कोड को चलाने की सुविधा, एक ऐसा टूल है जिसकी मदद से मॉडल, Python कोड जनरेट और रन कर सकता है. मॉडल, कोड को चलाने के बाद मिले नतीजों से बार-बार सीख सकता है. ऐसा तब तक किया जा सकता है, जब तक उसे फ़ाइनल आउटपुट न मिल जाए.
कोड लागू करने की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करके, ऐसी सुविधाएं बनाई जा सकती हैं जो कोड के आधार पर तर्क देने की क्षमता से फ़ायदा पाती हैं और टेक्स्ट आउटपुट जनरेट करती हैं. उदाहरण के लिए, समीकरणों को हल करने या टेक्स्ट को प्रोसेस करने के लिए, कोड लागू करने की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. कोड को लागू करने के एनवायरमेंट में शामिल लाइब्रेरी का इस्तेमाल करके, ज़्यादा खास टास्क भी पूरे किए जा सकते हैं.
मॉडल को दिए गए सभी टूल की तरह ही, मॉडल यह तय करता है कि कोड को कब लागू करना है.
कोड लागू करने से जुड़ी जानकारी पर जाएं
कोड को लागू करने और फ़ंक्शन को कॉल करने की तुलना
कोड को लागू करना और फ़ंक्शन कॉलिंग, एक जैसी सुविधाएं हैं. आम तौर पर, अगर मॉडल आपके इस्तेमाल के उदाहरण को हैंडल कर सकता है, तो आपको कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन का इस्तेमाल करना चाहिए. कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूट करने की सुविधा को इस्तेमाल करना भी आसान है, क्योंकि आपको बस इसे चालू करना होता है.
कोड को लागू करने और फ़ंक्शन को कॉल करने के बीच कुछ और अंतर यहां दिए गए हैं:
| कोड को चलाने की प्रोसेस | फ़ंक्शन कॉलिंग |
|---|---|
| अगर आपको मॉडल से Python कोड लिखवाना है और उसे रन करके नतीजे पाने हैं, तो कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करें. | अगर आपके पास पहले से ही ऐसे फ़ंक्शन हैं जिन्हें आपको स्थानीय तौर पर चलाना है, तो फ़ंक्शन कॉलिंग का इस्तेमाल करें. |
| कोड को लागू करने की सुविधा की मदद से, मॉडल एपीआई के बैकएंड में कोड को एक तय और अलग एनवायरमेंट में चला सकता है. | फ़ंक्शन कॉलिंग की सुविधा की मदद से, मॉडल के अनुरोध किए गए फ़ंक्शन को किसी भी एनवायरमेंट में चलाया जा सकता है. |
| कोड को चलाने की प्रोसेस, एक ही अनुरोध में पूरी हो जाती है. चैट की सुविधा के साथ कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन का इस्तेमाल करना ज़रूरी नहीं है. हालांकि, आपके पास इसका इस्तेमाल करने का विकल्प होता है. | फ़ंक्शन कॉलिंग के लिए, हर फ़ंक्शन कॉल से मिले आउटपुट को वापस भेजने के लिए एक अतिरिक्त अनुरोध की ज़रूरत होती है. इसलिए, आपको चैट करने की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करना होगा. |
काम करने वाले मॉडल
gemini-3-pro-previewgemini-2.5-progemini-2.5-flashgemini-2.5-flash-litegemini-2.0-flash-001(और इसका अपने-आप अपडेट होने वाला उपनामgemini-2.0-flash)gemini-2.0-flash-live-preview-04-09
कोड चलाने की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करना
कोड को एक्ज़ीक्यूट करने की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल, सिर्फ़ टेक्स्ट वाले इनपुट और मल्टीमॉडल इनपुट, दोनों के साथ किया जा सकता है. हालांकि, जवाब हमेशा टेक्स्ट या कोड के तौर पर ही मिलेगा.
शुरू करने से पहले
|
इस पेज पर, सेवा देने वाली कंपनी के हिसाब से कॉन्टेंट और कोड देखने के लिए, Gemini API सेवा देने वाली कंपनी पर क्लिक करें. |
अगर आपने अब तक शुरुआती गाइड नहीं पढ़ी है, तो इसे पढ़ें. इसमें बताया गया है कि Firebase प्रोजेक्ट कैसे सेट अप करें, अपने ऐप्लिकेशन को Firebase से कैसे कनेक्ट करें, एसडीके कैसे जोड़ें, चुने गए Gemini API प्रोवाइडर के लिए बैकएंड सेवा को कैसे शुरू करें, और GenerativeModel इंस्टेंस कैसे बनाएं.
अपने प्रॉम्प्ट की जांच करने और उन्हें बेहतर बनाने के लिए, हम Google AI Studio का इस्तेमाल करने का सुझाव देते हैं.
कोड चलाने की सुविधा चालू करना
|
इस सैंपल को आज़माने से पहले, इस गाइड के शुरू करने से पहले सेक्शन में दिए गए निर्देशों को पूरा करें. इससे आपको अपना प्रोजेक्ट और ऐप्लिकेशन सेट अप करने में मदद मिलेगी. उस सेक्शन में, आपको Gemini API सेवा देने वाली कंपनी के लिए एक बटन पर भी क्लिक करना होगा, ताकि आपको इस पेज पर सेवा देने वाली कंपनी के हिसाब से कॉन्टेंट दिखे. |
GenerativeModel इंस्टेंस बनाते समय, CodeExecution को एक ऐसे टूल के तौर पर उपलब्ध कराएं जिसका इस्तेमाल मॉडल, जवाब जनरेट करने के लिए कर सकता है. इससे मॉडल को Python कोड जनरेट करने और उसे चलाने की अनुमति मिलती है.
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
let ai = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI())
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = ai.generativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [.codeExecution()]
)
let prompt = """
What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers?
Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.
"""
let response = try await model.generateContent(prompt)
guard let candidate = response.candidates.first else {
print("No candidates in response.")
return
}
for part in candidate.content.parts {
if let textPart = part as? TextPart {
print("Text = \(textPart.text)")
} else if let executableCode = part as? ExecutableCodePart {
print("Code = \(executableCode.code), Language = \(executableCode.language)")
} else if let executionResult = part as? CodeExecutionResultPart {
print("Outcome = \(executionResult.outcome), Result = \(executionResult.output ?? "no output")")
}
}
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools = listOf(Tool.codeExecution())
)
val prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
val response = model.generateContent(prompt)
response.candidates.first().content.parts.forEach {
if(it is TextPart) {
println("Text = ${it.text}")
}
if(it is ExecutableCodePart) {
println("Code = ${it.code}, Language = ${it.language}")
}
if(it is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
println("Outcome = ${it.outcome}, Result = ${it.output}")
}
}
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
null,
null,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
List.of(Tool.codeExecution()));
// Use the GenerativeModelFutures Java compatibility layer which offers
// support for ListenableFuture and Publisher APIs
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
String text = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText(text)
.build();
ListenableFuture response = model.generateContent(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse response) {
// Access the first candidate's content parts
List parts = response.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts();
for (Part part : parts) {
if (part instanceof TextPart) {
TextPart textPart = (TextPart) part;
System.out.println("Text = " + textPart.getText());
} else if (part instanceof ExecutableCodePart) {
ExecutableCodePart codePart = (ExecutableCodePart) part;
System.out.println("Code = " + codePart.getCode() + ", Language = " + codePart.getLanguage());
} else if (part instanceof CodeExecutionResultPart) {
CodeExecutionResultPart resultPart = (CodeExecutionResultPart) part;
System.out.println("Outcome = " + resultPart.getOutcome() + ", Result = " + resultPart.getOutput());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const ai = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(
ai,
{
model: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }]
}
);
const prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
const result = await model.generateContent(prompt);
const response = await result.response;
const parts = response.candidates?.[0].content.parts;
if (parts) {
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(`Text: ${part.text}`);
} else if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(
`Code: ${part.executableCode.code}, Language: ${part.executableCode.language}`
);
} else if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(
`Outcome: ${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}, Result: ${part.codeExecutionResult.output}`
);
}
});
}
Dart
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
final model = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'GEMINI_MODEL_NAME',
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [
Tool.codeExecution(),
],
);
const prompt = 'What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? '
'Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.';
final response = await model.generateContent([Content.text(prompt)]);
final buffer = StringBuffer();
for (final part in response.candidates.first.content.parts) {
if (part is TextPart) {
buffer.writeln(part.text);
} else if (part is ExecutableCodePart) {
buffer.writeln('Executable Code:');
buffer.writeln('Language: ${part.language}');
buffer.writeln('Code:');
buffer.writeln(part.code);
} else if (part is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
buffer.writeln('Code Execution Result:');
buffer.writeln('Outcome: ${part.outcome}');
buffer.writeln('Output:');
buffer.writeln(part.output);
}
}
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
var ai = FirebaseAI.GetInstance(FirebaseAI.Backend.GoogleAI());
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = ai.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: new Tool[] { new Tool(new CodeExecution()) }
);
var prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
var response = await model.GenerateContentAsync(prompt);
foreach (var part in response.Candidates.First().Content.Parts) {
if (part is ModelContent.TextPart tp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Text = {tp.Text}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.ExecutableCodePart esp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Code = {esp.Code}, Language = {esp.Language}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.CodeExecutionResultPart cerp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Outcome = {cerp.Outcome}, Output = {cerp.Output}");
}
}
अपने इस्तेमाल के उदाहरण और ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, सही मॉडल चुनने का तरीका जानें.
चैट में कोड चलाने की सुविधा का इस्तेमाल करना
चैट के दौरान भी कोड को एक्ज़ीक्यूट किया जा सकता है:
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
let ai = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI())
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = ai.generativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [.codeExecution()]
)
let prompt = """
What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers?
Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.
"""
let chat = model.startChat()
let response = try await chat.sendMessage(prompt)
guard let candidate = response.candidates.first else {
print("No candidates in response.")
return
}
for part in candidate.content.parts {
if let textPart = part as? TextPart {
print("Text = \(textPart.text)")
} else if let executableCode = part as? ExecutableCodePart {
print("Code = \(executableCode.code), Language = \(executableCode.language)")
} else if let executionResult = part as? CodeExecutionResultPart {
print("Outcome = \(executionResult.outcome), Result = \(executionResult.output ?? "no output")")
}
}
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools = listOf(Tool.codeExecution())
)
val prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
val chat = model.startChat()
val response = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
response.candidates.first().content.parts.forEach {
if(it is TextPart) {
println("Text = ${it.text}")
}
if(it is ExecutableCodePart) {
println("Code = ${it.code}, Language = ${it.language}")
}
if(it is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
println("Outcome = ${it.outcome}, Result = ${it.output}")
}
}
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
null,
null,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
List.of(Tool.codeExecution()));
// Use the GenerativeModelFutures Java compatibility layer which offers
// support for ListenableFuture and Publisher APIs
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
String text = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText(text)
.build();
ChatFutures chat = model.startChat();
ListenableFuture response = chat.sendMessage(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse response) {
// Access the first candidate's content parts
List parts = response.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts();
for (Part part : parts) {
if (part instanceof TextPart) {
TextPart textPart = (TextPart) part;
System.out.println("Text = " + textPart.getText());
} else if (part instanceof ExecutableCodePart) {
ExecutableCodePart codePart = (ExecutableCodePart) part;
System.out.println("Code = " + codePart.getCode() + ", Language = " + codePart.getLanguage());
} else if (part instanceof CodeExecutionResultPart) {
CodeExecutionResultPart resultPart = (CodeExecutionResultPart) part;
System.out.println("Outcome = " + resultPart.getOutcome() + ", Result = " + resultPart.getOutput());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const ai = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(
ai,
{
model: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }]
}
);
const prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
const chat = model.startChat()
const result = await chat.sendMessage(prompt);
const parts = result.response.candidates?.[0].content.parts;
if (parts) {
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(`Text: ${part.text}`);
} else if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(
`Code: ${part.executableCode.code}, Language: ${part.executableCode.language}`
);
} else if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(
`Outcome: ${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}, Result: ${part.codeExecutionResult.output}`
);
}
});
}
Dart
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
final model = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'GEMINI_MODEL_NAME',
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [
Tool.codeExecution(),
],
);
final codeExecutionChat = await model.startChat();
const prompt = 'What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? '
'Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.';
final response = await codeExecutionChat.sendMessage(Content.text(prompt));
final buffer = StringBuffer();
for (final part in response.candidates.first.content.parts) {
if (part is TextPart) {
buffer.writeln(part.text);
} else if (part is ExecutableCodePart) {
buffer.writeln('Executable Code:');
buffer.writeln('Language: ${part.language}');
buffer.writeln('Code:');
buffer.writeln(part.code);
} else if (part is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
buffer.writeln('Code Execution Result:');
buffer.writeln('Outcome: ${part.outcome}');
buffer.writeln('Output:');
buffer.writeln(part.output);
}
}
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
var ai = FirebaseAI.GetInstance(FirebaseAI.Backend.GoogleAI());
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = ai.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: new Tool[] { new Tool(new CodeExecution()) }
);
var prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
var chat = model.StartChat();
var response = await chat.SendMessageAsync(prompt);
foreach (var part in response.Candidates.First().Content.Parts) {
if (part is ModelContent.TextPart tp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Text = {tp.Text}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.ExecutableCodePart esp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Code = {esp.Code}, Language = {esp.Language}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.CodeExecutionResultPart cerp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Outcome = {cerp.Outcome}, Output = {cerp.Output}");
}
}
अपने इस्तेमाल के उदाहरण और ऐप्लिकेशन के लिए, सही मॉडल चुनने का तरीका जानें.
कीमत
कोड को लागू करने की सुविधा चालू करने और इसे मॉडल के लिए टूल के तौर पर उपलब्ध कराने के लिए, कोई अतिरिक्त शुल्क नहीं लिया जाता. अगर मॉडल कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन का इस्तेमाल करने का फ़ैसला करता है, तो आपसे इनपुट और आउटपुट टोकन के लिए मौजूदा दर के हिसाब से शुल्क लिया जाएगा. यह शुल्क, इस्तेमाल किए जा रहे Gemini मॉडल के हिसाब से लिया जाएगा.
नीचे दिए गए डायग्राम में, कोड को लागू करने के लिए बिलिंग मॉडल दिखाया गया है:
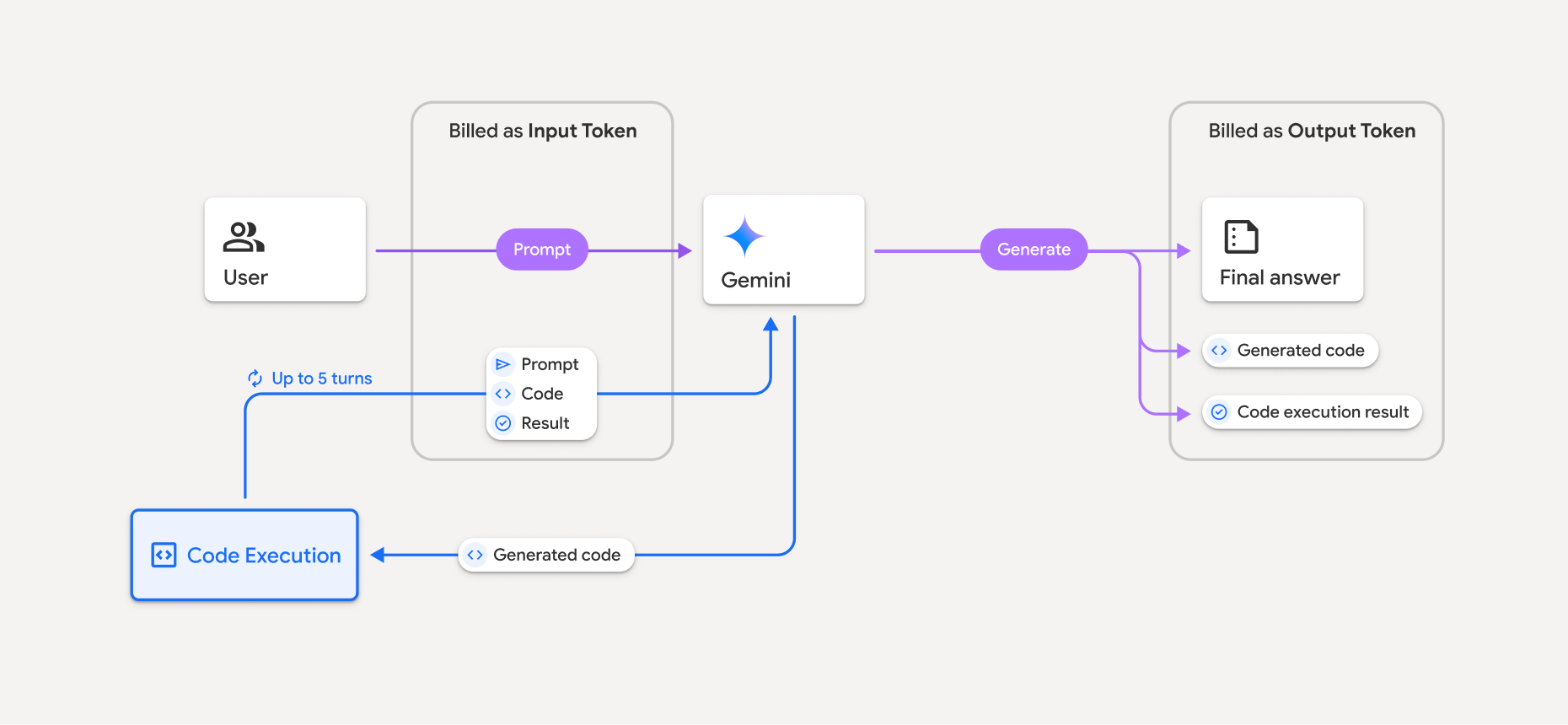
यहां इस बारे में खास जानकारी दी गई है कि जब कोई मॉडल कोड एक्ज़ीक्यूशन का इस्तेमाल करता है, तब टोकन के लिए बिल कैसे भेजा जाता है:
ओरिजनल प्रॉम्प्ट के लिए, एक बार बिल लिया जाता है. इसके टोकन को इंटरमीडिएट टोकन के तौर पर लेबल किया जाता है. इनका बिल इनपुट टोकन के तौर पर भेजा जाता है.
जनरेट किए गए कोड और चलाए गए कोड के नतीजे के लिए, इस तरह बिल भेजा जाता है:
कोड को एक्ज़ीक्यूट करते समय इस्तेमाल किए जाने पर, इन्हें इंटरमीडिएट टोकन के तौर पर लेबल किया जाता है. इनका बिल इनपुट टोकन के तौर पर भेजा जाता है.
जब इन्हें फ़ाइनल जवाब में शामिल किया जाता है, तब इन्हें आउटपुट टोकन के तौर पर बिल किया जाता है.
जवाब में मौजूद खास जानकारी को आउटपुट टोकन के तौर पर बिल किया जाता है.
Gemini API में, एपीआई के जवाब में इंटरमीडिएट टोकन की संख्या शामिल होती है. इससे आपको पता चलता है कि शुरुआती प्रॉम्प्ट के अलावा, इनपुट टोकन के लिए आपसे शुल्क क्यों लिया जा रहा है.
ध्यान दें कि जनरेट किए गए कोड में टेक्स्ट और मल्टीमॉडल आउटपुट, दोनों शामिल हो सकते हैं. जैसे, इमेज.
सीमाएं और सबसे सही तरीके
यह मॉडल सिर्फ़ Python कोड जनरेट कर सकता है और उसे लागू कर सकता है. यह मीडिया फ़ाइलों जैसे अन्य आर्टफ़ैक्ट वापस नहीं ला सकता.
कोड को ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा 30 सेकंड तक चलाया जा सकता है. इसके बाद, यह टाइम आउट हो जाएगा.
कुछ मामलों में, कोड को लागू करने की सुविधा चालू करने से, मॉडल के आउटपुट के अन्य हिस्सों में रिग्रेशन हो सकता है. उदाहरण के लिए, कहानी लिखना.
कोड को चलाने वाली टूल, फ़ाइल यूआरआई को इनपुट/आउटपुट के तौर पर इस्तेमाल नहीं कर सकती. हालांकि, कोड को चलाने वाला टूल, फ़ाइल इनपुट और ग्राफ़ आउटपुट को इनलाइन बाइट के तौर पर इस्तेमाल कर सकता है. इनपुट और आउटपुट की इन सुविधाओं का इस्तेमाल करके, CSV और टेक्स्ट फ़ाइलें अपलोड की जा सकती हैं. साथ ही, फ़ाइलों के बारे में सवाल पूछे जा सकते हैं. इसके अलावा, कोड को चलाने के बाद मिलने वाले नतीजे के तौर पर, Matplotlib ग्राफ़ जनरेट किए जा सकते हैं. इनलाइन किए गए बाइट के लिए, इन माइम टाइप का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है:
.cpp,.csv,.java,.jpeg,.js,.png,.py,.ts, और.xml.
इनके साथ काम करने वाली लाइब्रेरी
कोड को चलाने वाले एनवायरमेंट में ये लाइब्रेरी शामिल होती हैं. अपनी लाइब्रेरी इंस्टॉल नहीं की जा सकतीं.
Firebase AI Logic के साथ अपने अनुभव के बारे में सुझाव/राय दें या शिकायत करें
