แอปจำนวนมากมีเอกสารที่จัดทำดัชนีตามสถานที่ตั้งจริง เช่น แอปของคุณอาจอนุญาตให้ผู้ใช้เรียกดูร้านค้าใกล้กับตำแหน่งปัจจุบัน
โซลูชัน: Geohash
Geohash เป็นระบบสำหรับการเข้ารหัส(latitude, longitude)คู่เป็นสตริง Base32 เดียว ในระบบ Geohash โลกจะแบ่งออกเป็นตารางสี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้า
อักขระแต่ละตัวของสตริง Geohash จะระบุส่วนย่อย 1 ใน 32 ส่วนของแฮชคำนำหน้า เช่น Geohash abcd เป็นหนึ่งในแฮช 32 รายการที่มี 4 อักขระ
ซึ่งอยู่ภายใน Geohash abc ที่ใหญ่กว่า
ยิ่งคำนำหน้าร่วมกันระหว่างแฮช 2 รายการยาวเท่าใด แฮชทั้ง 2 รายการก็จะยิ่งใกล้กันมากขึ้น
เช่น abcdef อยู่ใกล้กับ abcdeg มากกว่า abcdff แต่
ในทางกลับกันไม่เป็นความจริง 2 พื้นที่อาจอยู่ใกล้กันมาก แต่มี Geohash ที่แตกต่างกันมากในกรณีต่อไปนี้
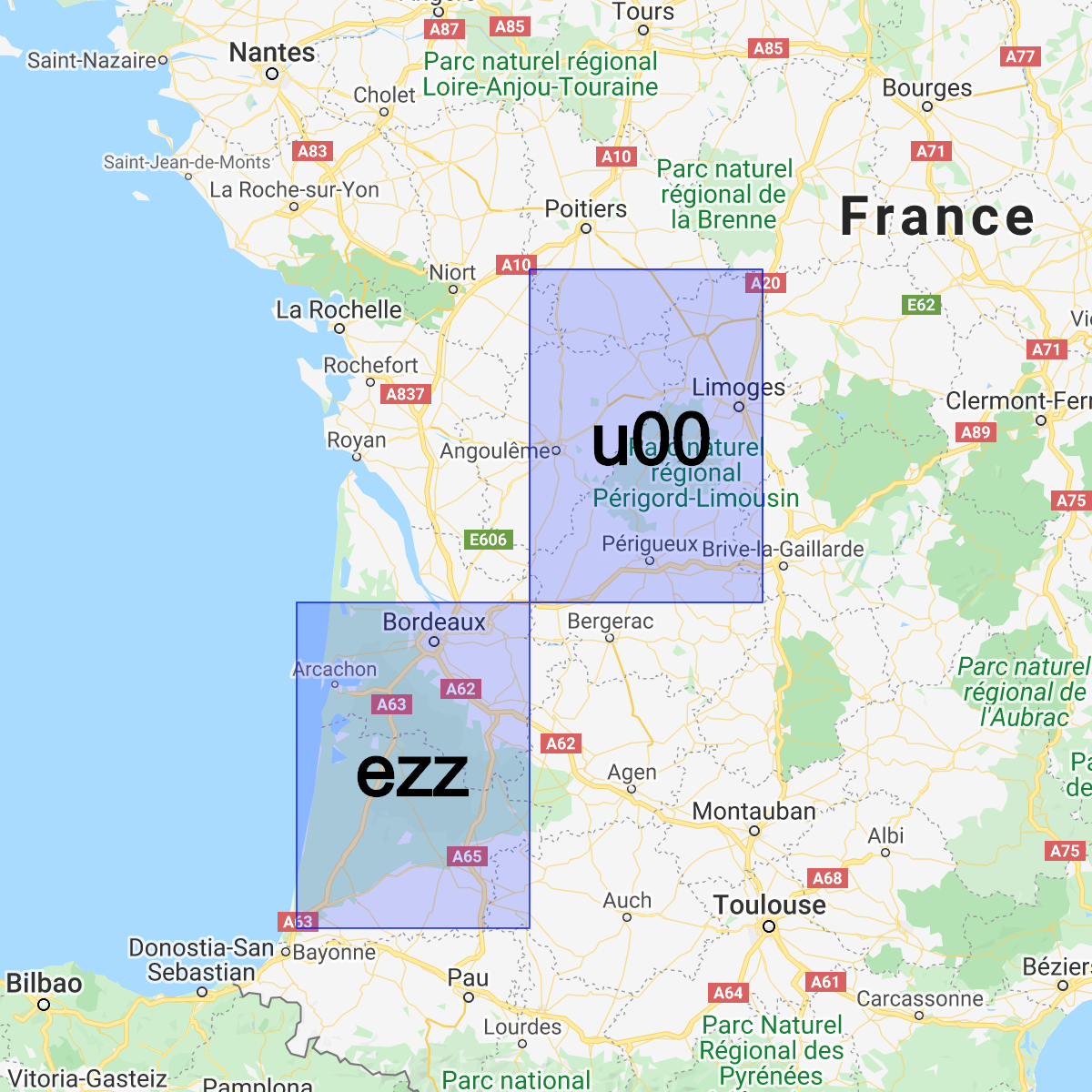
เราใช้ Geohash เพื่อจัดเก็บและค้นหาเอกสารตามตำแหน่งใน Cloud Firestore ได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพพอสมควรโดยต้องใช้ฟิลด์ที่จัดทำดัชนีเพียงฟิลด์เดียว
ติดตั้งไลบรารีผู้ช่วย
การสร้างและการแยกวิเคราะห์ Geohash ต้องใช้คณิตศาสตร์ที่ซับซ้อน เราจึงสร้างไลบรารีตัวช่วย เพื่อแยกส่วนที่ยากที่สุดใน Android, Apple และเว็บ
Web
// Install from NPM. If you prefer to use a static .js file visit
// https://github.com/firebase/geofire-js/releases and download
// geofire-common.min.js from the latest version
npm install --save geofire-common
Web
// Install from NPM. If you prefer to use a static .js file visit
// https://github.com/firebase/geofire-js/releases and download
// geofire-common.min.js from the latest version
npm install --save geofire-common
Swift
Kotlin
// Add this to your app/build.gradle
implementation 'com.firebase:geofire-android-common:3.2.0'
Java
// Add this to your app/build.gradle
implementation 'com.firebase:geofire-android-common:3.1.0'
Geohash ของร้านค้า
สำหรับเอกสารแต่ละรายการที่คุณต้องการจัดทำดัชนีตามสถานที่ตั้ง คุณจะต้องจัดเก็บ ฟิลด์ Geohash ดังนี้
Web
import { doc, updateDoc } from 'firebase/firestore'; // Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point const lat = 51.5074; const lng = 0.1278; const hash = geofire.geohashForLocation([lat, lng]); // Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash // for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons. const londonRef = doc(db, 'cities', 'LON'); await updateDoc(londonRef, { geohash: hash, lat: lat, lng: lng });
Web
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point const lat = 51.5074; const lng = 0.1278; const hash = geofire.geohashForLocation([lat, lng]); // Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash // for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons. const londonRef = db.collection('cities').doc('LON'); londonRef.update({ geohash: hash, lat: lat, lng: lng }).then(() => { // ... });
Swift
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point let latitude = 51.5074 let longitude = 0.12780 let location = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: latitude, longitude: longitude) let hash = GFUtils.geoHash(forLocation: location) // Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash // for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons. let documentData: [String: Any] = [ "geohash": hash, "lat": latitude, "lng": longitude ] let londonRef = db.collection("cities").document("LON") londonRef.updateData(documentData) { error in // ... }
Kotlin
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point val lat = 51.5074 val lng = 0.1278 val hash = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashForLocation(GeoLocation(lat, lng)) // Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash // for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons. val updates: MutableMap<String, Any> = mutableMapOf( "geohash" to hash, "lat" to lat, "lng" to lng, ) val londonRef = db.collection("cities").document("LON") londonRef.update(updates) .addOnCompleteListener { // ... }
Java
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point double lat = 51.5074; double lng = 0.1278; String hash = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashForLocation(new GeoLocation(lat, lng)); // Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash // for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons. Map<String, Object> updates = new HashMap<>(); updates.put("geohash", hash); updates.put("lat", lat); updates.put("lng", lng); DocumentReference londonRef = db.collection("cities").document("LON"); londonRef.update(updates) .addOnCompleteListener(new OnCompleteListener<Void>() { @Override public void onComplete(@NonNull Task<Void> task) { // ... } });
ค้นหา Geohash
Geohash ช่วยให้เราประมาณการค้นหาพื้นที่ได้โดยการรวมชุดการค้นหา ในฟิลด์ Geohash แล้วกรองผลลบลวงบางรายการออก
Web
import { collection, query, orderBy, startAt, endAt, getDocs } from 'firebase/firestore'; // Find cities within 50km of London const center = [51.5074, 0.1278]; const radiusInM = 50 * 1000; // Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue // a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds // depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4. // @ts-ignore const bounds = geofire.geohashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM); const promises = []; for (const b of bounds) { const q = query( collection(db, 'cities'), orderBy('geohash'), startAt(b[0]), endAt(b[1])); promises.push(getDocs(q)); } // Collect all the query results together into a single list const snapshots = await Promise.all(promises); const matchingDocs = []; for (const snap of snapshots) { for (const doc of snap.docs) { const lat = doc.get('lat'); const lng = doc.get('lng'); // We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash // accuracy, but most will match // @ts-ignore const distanceInKm = geofire.distanceBetween([lat, lng], center); const distanceInM = distanceInKm * 1000; if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) { matchingDocs.push(doc); } } }
Web
// Find cities within 50km of London const center = [51.5074, 0.1278]; const radiusInM = 50 * 1000; // Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue // a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds // depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4. const bounds = geofire.geohashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM); const promises = []; for (const b of bounds) { const q = db.collection('cities') .orderBy('geohash') .startAt(b[0]) .endAt(b[1]); promises.push(q.get()); } // Collect all the query results together into a single list Promise.all(promises).then((snapshots) => { const matchingDocs = []; for (const snap of snapshots) { for (const doc of snap.docs) { const lat = doc.get('lat'); const lng = doc.get('lng'); // We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash // accuracy, but most will match const distanceInKm = geofire.distanceBetween([lat, lng], center); const distanceInM = distanceInKm * 1000; if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) { matchingDocs.push(doc); } } } return matchingDocs; }).then((matchingDocs) => { // Process the matching documents // ... });
Swift
// Find cities within 50km of London let center = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 51.5074, longitude: 0.1278) let radiusInM: Double = 50 * 1000 // Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue // a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds // depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4. let queryBounds = GFUtils.queryBounds(forLocation: center, withRadius: radiusInM) let queries = queryBounds.map { bound -> Query in return db.collection("cities") .order(by: "geohash") .start(at: [bound.startValue]) .end(at: [bound.endValue]) } @Sendable func fetchMatchingDocs(from query: Query, center: CLLocationCoordinate2D, radiusInMeters: Double) async throws -> [QueryDocumentSnapshot] { let snapshot = try await query.getDocuments() // Collect all the query results together into a single list return snapshot.documents.filter { document in let lat = document.data()["lat"] as? Double ?? 0 let lng = document.data()["lng"] as? Double ?? 0 let coordinates = CLLocation(latitude: lat, longitude: lng) let centerPoint = CLLocation(latitude: center.latitude, longitude: center.longitude) // We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash accuracy, but // most will match let distance = GFUtils.distance(from: centerPoint, to: coordinates) return distance <= radiusInM } } // After all callbacks have executed, matchingDocs contains the result. Note that this code // executes all queries serially, which may not be optimal for performance. do { let matchingDocs = try await withThrowingTaskGroup(of: [QueryDocumentSnapshot].self) { group -> [QueryDocumentSnapshot] in for query in queries { group.addTask { try await fetchMatchingDocs(from: query, center: center, radiusInMeters: radiusInM) } } var matchingDocs = [QueryDocumentSnapshot]() for try await documents in group { matchingDocs.append(contentsOf: documents) } return matchingDocs } print("Docs matching geoquery: \(matchingDocs)") } catch { print("Unable to fetch snapshot data. \(error)") }
Kotlin
// Find cities within 50km of London val center = GeoLocation(51.5074, 0.1278) val radiusInM = 50.0 * 1000.0 // Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue // a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds // depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4. val bounds = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM) val tasks: MutableList<Task<QuerySnapshot>> = ArrayList() for (b in bounds) { val q = db.collection("cities") .orderBy("geohash") .startAt(b.startHash) .endAt(b.endHash) tasks.add(q.get()) } // Collect all the query results together into a single list Tasks.whenAllComplete(tasks) .addOnCompleteListener { val matchingDocs: MutableList<DocumentSnapshot> = ArrayList() for (task in tasks) { val snap = task.result for (doc in snap!!.documents) { val lat = doc.getDouble("lat")!! val lng = doc.getDouble("lng")!! // We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash // accuracy, but most will match val docLocation = GeoLocation(lat, lng) val distanceInM = GeoFireUtils.getDistanceBetween(docLocation, center) if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) { matchingDocs.add(doc) } } } // matchingDocs contains the results // ... }
Java
// Find cities within 50km of London final GeoLocation center = new GeoLocation(51.5074, 0.1278); final double radiusInM = 50 * 1000; // Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue // a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds // depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4. List<GeoQueryBounds> bounds = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM); final List<Task<QuerySnapshot>> tasks = new ArrayList<>(); for (GeoQueryBounds b : bounds) { Query q = db.collection("cities") .orderBy("geohash") .startAt(b.startHash) .endAt(b.endHash); tasks.add(q.get()); } // Collect all the query results together into a single list Tasks.whenAllComplete(tasks) .addOnCompleteListener(new OnCompleteListener<List<Task<?>>>() { @Override public void onComplete(@NonNull Task<List<Task<?>>> t) { List<DocumentSnapshot> matchingDocs = new ArrayList<>(); for (Task<QuerySnapshot> task : tasks) { QuerySnapshot snap = task.getResult(); for (DocumentSnapshot doc : snap.getDocuments()) { double lat = doc.getDouble("lat"); double lng = doc.getDouble("lng"); // We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash // accuracy, but most will match GeoLocation docLocation = new GeoLocation(lat, lng); double distanceInM = GeoFireUtils.getDistanceBetween(docLocation, center); if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) { matchingDocs.add(doc); } } } // matchingDocs contains the results // ... } });
ข้อจำกัด
การใช้ Geohash สำหรับการค้นหาสถานที่ทำให้เรามีความสามารถใหม่ๆ แต่ก็มีข้อจำกัดของตัวเองเช่นกัน ดังนี้
- ผลบวกลวง - การค้นหาด้วย Geohash ไม่ใช่การค้นหาที่แน่นอน และคุณต้องกรองผลบวกลวงในฝั่งไคลเอ็นต์ การอ่านเพิ่มเติมเหล่านี้ จะเพิ่มต้นทุนและเวลาในการตอบสนองให้กับแอป
- กรณีสุดโต่ง - วิธีการค้นหานี้อาศัยการประมาณระยะทางระหว่างเส้นลองจิจูด/ละติจูด ความแม่นยำของการประมาณนี้จะลดลงเมื่อ จุดอยู่ใกล้ขั้วโลกเหนือหรือใต้ ซึ่งหมายความว่าการค้นหา Geohash จะมีผลบวกลวงมากขึ้นที่ละติจูดสุดขั้ว
