد انجام میشود. اگرچه میتوانید به صورت اختیاری از اجرای کد با قابلیت چت استفاده کنید، اما الزامی وجود ندارد. | فراخوانی تابع نیاز به یک درخواست اضافی برای ارسال خروجی از هر فراخوانی تابع دارد. بنابراین، شما ملزم به استفاده از قابلیت چت هستید. |
مدلهای پشتیبانیشده
-
gemini-3-pro-preview -
gemini-3-flash-preview -
gemini-2.5-pro -
gemini-2.5-flash -
gemini-2.5-flash-lite -
gemini-2.0-flash-001(و نام مستعار بهروزرسانیشده خودکار آنgemini-2.0-flash)
استفاده از اجرای کد
شما میتوانید از اجرای کد هم با ورودی فقط متنی و هم با ورودی چندوجهی استفاده کنید، اما پاسخ همیشه فقط متن یا کد خواهد بود.
قبل از اینکه شروع کنی
برای مشاهده محتوا و کد مخصوص ارائهدهنده در این صفحه، روی ارائهدهنده API Gemini خود کلیک کنید. |
اگر هنوز این کار را نکردهاید، راهنمای شروع به کار را تکمیل کنید، که نحوه راهاندازی پروژه Firebase، اتصال برنامه به Firebase، افزودن SDK، راهاندازی سرویس backend برای ارائهدهنده API انتخابی Gemini و ایجاد یک نمونه GenerativeModel شرح میدهد.
فعال کردن اجرای کد
| قبل از امتحان کردن این نمونه، بخش «قبل از شروع» این راهنما را برای راهاندازی پروژه و برنامه خود تکمیل کنید. در آن بخش، شما همچنین میتوانید روی دکمهای برای ارائهدهندهی API Gemini انتخابی خود کلیک کنید تا محتوای خاص ارائهدهنده را در این صفحه مشاهده کنید . |
وقتی نمونهی GenerativeModel را ایجاد میکنید، CodeExecution به عنوان ابزاری که مدل میتواند برای تولید پاسخ خود از آن استفاده کند، ارائه دهید. این به مدل اجازه میدهد تا کد پایتون را تولید و اجرا کند.
سویفت
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
let ai = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI())
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = ai.generativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [.codeExecution()]
)
let prompt = """
What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers?
Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.
"""
let response = try await model.generateContent(prompt)
guard let candidate = response.candidates.first else {
print("No candidates in response.")
return
}
for part in candidate.content.parts {
if let textPart = part as? TextPart {
print("Text = \(textPart.text)")
} else if let executableCode = part as? ExecutableCodePart {
print("Code = \(executableCode.code), Language = \(executableCode.language)")
} else if let executionResult = part as? CodeExecutionResultPart {
print("Outcome = \(executionResult.outcome), Result = \(executionResult.output ?? "no output")")
}
}
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools = listOf(Tool.codeExecution())
)
val prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
val response = model.generateContent(prompt)
response.candidates.first().content.parts.forEach {
if(it is TextPart) {
println("Text = ${it.text}")
}
if(it is ExecutableCodePart) {
println("Code = ${it.code}, Language = ${it.language}")
}
if(it is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
println("Outcome = ${it.outcome}, Result = ${it.output}")
}
}
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
null,
null,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
List.of(Tool.codeExecution()));
// Use the GenerativeModelFutures Java compatibility layer which offers
// support for ListenableFuture and Publisher APIs
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
String text = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText(text)
.build();
ListenableFuture response = model.generateContent(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse response) {
// Access the first candidate's content parts
List parts = response.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts();
for (Part part : parts) {
if (part instanceof TextPart) {
TextPart textPart = (TextPart) part;
System.out.println("Text = " + textPart.getText());
} else if (part instanceof ExecutableCodePart) {
ExecutableCodePart codePart = (ExecutableCodePart) part;
System.out.println("Code = " + codePart.getCode() + ", Language = " + codePart.getLanguage());
} else if (part instanceof CodeExecutionResultPart) {
CodeExecutionResultPart resultPart = (CodeExecutionResultPart) part;
System.out.println("Outcome = " + resultPart.getOutcome() + ", Result = " + resultPart.getOutput());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const ai = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(
ai,
{
model: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }]
}
);
const prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
const result = await model.generateContent(prompt);
const response = await result.response;
const parts = response.candidates?.[0].content.parts;
if (parts) {
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(`Text: ${part.text}`);
} else if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(
`Code: ${part.executableCode.code}, Language: ${part.executableCode.language}`
);
} else if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(
`Outcome: ${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}, Result: ${part.codeExecutionResult.output}`
);
}
});
}
Dart
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
final model = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'GEMINI_MODEL_NAME',
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [
Tool.codeExecution(),
],
);
const prompt = 'What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? '
'Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.';
final response = await model.generateContent([Content.text(prompt)]);
final buffer = StringBuffer();
for (final part in response.candidates.first.content.parts) {
if (part is TextPart) {
buffer.writeln(part.text);
} else if (part is ExecutableCodePart) {
buffer.writeln('Executable Code:');
buffer.writeln('Language: ${part.language}');
buffer.writeln('Code:');
buffer.writeln(part.code);
} else if (part is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
buffer.writeln('Code Execution Result:');
buffer.writeln('Outcome: ${part.outcome}');
buffer.writeln('Output:');
buffer.writeln(part.output);
}
}
وحدت
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
var ai = FirebaseAI.GetInstance(FirebaseAI.Backend.GoogleAI());
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = ai.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: new Tool[] { new Tool(new CodeExecution()) }
);
var prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
var response = await model.GenerateContentAsync(prompt);
foreach (var part in response.Candidates.First().Content.Parts) {
if (part is ModelContent.TextPart tp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Text = {tp.Text}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.ExecutableCodePart esp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Code = {esp.Code}, Language = {esp.Language}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.CodeExecutionResultPart cerp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Outcome = {cerp.Outcome}, Output = {cerp.Output}");
}
}
یاد بگیرید که چگونه یک مدل را انتخاب کنیدمناسب برای مورد استفاده و برنامه شما.
خروجی ممکن است چیزی شبیه به زیر باشد که برای خوانایی بیشتر قالببندی شده است:
Okay, I need to calculate the sum of the first 50 prime numbers. Here's how I'll
approach this:
1. **Generate Prime Numbers:** I'll use an iterative method to find prime
numbers. I'll start with 2 and check if each subsequent number is divisible
by any number between 2 and its square root. If not, it's a prime.
2. **Store Primes:** I'll store the prime numbers in a list until I have 50 of
them.
3. **Calculate the Sum:** Finally, I'll sum the prime numbers in the list.
Here's the Python code to do this:
def is_prime(n):
"""Efficiently checks if a number is prime."""
if n <= 1:
return False
if n <= 3:
return True
if n % 2 == 0 or n % 3 == 0:
return False
i = 5
while i * i <= n:
if n % i == 0 or n % (i + 2) == 0:
return False
i += 6
return True
primes = []
num = 2
while len(primes) < 50:
if is_prime(num):
primes.append(num)
num += 1
sum_of_primes = sum(primes)
print(f'{primes=}')
print(f'{sum_of_primes=}')
primes=[2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67,
71, 73, 79, 83, 89, 97, 101, 103, 107, 109, 113, 127, 131, 137, 139, 149, 151,
157, 163, 167, 173, 179, 181, 191, 193, 197, 199, 211, 223, 227, 229]
sum_of_primes=5117
The sum of the first 50 prime numbers is 5117.
این خروجی چندین بخش محتوا را که مدل هنگام استفاده از اجرای کد برمیگرداند، ترکیب میکند:
-
text: متن درونخطی تولید شده توسط مدل -
executableCode: کدی که توسط مدل تولید میشود و قرار است اجرا شود -
codeExecutionResult: نتیجه کد اجرا شده
قراردادهای نامگذاری برای این بخشها بسته به زبان برنامهنویسی متفاوت است.
استفاده از اجرای کد در چت
همچنین میتوانید از اجرای کد به عنوان بخشی از چت استفاده کنید:
سویفت
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
let ai = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI())
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = ai.generativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [.codeExecution()]
)
let prompt = """
What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers?
Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.
"""
let chat = model.startChat()
let response = try await chat.sendMessage(prompt)
guard let candidate = response.candidates.first else {
print("No candidates in response.")
return
}
for part in candidate.content.parts {
if let textPart = part as? TextPart {
print("Text = \(textPart.text)")
} else if let executableCode = part as? ExecutableCodePart {
print("Code = \(executableCode.code), Language = \(executableCode.language)")
} else if let executionResult = part as? CodeExecutionResultPart {
print("Outcome = \(executionResult.outcome), Result = \(executionResult.output ?? "no output")")
}
}
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools = listOf(Tool.codeExecution())
)
val prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
val chat = model.startChat()
val response = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
response.candidates.first().content.parts.forEach {
if(it is TextPart) {
println("Text = ${it.text}")
}
if(it is ExecutableCodePart) {
println("Code = ${it.code}, Language = ${it.language}")
}
if(it is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
println("Outcome = ${it.outcome}, Result = ${it.output}")
}
}
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
null,
null,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
List.of(Tool.codeExecution()));
// Use the GenerativeModelFutures Java compatibility layer which offers
// support for ListenableFuture and Publisher APIs
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
String text = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText(text)
.build();
ChatFutures chat = model.startChat();
ListenableFuture response = chat.sendMessage(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse response) {
// Access the first candidate's content parts
List parts = response.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts();
for (Part part : parts) {
if (part instanceof TextPart) {
TextPart textPart = (TextPart) part;
System.out.println("Text = " + textPart.getText());
} else if (part instanceof ExecutableCodePart) {
ExecutableCodePart codePart = (ExecutableCodePart) part;
System.out.println("Code = " + codePart.getCode() + ", Language = " + codePart.getLanguage());
} else if (part instanceof CodeExecutionResultPart) {
CodeExecutionResultPart resultPart = (CodeExecutionResultPart) part;
System.out.println("Outcome = " + resultPart.getOutcome() + ", Result = " + resultPart.getOutput());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const ai = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(
ai,
{
model: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }]
}
);
const prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
const chat = model.startChat()
const result = await chat.sendMessage(prompt);
const parts = result.response.candidates?.[0].content.parts;
if (parts) {
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(`Text: ${part.text}`);
} else if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(
`Code: ${part.executableCode.code}, Language: ${part.executableCode.language}`
);
} else if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(
`Outcome: ${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}, Result: ${part.codeExecutionResult.output}`
);
}
});
}
Dart
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
final model = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'GEMINI_MODEL_NAME',
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [
Tool.codeExecution(),
],
);
final codeExecutionChat = await model.startChat();
const prompt = 'What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? '
'Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.';
final response = await codeExecutionChat.sendMessage(Content.text(prompt));
final buffer = StringBuffer();
for (final part in response.candidates.first.content.parts) {
if (part is TextPart) {
buffer.writeln(part.text);
} else if (part is ExecutableCodePart) {
buffer.writeln('Executable Code:');
buffer.writeln('Language: ${part.language}');
buffer.writeln('Code:');
buffer.writeln(part.code);
} else if (part is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
buffer.writeln('Code Execution Result:');
buffer.writeln('Outcome: ${part.outcome}');
buffer.writeln('Output:');
buffer.writeln(part.output);
}
}
وحدت
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
var ai = FirebaseAI.GetInstance(FirebaseAI.Backend.GoogleAI());
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = ai.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: new Tool[] { new Tool(new CodeExecution()) }
);
var prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
var chat = model.StartChat();
var response = await chat.SendMessageAsync(prompt);
foreach (var part in response.Candidates.First().Content.Parts) {
if (part is ModelContent.TextPart tp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Text = {tp.Text}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.ExecutableCodePart esp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Code = {esp.Code}, Language = {esp.Language}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.CodeExecutionResultPart cerp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Outcome = {cerp.Outcome}, Output = {cerp.Output}");
}
}
یاد بگیرید که چگونه یک مدل را انتخاب کنیدمناسب برای مورد استفاده و برنامه شما.
قیمتگذاری
هیچ هزینه اضافی برای فعال کردن اجرای کد و ارائه آن به عنوان ابزاری برای مدل وجود ندارد. اگر مدل تصمیم به استفاده از اجرای کد بگیرد، هزینه آن بر اساس نرخ فعلی توکنهای ورودی و خروجی بر اساس مدل Gemini که استفاده میکنید، از شما دریافت میشود.
نمودار زیر مدل صدور صورتحساب برای اجرای کد را نشان میدهد:
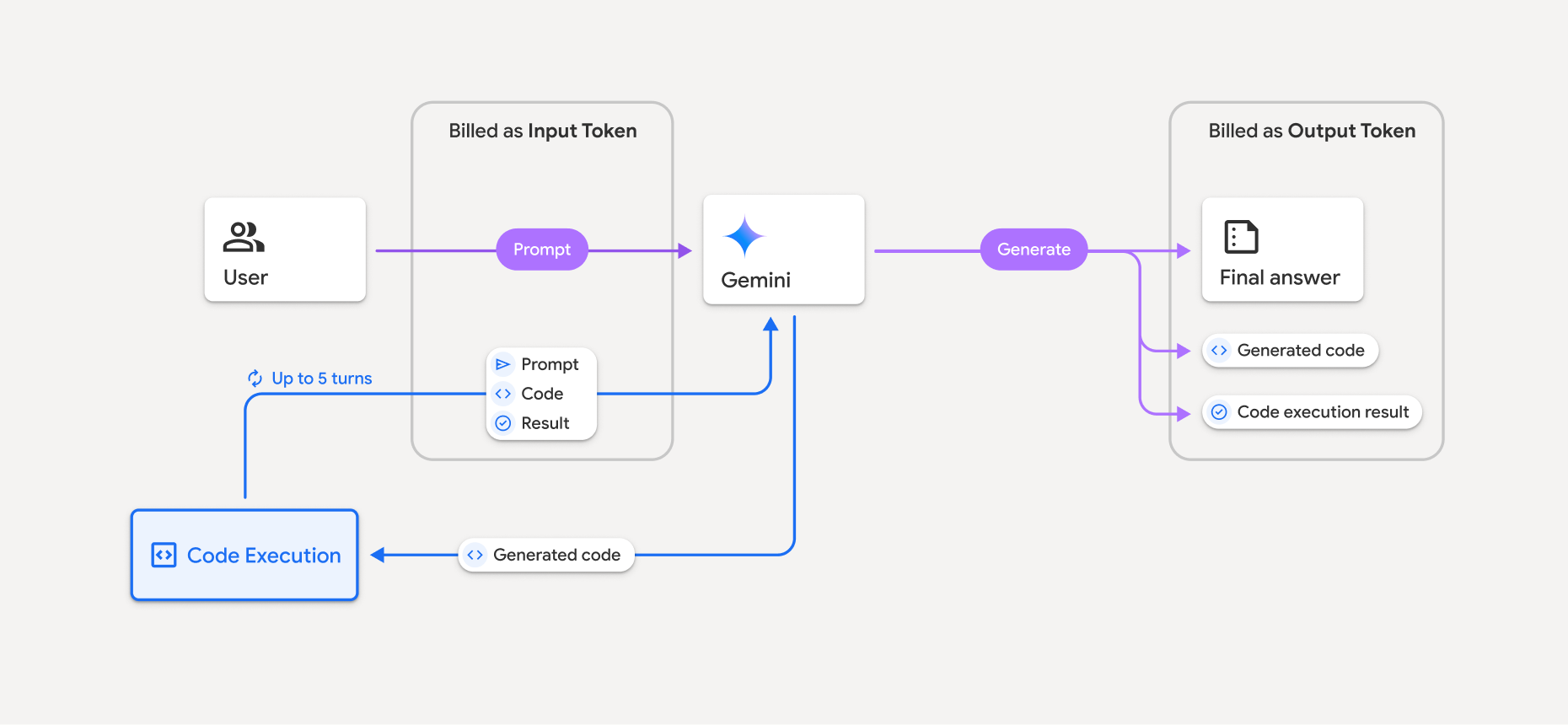
در اینجا خلاصهای از نحوهی محاسبهی توکنها هنگام استفاده از اجرای کد در مدل، آورده شده است:
اعلان اصلی یک بار صورتحساب میشود. توکنهای آن به عنوان توکنهای میانی برچسبگذاری شدهاند که به عنوان توکنهای ورودی صورتحساب میشوند.
کد تولید شده و نتیجه کد اجرا شده به صورت زیر محاسبه میشوند:
وقتی در حین اجرای کد استفاده میشوند، به عنوان توکنهای میانی برچسبگذاری میشوند که به عنوان توکنهای ورودی محاسبه میشوند.
وقتی آنها به عنوان بخشی از پاسخ نهایی گنجانده میشوند، به عنوان توکنهای خروجی ثبت میشوند.
خلاصه نهایی در پاسخ نهایی به عنوان توکنهای خروجی ثبت میشود.
رابط برنامهنویسی Gemini شامل تعداد توکنهای میانی در پاسخ API است، بنابراین میدانید که چرا برای توکنهای ورودی فراتر از درخواست اولیهتان هزینه دریافت میکنید.
توجه داشته باشید که کد تولید شده میتواند شامل متن و خروجیهای چندوجهی مانند تصاویر باشد.
محدودیتها و بهترین شیوهها
این مدل فقط میتواند کد پایتون را تولید و اجرا کند. نمیتواند مصنوعات دیگری مانند فایلهای رسانهای را برگرداند.
اجرای کد میتواند حداکثر 30 ثانیه قبل از اتمام زمانبندی ادامه یابد.
در برخی موارد، فعال کردن اجرای کد میتواند منجر به رگرسیون در سایر حوزههای خروجی مدل شود (برای مثال، نوشتن یک داستان).
ابزار اجرای کد از URI های فایل به عنوان ورودی/خروجی پشتیبانی نمیکند. با این حال، ابزار اجرای کد از ورودی فایل و خروجی نمودار به عنوان بایتهای درونخطی پشتیبانی میکند. با استفاده از این قابلیتهای ورودی و خروجی، میتوانید فایلهای CSV و متنی را آپلود کنید، در مورد فایلها سؤال بپرسید و نمودارهای Matplotlib را به عنوان بخشی از نتیجه اجرای کد تولید کنید. انواع MIME پشتیبانی شده برای بایتهای درونخطی عبارتند از
.cpp،.csv،.java،.jpeg،.js،.png،.py،.tsو.xml.
کتابخانههای پشتیبانیشده
محیط اجرای کد شامل کتابخانههای زیر است. شما نمیتوانید کتابخانههای خودتان را نصب کنید.
- جذابیتها
- شطرنج
- کانتورپی
- اف پی دی اف
- ژئوپانداها
- ایمیجیو
- جینجا۲
- شغلمحور
- جیسوناسکِما
- مشخصات jsonschema
- lxml
- کتابخانه متپلات
- ام پی مت
- نامپی
- opencv-python
- اوپنپایکسل
- بسته بندی
- پانداها
- بالش
- پروتوباف
- پیلاتکس
- پیپارسینگ
- پایPDF2
- پایتون-dateutil
- پایتون-docx
- پایتون-pptx
- گزارش آزمایشگاه
- سایکیت-لرن
- اسکیپی
- دریازاده
- شش
- استریپآرتیاف
- سمپی
- جدول بندی کردن
- تنسورفلو
- ابزار
- ایکس ال آر دی
- آلتایر
- شطرنج
- سی وی ۲
- متپلاتلیب
- مپمات
- نامپای
- پانداها
- پیدیافماینر
- گزارش آزمایشگاه
- سیبورن
- اسکلرین
- مدلهای آماری
- استریپتف
- سیمپی
- جدول بندی
درباره تجربه خود با Firebase AI Logic بازخورد دهید

