Генеративные модели эффективно решают множество задач. Однако они имеют ряд ограничений, таких как:
- После обучения их знания застывают, что приводит к их устареванию.
- Они не могут запрашивать или изменять внешние данные.
Вызов функций может помочь преодолеть некоторые из этих ограничений. Вызов функций иногда называют использованием инструментов , поскольку он позволяет модели использовать внешние инструменты, такие как API и функции, для генерации конечного результата.
В этом руководстве показано, как можно реализовать настройку вызова функции, аналогичную сценарию, описанному в следующем основном разделе этой страницы. В общих чертах, вот шаги по настройке вызова функций в вашем приложении:
Шаг 1 : Напишите функцию, которая может предоставлять модели информацию, необходимую для генерации окончательного ответа (например, функция может вызывать внешний API).
Шаг 2 : Создайте объявление функции, описывающее функцию и её параметры.
Шаг 3 : Укажите объявление функции во время инициализации модели, чтобы модель знала, как использовать эту функцию, если это необходимо.
Шаг 4 : Настройте ваше приложение таким образом, чтобы модель могла передавать необходимую информацию для вызова функции вашим приложением.
Шаг 5 : Передайте ответ функции обратно в модель, чтобы модель могла сгенерировать свой окончательный ответ.
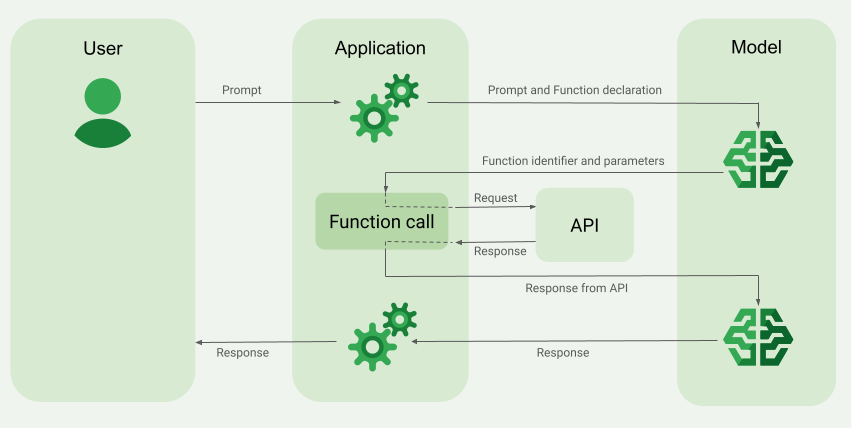
Обзор примера вызова функции.
При отправке запроса модели вы также можете предоставить ей набор «инструментов» (например, функций), которые она сможет использовать для генерации окончательного ответа. Для использования этих функций и их вызова («вызов функций») модели и вашему приложению необходимо обмениваться информацией, поэтому рекомендуемый способ использования вызова функций — это многошаговый интерфейс чата.
Представьте, что у вас есть приложение, в котором пользователь может ввести запрос, например: What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?
Модели Gemini могут не располагать этой информацией о погоде; однако представьте, что вам известен внешний API-интерфейс метеорологического сервиса, который может ее предоставить. Вы можете использовать вызов функций, чтобы предоставить модели Gemini путь к этому API и его информации о погоде.
Сначала вы пишете в своем приложении функцию fetchWeather которая взаимодействует с этим гипотетическим внешним API, имеющим следующие входные и выходные данные:
| Параметр | Тип | Необходимый | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
| Вход | |||
location | Объект | Да | Название города и штата, для которого необходимо получить информацию о погоде. Поддерживаются только города в США. Должен быть вложенный объект, состоящий из city и state . |
date | Нить | Да | Дата, на которую необходимо получить прогноз погоды (всегда должна быть в формате YYYY-MM-DD ). |
| Выход | |||
temperature | Целое число | Да | Температура (в градусах Фаренгейта) |
chancePrecipitation | Нить | Да | Вероятность осадков (выраженная в процентах) |
cloudConditions | Нить | Да | Облачность (одно из следующих значений: clear , partlyCloudy , mostlyCloudy , cloudy ) |
При инициализации модели вы сообщаете ей о существовании функции fetchWeather и о том, как её можно использовать для обработки входящих запросов, если это необходимо. Это называется «объявлением функции». Модель не вызывает функцию напрямую . Вместо этого, в процессе обработки входящего запроса, модель решает, может ли функция fetchWeather помочь ей ответить на запрос. Если модель решает, что функция действительно может быть полезна, она генерирует структурированные данные, которые помогут вашему приложению вызвать эту функцию .
Взгляните еще раз на входящий запрос: What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? Модель, вероятно, решит, что функция fetchWeather может помочь ей сгенерировать ответ. Модель проанализирует, какие входные параметры необходимы для fetchWeather , а затем сгенерирует структурированные входные данные для функции, которые будут выглядеть примерно так:
{
functionName: fetchWeather,
location: {
city: Boston,
state: Massachusetts // the model can infer the state from the prompt
},
date: 2024-10-17
}
Модель передает эти структурированные входные данные вашему приложению, чтобы оно могло вызвать функцию fetchWeather . Когда ваше приложение получает данные о погоде от API, оно передает эту информацию модели. Эта информация о погоде позволяет модели завершить окончательную обработку и сгенерировать ответ на первоначальный запрос: « What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?
Модель может выдать окончательный ответ на естественном языке, например: On October 17, 2024, in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
Реализуйте вызов функции.
Следующие шаги в этом руководстве покажут вам, как реализовать настройку вызова функции, аналогичную рабочему процессу, описанному в разделе «Обзор примера вызова функции» (см. верхнюю часть этой страницы).
Прежде чем начать
Чтобы просмотреть контент и код, относящиеся к вашему поставщику API Gemini , нажмите на него. |
Если вы еще этого не сделали, пройдите руководство по началу работы , в котором описывается, как настроить проект Firebase, подключить приложение к Firebase, добавить SDK, инициализировать бэкэнд-сервис для выбранного вами поставщика API Gemini и создать экземпляр GenerativeModel .
Шаг 1 : Напишите функцию
Представьте, что у вас есть приложение, в котором пользователь может ввести запрос, например: What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? . Модели Gemini могут не знать этой информации о погоде; однако представьте, что вам известен внешний API-сервис погоды, который может её предоставить. Сценарий в этом руководстве основан на этом гипотетическом внешнем API.
Напишите в своем приложении функцию, которая будет взаимодействовать с гипотетическим внешним API и предоставлять модели необходимую информацию для генерации окончательного запроса. В этом примере с погодой это будет функция fetchWeather , которая будет вызывать этот гипотетический внешний API.
Быстрый
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
func fetchWeather(city: String, state: String, date: String) -> JSONObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return [
"temperature": .number(38),
"chancePrecipitation": .string("56%"),
"cloudConditions": .string("partlyCloudy"),
]
}
Kotlin
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
data class Location(val city: String, val state: String)
suspend fun fetchWeather(location: Location, date: String): JsonObject {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return JsonObject(mapOf(
"temperature" to JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation" to JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions" to JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")
))
}
Java
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
public JsonObject fetchWeather(Location location, String date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new JsonObject(Map.of(
"temperature", JsonPrimitive(38),
"chancePrecipitation", JsonPrimitive("56%"),
"cloudConditions", JsonPrimitive("partlyCloudy")));
}
Web
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
async function fetchWeather({ location, date }) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return {
temperature: 38,
chancePrecipitation: "56%",
cloudConditions: "partlyCloudy",
};
}
Dart
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
// `location` is an object of the form { city: string, state: string }
Future<Map<String, Object?>> fetchWeather(
Location location, String date
) async {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call to an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
final apiResponse = {
'temperature': 38,
'chancePrecipitation': '56%',
'cloudConditions': 'partlyCloudy',
};
return apiResponse;
}
Единство
// This function calls a hypothetical external API that returns
// a collection of weather information for a given location on a given date.
System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object> FetchWeather(
string city, string state, string date) {
// TODO(developer): Write a standard function that would call an external weather API.
// For demo purposes, this hypothetical response is hardcoded here in the expected format.
return new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, object>() {
{"temperature", 38},
{"chancePrecipitation", "56%"},
{"cloudConditions", "partlyCloudy"},
};
}
Шаг 2 : Создайте объявление функции.
Создайте объявление функции, которую вы позже предоставите модели (следующий шаг этого руководства).
В объявлении функции укажите как можно больше подробностей, включая описание функции и её параметров.
Модель использует информацию из объявления функции для определения того, какую функцию выбрать и как передать значения параметров для фактического вызова функции. См. раздел «Дополнительные параметры и возможности» далее на этой странице, где описано, как модель может выбирать между функциями, а также как вы можете управлять этим выбором.
Обратите внимание на следующие особенности предоставленной вами схемы:
Необходимо предоставлять объявления функций в формате схемы, совместимом со схемой OpenAPI . Vertex AI предоставляет ограниченную поддержку схемы OpenAPI.
Поддерживаются следующие атрибуты:
type,nullable,required,format,description,properties,items,enum.Следующие атрибуты не поддерживаются:
default,optional,maximum,oneOf.
По умолчанию в SDK Firebase AI Logic все поля считаются обязательными , если вы не укажете их как необязательные в массиве
optionalProperties. Для этих необязательных полей модель может заполнить их самостоятельно или пропустить. Обратите внимание, что это противоположно поведению по умолчанию двух поставщиков API Gemini , если вы используете их серверные SDK или API напрямую.
Рекомендации по объявлению функций, включая советы по их именованию и описанию, см. в разделе [ссылка на соответствующий раздел].Рекомендации по использованию API Gemini для разработчиков описаны в документации.
Вот как можно написать объявление функции:
Быстрый
let fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: [
"location": .object(
properties: [
"city": .string(description: "The city of the location."),
"state": .string(description: "The US state of the location."),
],
description: """
The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the
USA are supported.
"""
),
"date": .string(
description: """
The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.
"""
),
]
)
Kotlin
val fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
mapOf(
"location" to Schema.obj(
mapOf(
"city" to Schema.string("The city of the location."),
"state" to Schema.string("The US state of the location."),
),
description = "The name of the city and its state for which " +
"to get the weather. Only cities in the " +
"USA are supported."
),
"date" to Schema.string("The date for which to get the weather." +
" Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
),
),
)
Java
FunctionDeclaration fetchWeatherTool = new FunctionDeclaration(
"fetchWeather",
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
Map.of("location",
Schema.obj(Map.of(
"city", Schema.str("The city of the location."),
"state", Schema.str("The US state of the location."))),
"date",
Schema.str("The date for which to get the weather. " +
"Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.")),
Collections.emptyList());
Web
const fetchWeatherTool: FunctionDeclarationsTool = {
functionDeclarations: [
{
name: "fetchWeather",
description:
"Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date",
parameters: Schema.object({
properties: {
location: Schema.object({
description:
"The name of the city and its state for which to get " +
"the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.",
properties: {
city: Schema.string({
description: "The city of the location."
}),
state: Schema.string({
description: "The US state of the location."
}),
},
}),
date: Schema.string({
description:
"The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the" +
" format: YYYY-MM-DD.",
}),
},
}),
},
],
};
Dart
final fetchWeatherTool = FunctionDeclaration(
'fetchWeather',
'Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.',
parameters: {
'location': Schema.object(
description:
'The name of the city and its state for which to get'
'the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported.',
properties: {
'city': Schema.string(
description: 'The city of the location.'
),
'state': Schema.string(
description: 'The US state of the location.'
),
},
),
'date': Schema.string(
description:
'The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD.'
),
},
);
Единство
var fetchWeatherTool = new Tool(new FunctionDeclaration(
name: "fetchWeather",
description: "Get the weather conditions for a specific city on a specific date.",
parameters: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "location", Schema.Object(
properties: new System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<string, Schema>() {
{ "city", Schema.String(description: "The city of the location.") },
{ "state", Schema.String(description: "The US state of the location.")}
},
description: "The name of the city and its state for which to get the weather. Only cities in the USA are supported."
) },
{ "date", Schema.String(
description: "The date for which to get the weather. Date must be in the format: YYYY-MM-DD."
)}
}
));
Шаг 3 : Укажите объявление функции во время инициализации модели.
Максимальное количество объявлений функций, которые вы можете указать в запросе, составляет 128. См. раздел «Дополнительные параметры и поведение» далее на этой странице, где описано, как модель может выбирать между функциями, а также как вы можете управлять этим выбором (используя toolConfig для установки режима вызова функции ).
Быстрый
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool])]
)
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools = listOf(Tool.functionDeclarations(listOf(fetchWeatherTool)))
)
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(
FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("gemini-2.5-flash",
null,
null,
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
List.of(Tool.functionDeclarations(List.of(fetchWeatherTool)))));
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const firebaseAI = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(firebaseAI, {
model: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: fetchWeatherTool
});
Dart
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
_functionCallModel = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'gemini-2.5-flash',
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: [
Tool.functionDeclarations([fetchWeatherTool]),
],
);
Единство
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = FirebaseAI.DefaultInstance.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "gemini-2.5-flash",
// Provide the function declaration to the model.
tools: new Tool[] { fetchWeatherTool }
);
Узнайте, как выбрать модель.подходит для вашего сценария использования и приложения.
Шаг 4 : Вызовите функцию для обращения к внешнему API.
Если модель решит, что функция fetchWeather действительно может помочь ей сгенерировать окончательный ответ, вашему приложению необходимо фактически вызвать эту функцию, используя структурированные входные данные, предоставленные моделью.
Поскольку между моделью и приложением необходимо постоянно обмениваться информацией, рекомендуемый способ вызова функций — использование многошагового интерфейса чата.
Приведенный ниже фрагмент кода показывает, как ваше приложение получает информацию о том, что модель хочет использовать функцию fetchWeather . Он также показывает, что модель предоставила необходимые значения входных параметров для вызова функции (и ее базового внешнего API).
В этом примере входящий запрос содержал подсказку What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024? . На основе этой подсказки модель определила входные параметры, необходимые для функции fetchWeather (а именно, city , state и date ).
Быстрый
let chat = model.startChat()
let prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let response = try await chat.sendMessage(prompt)
var functionResponses = [FunctionResponsePart]()
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
for functionCall in response.functionCalls {
if functionCall.name == "fetchWeather" {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
guard case let .object(location) = functionCall.args["location"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(city) = location["city"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(state) = location["state"] else { fatalError() }
guard case let .string(date) = functionCall.args["date"] else { fatalError() }
functionResponses.append(FunctionResponsePart(
name: functionCall.name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: fetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
))
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
Kotlin
val prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?"
val chat = model.startChat()
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
val result = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
val functionCalls = result.functionCalls
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
val fetchWeatherCall = functionCalls.find { it.name == "fetchWeather" }
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
val functionResponse = fetchWeatherCall?.let {
// Alternatively, if your `Location` class is marked as @Serializable, you can use
// val location = Json.decodeFromJsonElement<Location>(it.args["location"]!!)
val location = Location(
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["city"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content,
it.args["location"]!!.jsonObject["state"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
)
val date = it.args["date"]!!.jsonPrimitive.content
fetchWeather(location, date)
}
Java
String prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
ChatFutures chatFutures = model.startChat();
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> response =
chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("user", List.of(new TextPart(prompt))));
ListenableFuture<JsonObject> handleFunctionCallFuture = Futures.transform(response, result -> {
for (FunctionCallPart functionCall : result.getFunctionCalls()) {
if (functionCall.getName().equals("fetchWeather")) {
Map<String, JsonElement> args = functionCall.getArgs();
JsonObject locationJsonObject =
JsonElementKt.getJsonObject(args.get("location"));
String city =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("city")));
String state =
JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
locationJsonObject.get("state")));
Location location = new Location(city, state);
String date = JsonElementKt.getContentOrNull(
JsonElementKt.getJsonPrimitive(
args.get("date")));
return fetchWeather(location, date);
}
}
return null;
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
const chat = model.startChat();
const prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
let result = await chat.sendMessage(prompt);
const functionCalls = result.response.functionCalls();
let functionCall;
let functionResult;
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.length > 0) {
for (const call of functionCalls) {
if (call.name === "fetchWeather") {
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
functionResult = await fetchWeather(call.args);
functionCall = call;
}
}
}
Dart
final chat = _functionCallModel.startChat();
const prompt = 'What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?';
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.sendMessage(Content.text(prompt));
final functionCalls = response.functionCalls.toList();
// When the model responds with one or more function calls, invoke the function(s).
if (functionCalls.isNotEmpty) {
for (final functionCall in functionCalls) {
if (functionCall.name == 'fetchWeather') {
Map<String, dynamic> location =
functionCall.args['location']! as Map<String, dynamic>;
var date = functionCall.args['date']! as String;
var city = location['city'] as String;
var state = location['state'] as String;
final functionResult =
await fetchWeather(Location(city, state), date);
// Send the response to the model so that it can use the result to
// generate text for the user.
response = await functionCallChat.sendMessage(
Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult),
);
}
}
} else {
throw UnimplementedError(
'Function not declared to the model: ${functionCall.name}',
);
}
Единство
var chat = model.StartChat();
var prompt = "What was the weather in Boston on October 17, 2024?";
// Send the user's question (the prompt) to the model using multi-turn chat.
var response = await chat.SendMessageAsync(prompt);
var functionResponses = new List<ModelContent>();
foreach (var functionCall in response.FunctionCalls) {
if (functionCall.Name == "fetchWeather") {
// TODO(developer): Handle invalid arguments.
var city = functionCall.Args["city"] as string;
var state = functionCall.Args["state"] as string;
var date = functionCall.Args["date"] as string;
functionResponses.Add(ModelContent.FunctionResponse(
name: functionCall.Name,
// Forward the structured input data prepared by the model
// to the hypothetical external API.
response: FetchWeather(city: city, state: state, date: date)
));
}
// TODO(developer): Handle other potential function calls, if any.
}
Шаг 5 : Передайте выходные данные функции модели для генерации окончательного ответа.
После того как функция fetchWeather вернет информацию о погоде, ваше приложение должно передать ее обратно в модель.
Затем модель выполняет заключительную обработку и генерирует окончательный ответ на естественном языке, например: On October 17, 2024 in Boston, it was 38 degrees Fahrenheit with partly cloudy skies.
Быстрый
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
let finalResponse = try await chat.sendMessage(
[ModelContent(role: "function", parts: functionResponses)]
)
// Log the text response.
print(finalResponse.text ?? "No text in response.")
Kotlin
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
val finalResponse = chat.sendMessage(content("function") {
part(FunctionResponsePart("fetchWeather", functionResponse!!))
})
// Log the text response.
println(finalResponse.text ?: "No text in response")
Java
ListenableFuture<GenerateContentResponse> modelResponseFuture = Futures.transformAsync(
handleFunctionCallFuture,
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
functionCallResult -> chatFutures.sendMessage(new Content("function",
List.of(new FunctionResponsePart(
"fetchWeather", functionCallResult)))),
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Futures.addCallback(modelResponseFuture, new FutureCallback<GenerateContentResponse>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse result) {
if (result.getText() != null) {
// Log the text response.
System.out.println(result.getText());
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
// handle error
}
}, Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor());
Web
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
result = await chat.sendMessage([
{
functionResponse: {
name: functionCall.name, // "fetchWeather"
response: functionResult,
},
},
]);
console.log(result.response.text());
Dart
// Send the response from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
response = await chat
.sendMessage(Content.functionResponse(functionCall.name, functionResult));
Единство
// Send the response(s) from the function back to the model
// so that the model can use it to generate its final response.
var finalResponse = await chat.SendMessageAsync(functionResponses);
// Log the text response.
UnityEngine.Debug.Log(finalResponse.Text ?? "No text in response.");
Дополнительные варианты поведения и возможности
Вот некоторые дополнительные особенности вызова функций, которые необходимо учесть в вашем коде, а также параметры, которые вы можете контролировать.
Модель может запросить повторный вызов функции или вызов другой функции.
Если ответа от одного вызова функции недостаточно для генерации окончательного результата моделью, она может запросить дополнительный вызов функции или вызов совершенно другой функции. Последнее возможно только в том случае, если вы предоставите модели более одной функции в списке объявлений функций.
Ваше приложение должно учитывать, что модель может запрашивать дополнительные вызовы функций.
Модель может запрашивать вызов нескольких функций одновременно.
В списке объявлений функций вы можете указать модели до 128 функций. Учитывая это, модель может решить, что для генерации окончательного ответа ей потребуется несколько функций. И она может решить вызвать некоторые из этих функций одновременно — это называется параллельным вызовом функций .
Ваше приложение должно учитывать, что модель может запрашивать одновременное выполнение нескольких функций, и ваше приложение должно передавать все ответы от этих функций обратно модели.
Вы можете контролировать, как и сможет ли модель запрашивать вызов функций.
Вы можете установить некоторые ограничения на то, как и следует ли модели использовать предоставленные объявления функций. Это называется настройкой режима вызова функций . Вот несколько примеров:
Вместо того чтобы позволять модели выбирать между немедленным ответом на естественном языке и вызовом функции, вы можете заставить её всегда использовать вызовы функций. Это называется принудительным вызовом функций .
Если вы предоставите несколько объявлений функций, вы сможете ограничить использование моделью только подмножества предоставленных функций.
Эти ограничения (или режимы) реализуются путем добавления конфигурации инструмента ( toolConfig ) вместе с приглашением командной строки и объявлениями функций. В конфигурации инструмента можно указать один из следующих режимов . Наиболее полезный режим — ANY .
| Режим | Описание |
|---|---|
AUTO | Поведение модели по умолчанию. Модель решает, использовать ли вызов функции или ответ на естественном языке. |
ANY | Модель должна использовать вызовы функций («принудительный вызов функций»). Чтобы ограничить модель подмножеством функций, укажите разрешенные имена функций в allowedFunctionNames . |
NONE | В модели не должны использоваться вызовы функций. Такое поведение эквивалентно запросу модели без каких-либо связанных объявлений функций. |
Что еще можно сделать?
Попробуйте другие возможности.
- Создавайте многоэтапные диалоги (чат) .
- Генерация текста на основе текстовых подсказок .
- Генерируйте текст, запрашивая различные типы файлов, такие как изображения , PDF-файлы , видео и аудио .
Узнайте, как управлять генерацией контента.
- Разберитесь в разработке подсказок для заданий , включая лучшие практики, стратегии и примеры подсказок.
- Настройте параметры модели , такие как температура и максимальное количество выходных токенов (для Gemini ) или соотношение сторон и генерация людей (для Imagen ).
- Используйте настройки безопасности , чтобы скорректировать вероятность получения ответов, которые могут быть сочтены вредными.
Узнайте больше о поддерживаемых моделях
Узнайте о моделях, доступных для различных вариантов использования , а также об их квотах и ценах .Оставьте отзыв о вашем опыте использования Firebase AI Logic.

