This guide describes how to run an instrumentation, Robo, or Game Loop test using the gcloud CLI.
For a complete list of gcloud commands you can use
with your Android app in Test Lab, visit the
reference documentation for gcloud firebase test android.
Before you begin
If you haven't already, add Firebase to your Android project.
Step 1. Set up the gcloud CLI
- Download the Google Cloud SDK
- Make sure your installation is up-to-date:
gcloud components update
- Sign in to the gcloud CLI using your Google Account:
gcloud auth login
- Set your Firebase project in gcloud, where PROJECT_ID is
the ID of your Firebase project:
gcloud config set project PROJECT_ID
This includes the gcloud CLI tool.
Step 2. Check available test devices
Use the following gcloud commands to view test devices and locales that are available for your test.
As an option, you can also download the sample
Notepad app to start
running the commands right away. Use the binary file app-debug-unaligned.apk
and instrumentation tests file app-debug-test-unaligned.apk, which are located
in NotePad/app/build/outputs/apk/.
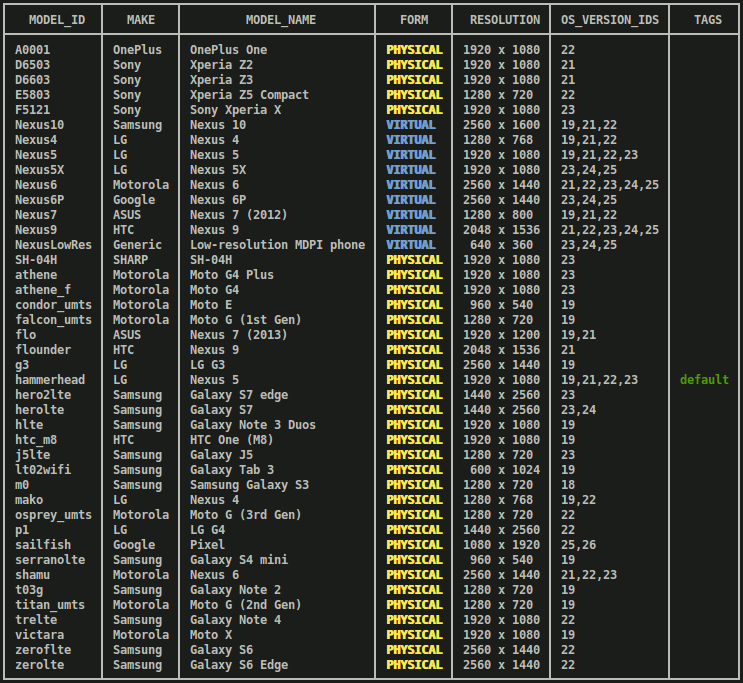
models list: Get a current list of Android devices available for you to test against.gcloud firebase test android models listIn the command output:
- Column
MODEL_IDcontains the identifier you can later use to run tests on the device model. - Column
OS_VERSION_IDcontains the operating system versions supported by the device.
Example output
- Column
models describe: Get more information about a specific AndroidMODEL_ID.gcloud firebase test android models describe MODEL_IDThe output contains the device model's brand, manufacturer, OS versions, supported API levels, supported Application Binary Interfaces (ABI), release dates, and whether the device is physical or virtual.
versions list: Get a list of currently available OS versions to test against.gcloud firebase test android versions listYou can use an identifier from either of the first two columns of command output (
OS_VERSION_IDandVERSION), to later run tests against an Android OS version. If you don't specify the Android OS versions to test against, the default noted under theTAGScolumn is used.Example output
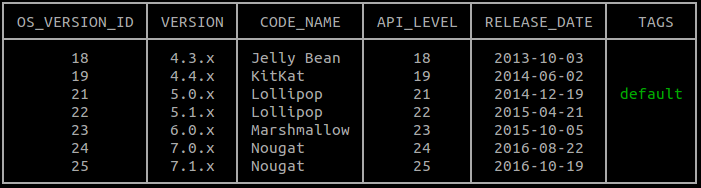
locales list: Get the current list of locales available to test against.gcloud firebase test android locales listThe first column of the command output,
LOCALE, contains the identifier that you can use later to run tests against a locale. If you don't specify the locales to test against, English is used as the default locale.
Step 3. Run your test
Now that you know the range of device models, locales, and OS versions available
for testing your app, you can specify devices using the
gcloud firebase test android run command and the
--device flag to run Robo or instrumentation tests.
Run a Robo test
Even if you don't have any instrumentation tests, you can still look for bugs in your app. Use the Robo test to perform an automated review of your app's user interface. Robo test exercises the app by performing a static analysis of the various paths through the app's user interface, and then crawls through the app to find crashes and other potential issues.
To run a Robo test, run the following example command:
gcloud firebase test android run \ --type robo \ --app app-debug-unaligned.apk \ --device model=Nexus6,version=21,locale=en,orientation=portrait \ --device model=Nexus7,version=19,locale=fr,orientation=landscape \ --timeout 90s \ --client-details matrixLabel="Example matrix label"
- The
--type roboparameter is implicit if no--typevalue is specified. - To help you identify and locate your test matrices in the Firebase console,
you can use the optional
--client-details matrixLabel="Example matrix label"flag to label your test matrix. - You can see the complete set of command line options for
running tests by typing:
gcloud help firebase test android run.
As an alternative to specifying these arguments on the command line, you can
optionally specify your arguments in a YAML-formatted argument file. Run
gcloud topic arg-files to learn how to use this feature.
To learn how to investigate the test results from the Robo test, See Analyze your test results.
Run an instrumentation test
Now use the gcloud command line tool to run the Notepad app's
Espresso
tests on your specified Android device configurations. Use the
instrumentation test type to run the tests in app-debug-test-unaligned.apk
as follows:
gcloud firebase test android run \ --type instrumentation \ --app app-debug-unaligned.apk \ --test app-debug-test-unaligned.apk \ --device model=Nexus6,version=21,locale=en,orientation=portrait \ --device model=Nexus7,version=19,locale=fr,orientation=landscape --client-details matrixLabel="Example matrix label"
- The
--typeinstrumentation parameter is implicit if a test APK is specified with--test. - To help you identify and locate your test matrices in the Firebase console,
you can use the optional
--client-details matrixLabel="Example matrix label"flag to label your test matrix. - You can see the complete set of command line options for
running tests by typing
gcloud help firebase test android run.
As an alternative to specifying these arguments on the command line, you can
optionally specify your arguments in a YAML-formatted argument file. Run
gcloud topic arg-files to learn how to use this feature.
The gcloud CLI supports Android Test Orchestrator.
Orchestrator requires AndroidJUnitRunner v1.1 or higher. To enable it, use
gcloud firebase test android run with the --use-orchestrator
flag. To disable it use the --no-use-orchestrator flag.
You can also control how Test Lab runs your instrumentation tests
using additional flags that are not shown above. For example, you can use the
--test-targets flag to test a single class or a class method used by your test
APK. You can also find out whether your test that failed was actually flaky or
not by using --num-flaky-test-attempts flag, which specifies the number of
times a test execution should be re-attempted if one or more of its test cases
fail for any reason. To learn more, see gcloud firebase test android run.
Code coverage reports for instrumentation tests
Test Lab supports code coverage reporting tools
EMMA and
JaCoCo. If you have either tool
integrated into the build for your app, you can get a code coverage report for
Test Lab tests by running gcloud firebase test android run with some
additional arguments. If Android Test Orchestrator is not enabled, use the
following:
gcloud firebase test android run \ --type instrumentation \ --app your-app.apk \ --test your-app-test.apk \ --device model=TestDevice,version=AndroidVersion \ --environment-variables coverage=true,coverageFile="/sdcard/Download/coverage.ec" \ --directories-to-pull /sdcard/Download
If you are generating code coverage reports while also using Android Test Orchestrator, modify your environment variables as follows:
gcloud firebase test android run \ --type instrumentation \ --app your-app.apk \ --test your-app-test.apk \ --device model=TestDevice,version=AndroidVersion \ --environment-variables clearPackageData=true,coverage=true,coverageFilePath="/sdcard/Download/" \ --directories-to-pull /sdcard/Download
When Test Lab finishes running your tests, find your code coverage reports in Google Cloud Storage:
- Open the Firebase console link that the
gcloudtool printed above the test result table in your terminal. - Click a test execution from the list at that link to open that execution's details page.
- Click Test results to go to the Cloud Storage bucket with that execution's test results.
- Open
artifacts/coverage.ecto see your code coverage report.
Analyze your test results
After a few minutes, a basic summary of your test results is printed by the gcloud tool:
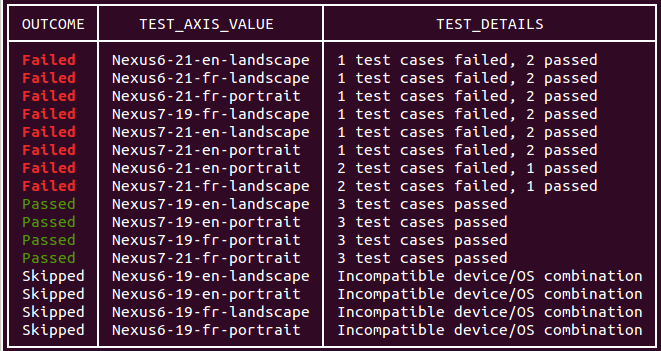
The output of your command line test run also includes a link to view test results. To learn more about how to interpret these results, see Analyzing Firebase Test Lab for Android Results.
Custom login and text input with Robo test
Robo test automatically completes sign-in screens that use a Google account
for authentication, unless you use the
--no-auto-google-login
parameter. It can also complete custom login screens using test account
credentials that you provide. You can also use this parameter to provide custom
input text for other text fields used by your app.
To complete text fields in your app, use the
--robo-directives
parameter and provide a comma-separated list of key-value pairs, where the
key is the Android resource name of the target UI element, and the value is
the text string. You can also use this flag to tell Robo to ignore specific
UI elements (e.g., "logout" button).
EditText
fields are supported but not text fields in WebView UI elements.
For example, you could use the following parameter for custom login:
--robo-directives username_resource=username,password_resource=password
Available commands and flags
The Test Lab gcloud CLI has several commands and flags available that let you run tests with different specifications:
Android Test Orchestrator flag: A flag to enable Orchestrator, a tool that allows you to run each of your app's tests in its own invocation of
Instrumentation. Test Lab always runs the latest version of Orchestrator.Game Loop test flags: A set of config flags that enable and control a "demo mode" to simulate player actions in game apps. Learn more about running Game Loop tests with Test Lab.
Uniform Sharding flag (in beta): A flag that specifies the number of shards into which you want to evenly distribute test cases. The shards are run in parallel on separate devices.
Manual Sharding flag (in beta): A flag that specifies a group of packages, classes, and/or test cases to run in a shard (a group of test cases). The shards are run in parallel on separate devices.
Network traffic profiles flag (in beta): A flag that specifies which network profile your tests use with physical devices. Network profiles emulate a variety of networks conditions, allowing you to test your app's performance on unreliable or unpredictable networks.
Scripting gcloud commands with Test Lab
You can use shell scripts or batch files to automate mobile app testing commands that you would otherwise run using the gcloud command line. The following example bash script runs an instrumentation test with a two-minute timeout, and reports if the test run completed successfully:
if gcloud firebase test android run --app my-app.apk --test my-test.apk --timeout 2m
then
echo "Test matrix successfully finished"
else
echo "Test matrix exited abnormally with non-zero exit code: " $?
fi
Script exit codes
Test Lab provides several exit codes that you can use to better understand the results of tests that you run using scripts or batch files.
Scripting exit codes for Test Lab
| Exit code | Notes |
|---|---|
| 0 | All test executions passed. |
| 1 | A general failure occurred. Possible causes include: a filename that does not exist or an HTTP/network error. |
| 2 | Testing exited because unknown commands or arguments were provided. |
| 10 | One or more test cases (tested classes or class methods) within a test execution did not pass. |
| 15 | Firebase Test Lab could not determine if the test matrix passed or failed, because of an unexpected error. |
| 18 | The test environment for this test execution is not supported because of incompatible test dimensions. This error might occur if the selected Android API level is not supported by the selected device type. |
| 19 | The test matrix was canceled by the user. |
| 20 | A test infrastructure error occurred. |
