コード実行は、モデルが Python コードを生成して実行できるようにするツールです。モデルは、最終的な出力に到達するまで、コード実行の結果から反復的に学習できます。
コード実行を使用すると、コードベースの推論を活用し、テキスト出力を生成する機能を構築できます。たとえば、コード実行を使用して方程式を解いたり、テキストを処理したりできます。コード実行環境に含まれるライブラリを使用して、より特殊なタスクを実行することもできます。
モデルに提供する他のツールと同様に、コード実行を使用するタイミングはモデルが判断します。
コード実行と関数呼び出しの比較
コード実行と関数呼び出しは類似した機能です。一般に、モデルでユースケースに対処できる場合は、コード実行を使用することをおすすめします。コード実行は、有効にするだけで使用できるため、使いやすさも向上しています。
コード実行と関数呼び出しには、他にも次のような違いがあります。
| コードの実行 | 関数呼び出し |
|---|---|
| モデルで Python コードを記述して実行し、結果を返すようにする場合は、コード実行を使用します。 | ローカルで実行する独自の関数がすでにある場合は、関数呼び出しを使用します。 |
| コード実行では、モデルは固定された隔離環境で API バックエンドのコードを実行できます。 | 関数呼び出しでは、モデルがリクエストする関数を任意の環境で実行できます。 |
| コード実行は 1 回のリクエストで解決されます。チャット機能でコード実行を任意で使用できますが、必須ではありません。 | 関数呼び出しでは、各関数呼び出しの出力を返すために追加のリクエストが必要です。そのため、チャット機能を使用する必要があります。 |
サポートされているモデル
gemini-3-pro-previewgemini-2.5-progemini-2.5-flashgemini-2.5-flash-litegemini-2.0-flash-001(および自動更新エイリアスgemini-2.0-flash)gemini-2.0-flash-live-preview-04-09
コード実行を使用する
コード実行はテキストのみの入力とマルチモーダル入力の両方で使用できますが、レスポンスは常にテキストまたはコードのみになります。
始める前に
|
Gemini API プロバイダをクリックして、このページでプロバイダ固有のコンテンツとコードを表示します。 |
まだ完了していない場合は、スタートガイドに沿って、記載されている手順(Firebase プロジェクトの設定、アプリと Firebase の連携、SDK の追加、選択した Gemini API プロバイダのバックエンド サービスの初期化、GenerativeModel インスタンスの作成)を完了します。
プロンプトのテストと反復処理には、Google AI Studio の使用をおすすめします。
コード実行を有効にする
|
このサンプルを試す前に、このガイドの始める前にのセクションを完了して、プロジェクトとアプリを設定してください。 このセクションでは、選択した Gemini API プロバイダのボタンをクリックして、このページにプロバイダ固有のコンテンツを表示します。 |
GenerativeModel インスタンスを作成するときに、モデルがレスポンスの生成に使用できるツールとして CodeExecution を指定します。これにより、モデルは Python コードを生成して実行できるようになります。
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
let ai = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI())
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = ai.generativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [.codeExecution()]
)
let prompt = """
What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers?
Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.
"""
let response = try await model.generateContent(prompt)
guard let candidate = response.candidates.first else {
print("No candidates in response.")
return
}
for part in candidate.content.parts {
if let textPart = part as? TextPart {
print("Text = \(textPart.text)")
} else if let executableCode = part as? ExecutableCodePart {
print("Code = \(executableCode.code), Language = \(executableCode.language)")
} else if let executionResult = part as? CodeExecutionResultPart {
print("Outcome = \(executionResult.outcome), Result = \(executionResult.output ?? "no output")")
}
}
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools = listOf(Tool.codeExecution())
)
val prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
val response = model.generateContent(prompt)
response.candidates.first().content.parts.forEach {
if(it is TextPart) {
println("Text = ${it.text}")
}
if(it is ExecutableCodePart) {
println("Code = ${it.code}, Language = ${it.language}")
}
if(it is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
println("Outcome = ${it.outcome}, Result = ${it.output}")
}
}
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
null,
null,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
List.of(Tool.codeExecution()));
// Use the GenerativeModelFutures Java compatibility layer which offers
// support for ListenableFuture and Publisher APIs
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
String text = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText(text)
.build();
ListenableFuture response = model.generateContent(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse response) {
// Access the first candidate's content parts
List parts = response.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts();
for (Part part : parts) {
if (part instanceof TextPart) {
TextPart textPart = (TextPart) part;
System.out.println("Text = " + textPart.getText());
} else if (part instanceof ExecutableCodePart) {
ExecutableCodePart codePart = (ExecutableCodePart) part;
System.out.println("Code = " + codePart.getCode() + ", Language = " + codePart.getLanguage());
} else if (part instanceof CodeExecutionResultPart) {
CodeExecutionResultPart resultPart = (CodeExecutionResultPart) part;
System.out.println("Outcome = " + resultPart.getOutcome() + ", Result = " + resultPart.getOutput());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const ai = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(
ai,
{
model: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }]
}
);
const prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
const result = await model.generateContent(prompt);
const response = await result.response;
const parts = response.candidates?.[0].content.parts;
if (parts) {
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(`Text: ${part.text}`);
} else if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(
`Code: ${part.executableCode.code}, Language: ${part.executableCode.language}`
);
} else if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(
`Outcome: ${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}, Result: ${part.codeExecutionResult.output}`
);
}
});
}
Dart
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
final model = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'GEMINI_MODEL_NAME',
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [
Tool.codeExecution(),
],
);
const prompt = 'What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? '
'Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.';
final response = await model.generateContent([Content.text(prompt)]);
final buffer = StringBuffer();
for (final part in response.candidates.first.content.parts) {
if (part is TextPart) {
buffer.writeln(part.text);
} else if (part is ExecutableCodePart) {
buffer.writeln('Executable Code:');
buffer.writeln('Language: ${part.language}');
buffer.writeln('Code:');
buffer.writeln(part.code);
} else if (part is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
buffer.writeln('Code Execution Result:');
buffer.writeln('Outcome: ${part.outcome}');
buffer.writeln('Output:');
buffer.writeln(part.output);
}
}
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
var ai = FirebaseAI.GetInstance(FirebaseAI.Backend.GoogleAI());
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = ai.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: new Tool[] { new Tool(new CodeExecution()) }
);
var prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
var response = await model.GenerateContentAsync(prompt);
foreach (var part in response.Candidates.First().Content.Parts) {
if (part is ModelContent.TextPart tp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Text = {tp.Text}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.ExecutableCodePart esp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Code = {esp.Code}, Language = {esp.Language}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.CodeExecutionResultPart cerp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Outcome = {cerp.Outcome}, Output = {cerp.Output}");
}
}
ユースケースとアプリに適したモデル を選択する方法について説明します。
チャットでコード実行を使用する
コード実行をチャットの一部として使用することもできます。
Swift
import FirebaseAILogic
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
let ai = FirebaseAI.firebaseAI(backend: .googleAI())
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
let model = ai.generativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [.codeExecution()]
)
let prompt = """
What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers?
Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.
"""
let chat = model.startChat()
let response = try await chat.sendMessage(prompt)
guard let candidate = response.candidates.first else {
print("No candidates in response.")
return
}
for part in candidate.content.parts {
if let textPart = part as? TextPart {
print("Text = \(textPart.text)")
} else if let executableCode = part as? ExecutableCodePart {
print("Code = \(executableCode.code), Language = \(executableCode.language)")
} else if let executionResult = part as? CodeExecutionResultPart {
print("Outcome = \(executionResult.outcome), Result = \(executionResult.output ?? "no output")")
}
}
Kotlin
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
val model = Firebase.ai(backend = GenerativeBackend.googleAI()).generativeModel(
modelName = "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools = listOf(Tool.codeExecution())
)
val prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
val chat = model.startChat()
val response = chat.sendMessage(prompt)
response.candidates.first().content.parts.forEach {
if(it is TextPart) {
println("Text = ${it.text}")
}
if(it is ExecutableCodePart) {
println("Code = ${it.code}, Language = ${it.language}")
}
if(it is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
println("Outcome = ${it.outcome}, Result = ${it.output}")
}
}
Java
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
GenerativeModel ai = FirebaseAI.getInstance(GenerativeBackend.googleAI())
.generativeModel("GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
null,
null,
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
List.of(Tool.codeExecution()));
// Use the GenerativeModelFutures Java compatibility layer which offers
// support for ListenableFuture and Publisher APIs
GenerativeModelFutures model = GenerativeModelFutures.from(ai);
String text = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
Content prompt = new Content.Builder()
.addText(text)
.build();
ChatFutures chat = model.startChat();
ListenableFuture response = chat.sendMessage(prompt);
Futures.addCallback(response, new FutureCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(GenerateContentResponse response) {
// Access the first candidate's content parts
List parts = response.getCandidates().get(0).getContent().getParts();
for (Part part : parts) {
if (part instanceof TextPart) {
TextPart textPart = (TextPart) part;
System.out.println("Text = " + textPart.getText());
} else if (part instanceof ExecutableCodePart) {
ExecutableCodePart codePart = (ExecutableCodePart) part;
System.out.println("Code = " + codePart.getCode() + ", Language = " + codePart.getLanguage());
} else if (part instanceof CodeExecutionResultPart) {
CodeExecutionResultPart resultPart = (CodeExecutionResultPart) part;
System.out.println("Outcome = " + resultPart.getOutcome() + ", Result = " + resultPart.getOutput());
}
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
}, executor);
Web
import { initializeApp } from "firebase/app";
import { getAI, getGenerativeModel, GoogleAIBackend } from "firebase/ai";
// TODO(developer) Replace the following with your app's Firebase configuration
// See: https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/learn-more#config-object
const firebaseConfig = {
// ...
};
// Initialize FirebaseApp
const firebaseApp = initializeApp(firebaseConfig);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
const ai = getAI(firebaseApp, { backend: new GoogleAIBackend() });
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
const model = getGenerativeModel(
ai,
{
model: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [{ codeExecution: {} }]
}
);
const prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50."
const chat = model.startChat()
const result = await chat.sendMessage(prompt);
const parts = result.response.candidates?.[0].content.parts;
if (parts) {
parts.forEach((part) => {
if (part.text) {
console.log(`Text: ${part.text}`);
} else if (part.executableCode) {
console.log(
`Code: ${part.executableCode.code}, Language: ${part.executableCode.language}`
);
} else if (part.codeExecutionResult) {
console.log(
`Outcome: ${part.codeExecutionResult.outcome}, Result: ${part.codeExecutionResult.output}`
);
}
});
}
Dart
import 'package:firebase_core/firebase_core.dart';
import 'package:firebase_ai/firebase_ai.dart';
import 'firebase_options.dart';
// Initialize FirebaseApp
await Firebase.initializeApp(
options: DefaultFirebaseOptions.currentPlatform,
);
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
final model = FirebaseAI.googleAI().generativeModel(
model: 'GEMINI_MODEL_NAME',
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: [
Tool.codeExecution(),
],
);
final codeExecutionChat = await model.startChat();
const prompt = 'What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? '
'Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.';
final response = await codeExecutionChat.sendMessage(Content.text(prompt));
final buffer = StringBuffer();
for (final part in response.candidates.first.content.parts) {
if (part is TextPart) {
buffer.writeln(part.text);
} else if (part is ExecutableCodePart) {
buffer.writeln('Executable Code:');
buffer.writeln('Language: ${part.language}');
buffer.writeln('Code:');
buffer.writeln(part.code);
} else if (part is CodeExecutionResultPart) {
buffer.writeln('Code Execution Result:');
buffer.writeln('Outcome: ${part.outcome}');
buffer.writeln('Output:');
buffer.writeln(part.output);
}
}
Unity
using Firebase;
using Firebase.AI;
// Initialize the Gemini Developer API backend service
var ai = FirebaseAI.GetInstance(FirebaseAI.Backend.GoogleAI());
// Create a `GenerativeModel` instance with a model that supports your use case
var model = ai.GetGenerativeModel(
modelName: "GEMINI_MODEL_NAME",
// Provide code execution as a tool that the model can use to generate its response.
tools: new Tool[] { new Tool(new CodeExecution()) }
);
var prompt = "What is the sum of the first 50 prime numbers? " +
"Generate and run code for the calculation, and make sure you get all 50.";
var chat = model.StartChat();
var response = await chat.SendMessageAsync(prompt);
foreach (var part in response.Candidates.First().Content.Parts) {
if (part is ModelContent.TextPart tp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Text = {tp.Text}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.ExecutableCodePart esp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Code = {esp.Code}, Language = {esp.Language}");
} else if (part is ModelContent.CodeExecutionResultPart cerp) {
UnityEngine.Debug.Log($"Outcome = {cerp.Outcome}, Output = {cerp.Output}");
}
}
ユースケースとアプリに適したモデル を選択する方法について説明します。
料金
コード実行を有効にして、モデルのツールとして提供しても、追加料金は発生しません。モデルがコード実行を使用すると判断した場合、使用している Gemini モデルに基づいて、入力トークンと出力トークンの現在のレートで課金されます。
次の図は、コード実行の課金モデルを示しています。
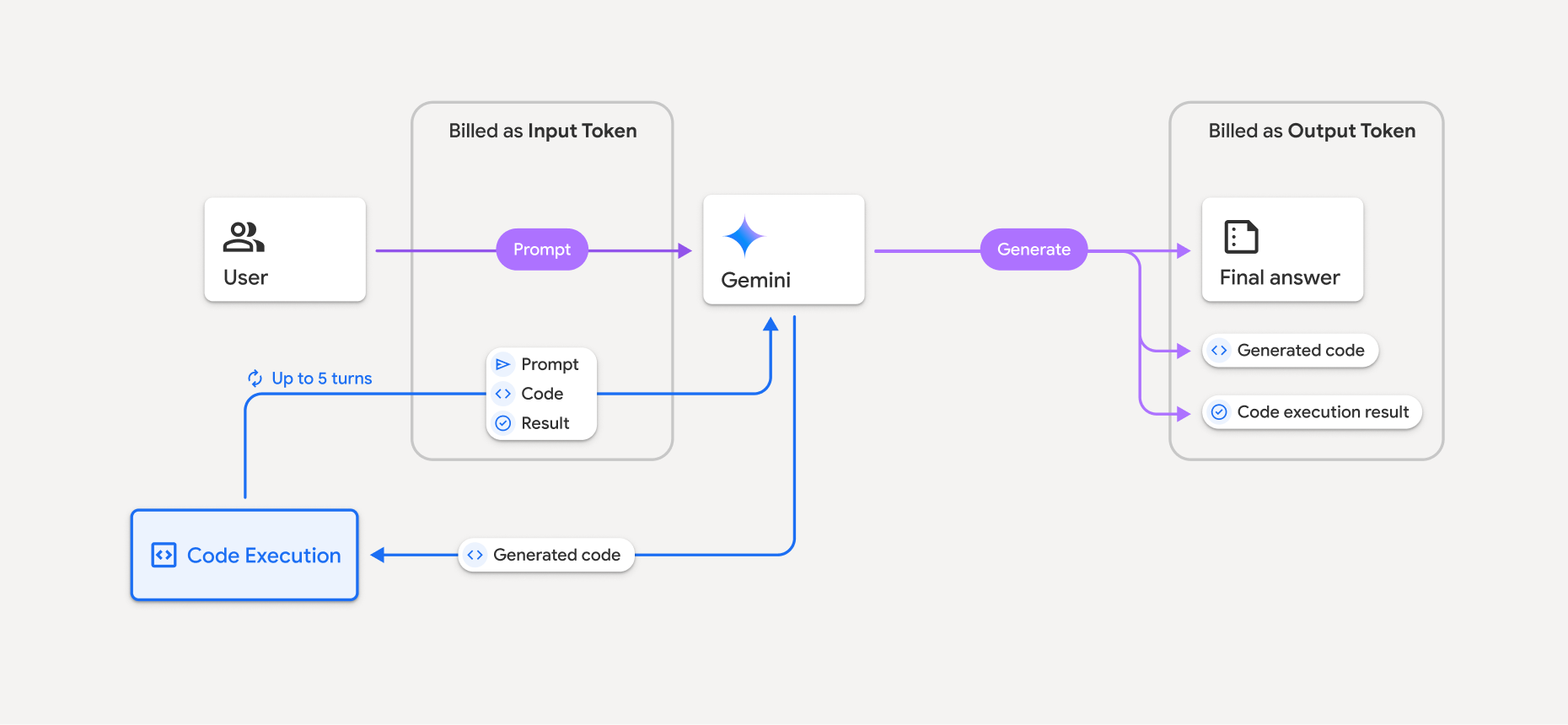
モデルがコード実行を使用する場合のトークンの課金方法の概要は次のとおりです。
元のプロンプトは 1 回請求されます。そのトークンは中間トークンとしてラベル付けされ、入力トークンとして課金されます。
生成されたコードと実行されたコードの結果は、次のように課金されます。
コード実行時に使用される場合 - 中間トークンとしてラベル付けされ、入力トークンとして課金されます。
最終的なレスポンスの一部として含まれる場合、出力トークンとして課金されます。
最終レスポンスの最終的な要約は、出力トークンとして課金されます。
Gemini API の API レスポンスには中間トークン数が含まれるため、最初のプロンプトで渡されたトークン以外の入力トークンに対して課金される理由を把握できます。
生成されたコードには、テキストとマルチモーダル出力(画像など)の両方を含めることができます。
制限事項とベスト プラクティス
モデルは Python コードの生成と実行のみが可能です。メディア ファイルなど、他のアーティファクトを返すことはできません。
コード実行は、タイムアウトするまで最大 30 秒間実行できます。
コード実行を有効にすると、モデル出力の他の領域(ストーリーの作成など)で回帰が発生することがあります。
コード実行ツールは、ファイル URI を入出力としては扱えません。ただし、ファイル入力と、グラフをインラインのバイトデータとして出力することは可能です。これらの入出力機能を使用すると、CSV ファイルとテキスト ファイルをアップロードし、ファイルに関する質問をしたり、コード実行結果の一部として Matplotlib グラフを生成したりできます。インライン バイトでサポートされている MIME タイプは、
.cpp、.csv、.java、.jpeg、.js、.png、.py、.ts、.xmlです。
サポートされているライブラリ
コード実行環境には、次のライブラリが含まれています。独自のライブラリをインストールすることはできません。
Firebase AI Logic の使用感についてフィードバックを送信する
