Wiele aplikacji zawiera dokumenty indeksowane według lokalizacji fizycznych. Na przykład aplikacja może umożliwiać użytkownikom przeglądanie sklepów w pobliżu ich bieżącej lokalizacji.
Rozwiązanie: geohashe
Geohash to system kodowania (latitude, longitude) w jeden ciąg znaków Base32. W systemie geohash świat jest podzielony na prostokątną siatkę.
Każdy znak ciągu Geohash określa jeden z 32 podziałów prefiksu haszującego. Na przykład kod Geohash abcd jest jednym z 32 czteroznakowych kodów w pełni zawartych w większym kodzie Geohash abc.
Im dłuższy jest wspólny przedrostek dwóch skrótów, tym bliżej siebie są. Na przykład abcdef jest bliżej abcdeg niż abcdff. Jednak
odwrotna sytuacja nie jest prawdziwa. Dwa obszary mogą być bardzo blisko siebie, ale mieć zupełnie inne geohashe:
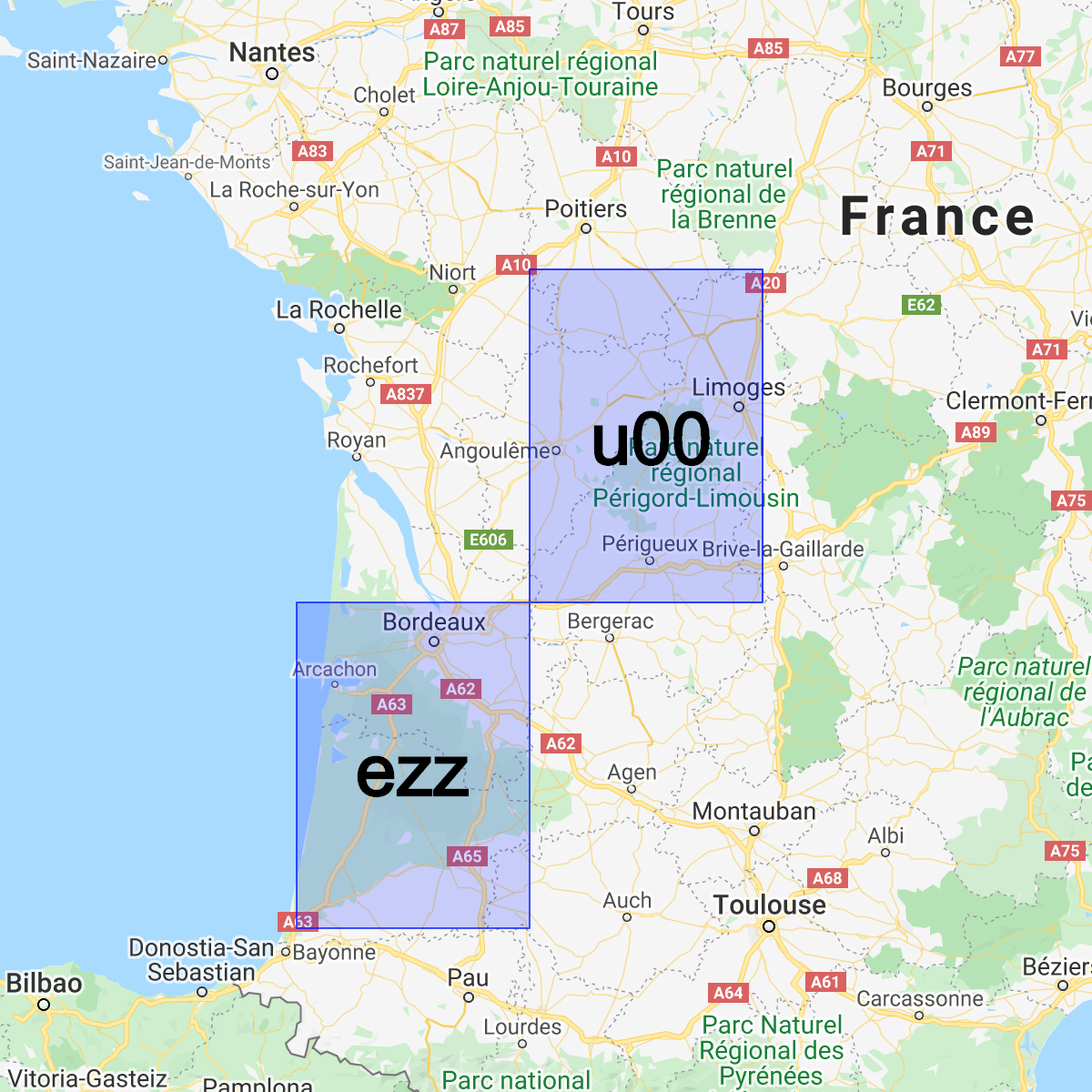
Możemy używać geohashów do przechowywania dokumentów i wykonywania zapytań dotyczących ich pozycji w Cloud Firestore z rozsądną wydajnością, wymagając tylko jednego indeksowanego pola.
Instalowanie biblioteki pomocniczej
Tworzenie i parsowanie geohashów wymaga skomplikowanych obliczeń, dlatego przygotowaliśmy biblioteki pomocnicze, które upraszczają najtrudniejsze części na Androidzie, Apple i w internecie:
Web
// Install from NPM. If you prefer to use a static .js file visit
// https://github.com/firebase/geofire-js/releases and download
// geofire-common.min.js from the latest version
npm install --save geofire-common
Web
// Install from NPM. If you prefer to use a static .js file visit
// https://github.com/firebase/geofire-js/releases and download
// geofire-common.min.js from the latest version
npm install --save geofire-common
Swift
Kotlin
// Add this to your app/build.gradle
implementation 'com.firebase:geofire-android-common:3.2.0'
Java
// Add this to your app/build.gradle
implementation 'com.firebase:geofire-android-common:3.1.0'
Geohashe sklepów
W przypadku każdego dokumentu, który chcesz indeksować według lokalizacji, musisz przechowywać pole Geohash:
Web
import { doc, updateDoc } from 'firebase/firestore'; // Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point const lat = 51.5074; const lng = 0.1278; const hash = geofire.geohashForLocation([lat, lng]); // Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash // for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons. const londonRef = doc(db, 'cities', 'LON'); await updateDoc(londonRef, { geohash: hash, lat: lat, lng: lng });
Web
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point const lat = 51.5074; const lng = 0.1278; const hash = geofire.geohashForLocation([lat, lng]); // Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash // for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons. const londonRef = db.collection('cities').doc('LON'); londonRef.update({ geohash: hash, lat: lat, lng: lng }).then(() => { // ... });
Swift
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point let latitude = 51.5074 let longitude = 0.12780 let location = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: latitude, longitude: longitude) let hash = GFUtils.geoHash(forLocation: location) // Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash // for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons. let documentData: [String: Any] = [ "geohash": hash, "lat": latitude, "lng": longitude ] let londonRef = db.collection("cities").document("LON") londonRef.updateData(documentData) { error in // ... }
Kotlin
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point val lat = 51.5074 val lng = 0.1278 val hash = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashForLocation(GeoLocation(lat, lng)) // Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash // for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons. val updates: MutableMap<String, Any> = mutableMapOf( "geohash" to hash, "lat" to lat, "lng" to lng, ) val londonRef = db.collection("cities").document("LON") londonRef.update(updates) .addOnCompleteListener { // ... }
Java
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point double lat = 51.5074; double lng = 0.1278; String hash = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashForLocation(new GeoLocation(lat, lng)); // Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash // for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons. Map<String, Object> updates = new HashMap<>(); updates.put("geohash", hash); updates.put("lat", lat); updates.put("lng", lng); DocumentReference londonRef = db.collection("cities").document("LON"); londonRef.update(updates) .addOnCompleteListener(new OnCompleteListener<Void>() { @Override public void onComplete(@NonNull Task<Void> task) { // ... } });
Geohasze zapytań
Geohashe umożliwiają przybliżone zapytania o obszar przez połączenie zestawu zapytań w polu Geohash, a następnie odfiltrowanie niektórych fałszywych wyników:
Web
import { collection, query, orderBy, startAt, endAt, getDocs } from 'firebase/firestore'; // Find cities within 50km of London const center = [51.5074, 0.1278]; const radiusInM = 50 * 1000; // Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue // a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds // depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4. // @ts-ignore const bounds = geofire.geohashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM); const promises = []; for (const b of bounds) { const q = query( collection(db, 'cities'), orderBy('geohash'), startAt(b[0]), endAt(b[1])); promises.push(getDocs(q)); } // Collect all the query results together into a single list const snapshots = await Promise.all(promises); const matchingDocs = []; for (const snap of snapshots) { for (const doc of snap.docs) { const lat = doc.get('lat'); const lng = doc.get('lng'); // We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash // accuracy, but most will match // @ts-ignore const distanceInKm = geofire.distanceBetween([lat, lng], center); const distanceInM = distanceInKm * 1000; if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) { matchingDocs.push(doc); } } }
Web
// Find cities within 50km of London const center = [51.5074, 0.1278]; const radiusInM = 50 * 1000; // Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue // a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds // depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4. const bounds = geofire.geohashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM); const promises = []; for (const b of bounds) { const q = db.collection('cities') .orderBy('geohash') .startAt(b[0]) .endAt(b[1]); promises.push(q.get()); } // Collect all the query results together into a single list Promise.all(promises).then((snapshots) => { const matchingDocs = []; for (const snap of snapshots) { for (const doc of snap.docs) { const lat = doc.get('lat'); const lng = doc.get('lng'); // We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash // accuracy, but most will match const distanceInKm = geofire.distanceBetween([lat, lng], center); const distanceInM = distanceInKm * 1000; if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) { matchingDocs.push(doc); } } } return matchingDocs; }).then((matchingDocs) => { // Process the matching documents // ... });
Swift
// Find cities within 50km of London let center = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 51.5074, longitude: 0.1278) let radiusInM: Double = 50 * 1000 // Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue // a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds // depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4. let queryBounds = GFUtils.queryBounds(forLocation: center, withRadius: radiusInM) let queries = queryBounds.map { bound -> Query in return db.collection("cities") .order(by: "geohash") .start(at: [bound.startValue]) .end(at: [bound.endValue]) } @Sendable func fetchMatchingDocs(from query: Query, center: CLLocationCoordinate2D, radiusInMeters: Double) async throws -> [QueryDocumentSnapshot] { let snapshot = try await query.getDocuments() // Collect all the query results together into a single list return snapshot.documents.filter { document in let lat = document.data()["lat"] as? Double ?? 0 let lng = document.data()["lng"] as? Double ?? 0 let coordinates = CLLocation(latitude: lat, longitude: lng) let centerPoint = CLLocation(latitude: center.latitude, longitude: center.longitude) // We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash accuracy, but // most will match let distance = GFUtils.distance(from: centerPoint, to: coordinates) return distance <= radiusInM } } // After all callbacks have executed, matchingDocs contains the result. Note that this code // executes all queries serially, which may not be optimal for performance. do { let matchingDocs = try await withThrowingTaskGroup(of: [QueryDocumentSnapshot].self) { group -> [QueryDocumentSnapshot] in for query in queries { group.addTask { try await fetchMatchingDocs(from: query, center: center, radiusInMeters: radiusInM) } } var matchingDocs = [QueryDocumentSnapshot]() for try await documents in group { matchingDocs.append(contentsOf: documents) } return matchingDocs } print("Docs matching geoquery: \(matchingDocs)") } catch { print("Unable to fetch snapshot data. \(error)") }
Kotlin
// Find cities within 50km of London val center = GeoLocation(51.5074, 0.1278) val radiusInM = 50.0 * 1000.0 // Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue // a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds // depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4. val bounds = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM) val tasks: MutableList<Task<QuerySnapshot>> = ArrayList() for (b in bounds) { val q = db.collection("cities") .orderBy("geohash") .startAt(b.startHash) .endAt(b.endHash) tasks.add(q.get()) } // Collect all the query results together into a single list Tasks.whenAllComplete(tasks) .addOnCompleteListener { val matchingDocs: MutableList<DocumentSnapshot> = ArrayList() for (task in tasks) { val snap = task.result for (doc in snap!!.documents) { val lat = doc.getDouble("lat")!! val lng = doc.getDouble("lng")!! // We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash // accuracy, but most will match val docLocation = GeoLocation(lat, lng) val distanceInM = GeoFireUtils.getDistanceBetween(docLocation, center) if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) { matchingDocs.add(doc) } } } // matchingDocs contains the results // ... }
Java
// Find cities within 50km of London final GeoLocation center = new GeoLocation(51.5074, 0.1278); final double radiusInM = 50 * 1000; // Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue // a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds // depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4. List<GeoQueryBounds> bounds = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM); final List<Task<QuerySnapshot>> tasks = new ArrayList<>(); for (GeoQueryBounds b : bounds) { Query q = db.collection("cities") .orderBy("geohash") .startAt(b.startHash) .endAt(b.endHash); tasks.add(q.get()); } // Collect all the query results together into a single list Tasks.whenAllComplete(tasks) .addOnCompleteListener(new OnCompleteListener<List<Task<?>>>() { @Override public void onComplete(@NonNull Task<List<Task<?>>> t) { List<DocumentSnapshot> matchingDocs = new ArrayList<>(); for (Task<QuerySnapshot> task : tasks) { QuerySnapshot snap = task.getResult(); for (DocumentSnapshot doc : snap.getDocuments()) { double lat = doc.getDouble("lat"); double lng = doc.getDouble("lng"); // We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash // accuracy, but most will match GeoLocation docLocation = new GeoLocation(lat, lng); double distanceInM = GeoFireUtils.getDistanceBetween(docLocation, center); if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) { matchingDocs.add(doc); } } } // matchingDocs contains the results // ... } });
Ograniczenia
Używanie geohashów do wysyłania zapytań o lokalizacje daje nam nowe możliwości, ale ma też pewne ograniczenia:
- Wyniki fałszywie pozytywne – wysyłanie zapytań według geohasha nie jest dokładne, dlatego musisz odfiltrować wyniki fałszywie pozytywne po stronie klienta. Te dodatkowe odczyty zwiększają koszt i opóźnienie w aplikacji.
- Przypadki brzegowe – ta metoda zapytań opiera się na szacowaniu odległości między liniami długości i szerokości geograficznej. Dokładność tego szacunku maleje, gdy punkty zbliżają się do bieguna północnego lub południowego, co oznacza, że zapytania Geohash mają więcej wyników fałszywie pozytywnych na ekstremalnych szerokościach geograficznych.
