L'esecuzione del codice è uno strumento che consente al modello di generare ed eseguire codice Python. Il modello può apprendere in modo iterativo dai risultati dell'esecuzione del codice fino a raggiungere un output finale.
Puoi utilizzare l'esecuzione del codice per creare funzionalità che traggono vantaggio dal ragionamento basato sul codice e che generano output di testo. Ad esempio, puoi utilizzare l'esecuzione del codice per risolvere equazioni o elaborare testo. Puoi anche utilizzare le librerie incluse nell'ambiente di esecuzione del codice per svolgere attività più specializzate.
Come per tutti gli strumenti che fornisci al modello, il modello decide quando utilizzare l'esecuzione del codice.
Vai all'implementazione del codice
Confronto tra esecuzione del codice e chiamata di funzione
L'esecuzione del codice e la chiamata di funzione sono funzionalità simili. In generale, dovresti preferire l'utilizzo dell'esecuzione del codice se il modello è in grado di gestire il tuo caso d'uso. L'esecuzione del codice è anche più semplice da usare perché basta attivarla.
Ecco alcune differenze aggiuntive tra l'esecuzione del codice e la chiamata di funzione:
| Esecuzione del codice | usa la chiamata di funzione |
|---|---|
| Utilizza l'esecuzione del codice se vuoi che il modello scriva ed esegua codice Python per te e restituisca il risultato. | Utilizza le chiamate di funzione se hai già le tue funzioni che vuoi eseguire localmente. |
| L'esecuzione del codice consente al modello di eseguire il codice nel backend dell'API in un ambiente fisso e isolato. | La chiamata di funzione ti consente di eseguire le funzioni richieste dal modello nell'ambiente che preferisci. |
| L'esecuzione del codice viene risolta in un'unica richiesta. Sebbene tu possa utilizzare facoltativamente l'esecuzione di codice con la funzionalità di chat, non è obbligatorio. | La chiamata di funzioni richiede una richiesta aggiuntiva per restituire l'output di ogni chiamata di funzione. Pertanto, devi utilizzare la funzionalità di chat. |
Modelli supportati
gemini-3-pro-previewgemini-2.5-progemini-2.5-flashgemini-2.5-flash-litegemini-2.0-flash-001(e il relativo alias aggiornato automaticamentegemini-2.0-flash)gemini-2.0-flash-live-preview-04-09
Utilizzare l'esecuzione del codice
Puoi utilizzare l'esecuzione del codice con input solo di testo e multimodali, ma la risposta sarà sempre solo testo o codice.
Prima di iniziare
|
Fai clic sul tuo fornitore Gemini API per visualizzare i contenuti e il codice specifici del fornitore in questa pagina. |
Se non l'hai ancora fatto, completa la guida introduttiva, che descrive come configurare il progetto Firebase, connettere l'app a Firebase, aggiungere l'SDK, inizializzare il servizio di backend per il provider Gemini API scelto e creare un'istanza GenerativeModel.
Per testare e perfezionare i prompt, ti consigliamo di utilizzare Google AI Studio.
Attiva l'esecuzione del codice
|
Prima di provare questo esempio, completa la sezione
Prima di iniziare di questa guida
per configurare il progetto e l'app. In questa sezione, fai clic anche su un pulsante per il provider Gemini API che hai scelto, in modo da visualizzare i contenuti specifici del provider in questa pagina. |
Quando crei l'istanza GenerativeModel, fornisci CodeExecution come
strumento che il modello può utilizzare per generare la sua risposta. Ciò consente al modello di generare ed eseguire codice Python.
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
let ai = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI())
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = ai.generativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [.codeExecution()]
)
let prompt = """
What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers?
Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.
"""
let response = try await model.generateContent(prompt)
guard let candidate = response.candidates.first else {
print("No candidates in response.")
return
}
for part in candidate.content.parts {
if let textPart = part as? TextPart {
print("Text = \(textPart.text)")
} else if let executableCode = part as? ExecutableCodePart {
print("Code = \(executableCode.code), Language = \(executableCode.language)")
} else if let executionResult = part as? CodeExecutionResultPart {
print("Outcome = \(executionResult.outcome), Result = \(executionResult.output ?? "no output")")
}
}
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools = listOf(Tool.codeExecution())
)
val prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
val response = model.generateContent(prompt)
response.candidates.first().content.parts.forEach {
if(it is TextPart) {
println("Text = ${it.text}")
}
if(it is ExecutableCodePart) {
println("Code = ${it.code}, Language = ${it.language}")
}
if(it is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
println("Outcome = ${it.outcome}, Result = ${it.output}")
}
}
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
null,
null,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
List.of(Tool.codeExecution()));
// Use the GenerativeModelFutures Java compatibility layer which offers
// support for ListenableFuture and Publisher APIs
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
String text = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText(text)
.build();
ListenableFuture response = model.generateContent(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse response) {
// Access the first candidate's content parts
List parts = response.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts();
for (Part part : parts) {
if (part instanceof TextPart) {
TextPart textPart = (TextPart) part;
System.out.println("Text = " + textPart.getText());
} else if (part instanceof ExecutableCodePart) {
ExecutableCodePart codePart = (ExecutableCodePart) part;
System.out.println("Code = " + codePart.getCode() + ", Language = " + codePart.getLanguage());
} else if (part instanceof CodeExecutionResultPart) {
CodeExecutionResultPart resultPart = (CodeExecutionResultPart) part;
System.out.println("Outcome = " + resultPart.getOutcome() + ", Result = " + resultPart.getOutput());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const ai = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(
ai,
{
model: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }]
}
);
const prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
const result = await model.generateContent(prompt);
const response = await result.response;
const parts = response.candidates?.[0].content.parts;
if (parts) {
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(`Text: ${part.text}`);
} else if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(
`Code: ${part.executableCode.code}, Language: ${part.executableCode.language}`
);
} else if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(
`Outcome: ${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}, Result: ${part.codeExecutionResult.output}`
);
}
});
}
Dart
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
final model = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'GEMINI_MODEL_NAME',
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [
Tool.codeExecution(),
],
);
const prompt = 'What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? '
'Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.';
final response = await model.generateContent([Content.text(prompt)]);
final buffer = StringBuffer();
for (final part in response.candidates.first.content.parts) {
if (part is TextPart) {
buffer.writeln(part.text);
} else if (part is ExecutableCodePart) {
buffer.writeln('Executable Code:');
buffer.writeln('Language: ${part.language}');
buffer.writeln('Code:');
buffer.writeln(part.code);
} else if (part is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
buffer.writeln('Code Execution Result:');
buffer.writeln('Outcome: ${part.outcome}');
buffer.writeln('Output:');
buffer.writeln(part.output);
}
}
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
var ai = FirebaseAI.GetInstance(FirebaseAI.Backend.GoogleAI());
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = ai.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: new Tool[] { new Tool(new CodeExecution()) }
);
var prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
var response = await model.GenerateContentAsync(prompt);
foreach (var part in response.Candidates.First().Content.Parts) {
if (part is ModelContent.TextPart tp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Text = {tp.Text}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.ExecutableCodePart esp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Code = {esp.Code}, Language = {esp.Language}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.CodeExecutionResultPart cerp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Outcome = {cerp.Outcome}, Output = {cerp.Output}");
}
}
Scopri come scegliere un modello adatti al tuo caso d'uso e alla tua app.
Utilizzare l'esecuzione del codice in chat
Puoi anche utilizzare l'esecuzione di codice nell'ambito di una chat:
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
let ai = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI())
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = ai.generativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [.codeExecution()]
)
let prompt = """
What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers?
Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.
"""
let chat = model.startChat()
let response = try await chat.sendMessage(prompt)
guard let candidate = response.candidates.first else {
print("No candidates in response.")
return
}
for part in candidate.content.parts {
if let textPart = part as? TextPart {
print("Text = \(textPart.text)")
} else if let executableCode = part as? ExecutableCodePart {
print("Code = \(executableCode.code), Language = \(executableCode.language)")
} else if let executionResult = part as? CodeExecutionResultPart {
print("Outcome = \(executionResult.outcome), Result = \(executionResult.output ?? "no output")")
}
}
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools = listOf(Tool.codeExecution())
)
val prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
val chat = model.startChat()
val response = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
response.candidates.first().content.parts.forEach {
if(it is TextPart) {
println("Text = ${it.text}")
}
if(it is ExecutableCodePart) {
println("Code = ${it.code}, Language = ${it.language}")
}
if(it is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
println("Outcome = ${it.outcome}, Result = ${it.output}")
}
}
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
null,
null,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
List.of(Tool.codeExecution()));
// Use the GenerativeModelFutures Java compatibility layer which offers
// support for ListenableFuture and Publisher APIs
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
String text = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText(text)
.build();
ChatFutures chat = model.startChat();
ListenableFuture response = chat.sendMessage(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse response) {
// Access the first candidate's content parts
List parts = response.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts();
for (Part part : parts) {
if (part instanceof TextPart) {
TextPart textPart = (TextPart) part;
System.out.println("Text = " + textPart.getText());
} else if (part instanceof ExecutableCodePart) {
ExecutableCodePart codePart = (ExecutableCodePart) part;
System.out.println("Code = " + codePart.getCode() + ", Language = " + codePart.getLanguage());
} else if (part instanceof CodeExecutionResultPart) {
CodeExecutionResultPart resultPart = (CodeExecutionResultPart) part;
System.out.println("Outcome = " + resultPart.getOutcome() + ", Result = " + resultPart.getOutput());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const ai = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(
ai,
{
model: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }]
}
);
const prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
const chat = model.startChat()
const result = await chat.sendMessage(prompt);
const parts = result.response.candidates?.[0].content.parts;
if (parts) {
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(`Text: ${part.text}`);
} else if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(
`Code: ${part.executableCode.code}, Language: ${part.executableCode.language}`
);
} else if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(
`Outcome: ${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}, Result: ${part.codeExecutionResult.output}`
);
}
});
}
Dart
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
final model = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'GEMINI_MODEL_NAME',
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [
Tool.codeExecution(),
],
);
final codeExecutionChat = await model.startChat();
const prompt = 'What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? '
'Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.';
final response = await codeExecutionChat.sendMessage(Content.text(prompt));
final buffer = StringBuffer();
for (final part in response.candidates.first.content.parts) {
if (part is TextPart) {
buffer.writeln(part.text);
} else if (part is ExecutableCodePart) {
buffer.writeln('Executable Code:');
buffer.writeln('Language: ${part.language}');
buffer.writeln('Code:');
buffer.writeln(part.code);
} else if (part is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
buffer.writeln('Code Execution Result:');
buffer.writeln('Outcome: ${part.outcome}');
buffer.writeln('Output:');
buffer.writeln(part.output);
}
}
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
var ai = FirebaseAI.GetInstance(FirebaseAI.Backend.GoogleAI());
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = ai.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: new Tool[] { new Tool(new CodeExecution()) }
);
var prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
var chat = model.StartChat();
var response = await chat.SendMessageAsync(prompt);
foreach (var part in response.Candidates.First().Content.Parts) {
if (part is ModelContent.TextPart tp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Text = {tp.Text}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.ExecutableCodePart esp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Code = {esp.Code}, Language = {esp.Language}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.CodeExecutionResultPart cerp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Outcome = {cerp.Outcome}, Output = {cerp.Output}");
}
}
Scopri come scegliere un modello adatti al tuo caso d'uso e alla tua app.
Prezzi
Non sono previsti costi aggiuntivi per l'abilitazione dell'esecuzione del codice e la sua fornitura come strumento per il modello. Se il modello decide di utilizzare l'esecuzione del codice, ti viene addebitata la tariffa attuale dei token di input e output in base al modello Gemini che stai utilizzando.
Il seguente diagramma mostra il modello di fatturazione per l'esecuzione del codice:
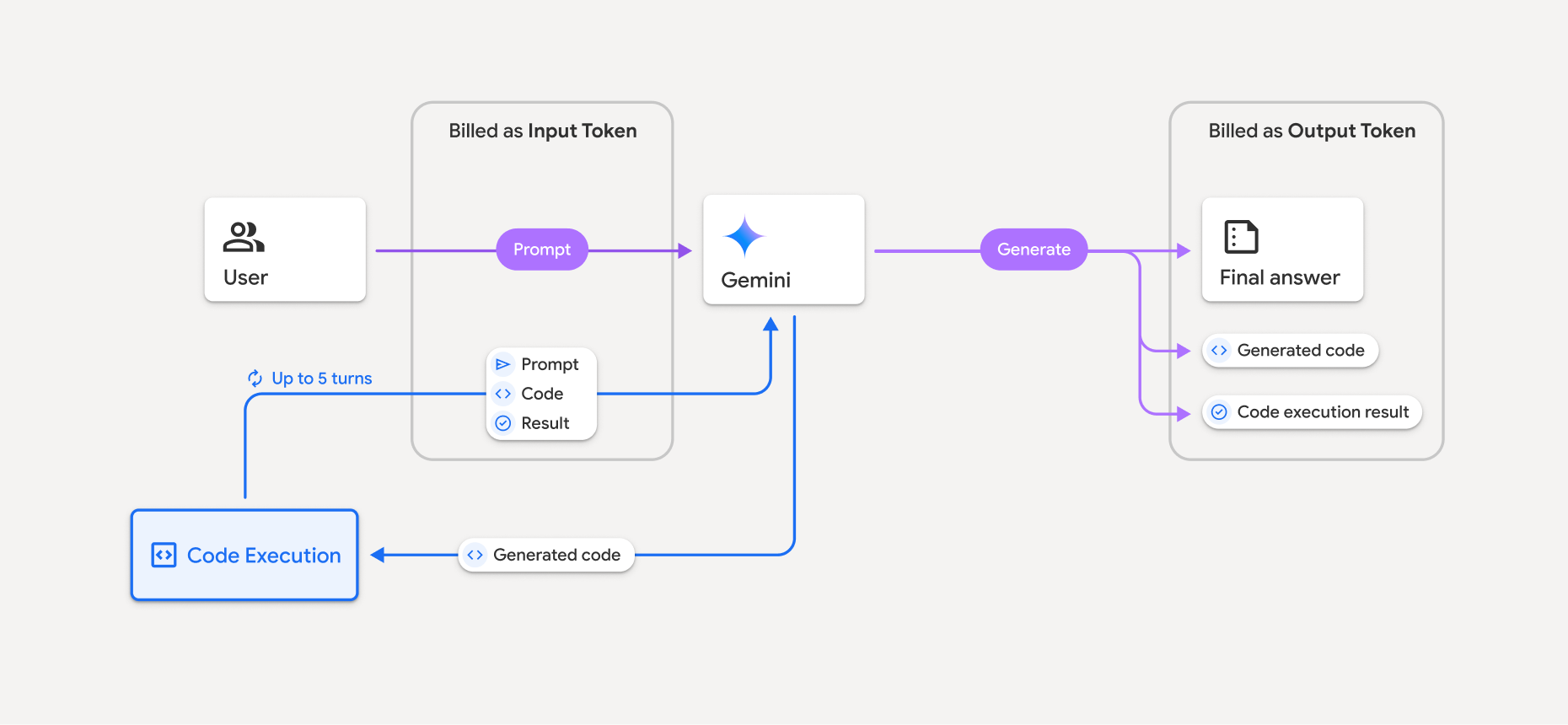
Ecco un riepilogo di come vengono fatturati i token quando un modello utilizza l'esecuzione di codice:
Il prompt originale viene fatturato una sola volta. I suoi token sono etichettati come token intermedi, che vengono fatturati come token di input.
Il codice generato e il risultato del codice eseguito vengono fatturati nel seguente modo:
Quando vengono utilizzati durante l'esecuzione del codice, vengono etichettati come token intermedi che vengono fatturati come token di input.
Quando sono inclusi nella risposta finale, vengono fatturati come token di output.
Il riepilogo finale nella risposta finale viene fatturato come token di output.
Gemini API include un conteggio dei token intermedi nella risposta dell'API, in modo da sapere perché ti vengono addebitati token di input oltre al prompt iniziale.
Tieni presente che il codice generato può includere sia testo che output multimodali, ad esempio immagini.
Limitazioni e best practice
Il modello può solo generare ed eseguire codice Python. Non può restituire altri artefatti come i file multimediali.
L'esecuzione del codice può durare al massimo 30 secondi prima del timeout.
In alcuni casi, l'attivazione dell'esecuzione del codice può comportare regressioni in altre aree dell'output del modello (ad esempio, la scrittura di una storia).
Lo strumento di esecuzione del codice non supporta gli URI di file come input/output. Tuttavia, lo strumento di esecuzione del codice supporta l'input di file e l'output del grafico come byte incorporati. Utilizzando queste funzionalità di input e output, puoi caricare file CSV e di testo, porre domande sui file e generare grafici Matplotlib come parte del risultato dell'esecuzione del codice. I tipi MIME supportati per i byte incorporati sono
.cpp,.csv,.java,.jpeg,.js,.png,.py,.tse.xml.
Librerie supportate
L'ambiente di esecuzione del codice include le seguenti librerie. Non puoi installare le tue librerie.
Fornisci un feedback sulla tua esperienza con Firebase AI Logic
