The Google Cloud plugin exports Firebase Genkit telemetry and logging data to the Cloud Observability suite, which powers the Firebase AI Monitoring dashboard.
Installation
npm i --save @genkit-ai/google-cloudWhen running Genkit code locally that includes this plugin, you will also need the Google Cloud CLI tool installed.
Set up a Google Cloud account
This plugin requires a Google Cloud account/project. All Firebase projects include one by default (GCP Console), or you can sign up at https://cloud.google.com.
Prior to adding the plugin, make sure that the following APIs are enabled for your GCP project:
These APIs should be listed in the API dashboard for your project.
Click here to learn more about enabling and disabling APIs.
Genkit configuration
To enable Cloud Tracing, Logging, and Monitoring (metrics), simply call
enableGoogleCloudTelemetry():
import { enableGoogleCloudTelemetry } from '@genkit-ai/google-cloud';
enableGoogleCloudTelemetry();
When running in production, telemetry will be exported automatically.
Authentication and authorization
The plugin requires a Google Cloud project ID and application credentials.
Google Cloud
If deploying your code to a Google Cloud environment (Cloud Functions, Cloud Run, etc), the project ID and credentials will be discovered automatically via Application Default Credentials.
You will need to apply the following roles to the service account that is running your code (i.e. 'attached service account') via the IAM Console:
roles/monitoring.metricWriterroles/cloudtrace.agentroles/logging.logWriter
Local Development
When doing local development, in order for your user credentials to be available to the plugin, additional steps are required.
Set the
GCLOUD_PROJECTenvironment variable to your Google Cloud project.Authenticate using the
gcloudCLI:gcloud auth application-default login
Production environments outside of Google Cloud
If possible, it is still recommended to leverage the Application Default Credentials process to make credentials available to the plugin.
Typically this involves generating a service account key/pair and deploying those credentials to your production environment.
Follow the instructions to set up a service account key.
Ensure the service account has the following roles:
roles/monitoring.metricWriterroles/cloudtrace.agentroles/logging.logWriter
Deploy the credential file to production (do not check into source code)
Set the
GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALSenvironment variable as the path to the credential file.GOOGLE_APPLICATION_CREDENTIALS = "path/to/your/key/file"
In some serverless environments, you may not be able to deploy a credential
file. In this case, as an alternative to steps 3 & 4 above, you can set the
GCLOUD_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_CREDS environment variable with the contents of the
credential file as follows:
GCLOUD_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_CREDS='{
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "your-project-id",
"private_key_id": "your-private-key-id",
"private_key": "your-private-key",
"client_email": "your-client-email",
"client_id": "your-client-id",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "your-cert-url"
}'
Plugin configuration
The enableGoogleCloudTelemetry() function takes an optional configuration
object which configures the
OpenTelemetry NodeSDK
instance.
import { AlwaysOnSampler } from '@opentelemetry/sdk-trace-base';
enableGoogleCloudTelemetry({
forceDevExport: false, // Set this to true to export telemetry for local runs
sampler: new AlwaysOnSampler(),
autoInstrumentation: true,
autoInstrumentationConfig: {
'@opentelemetry/instrumentation-fs': { enabled: false },
'@opentelemetry/instrumentation-dns': { enabled: false },
'@opentelemetry/instrumentation-net': { enabled: false },
},
metricExportIntervalMillis: 5_000,
});
The configuration objects allows fine grained control over various aspects of the telemetry export outlined below.
credentials
Allows specifying credentials directly using JWTInput from the google-auth library.
sampler
For cases where exporting all traces isn't practical, OpenTelemetry allows trace sampling.
There are four preconfigured samplers:
- AlwaysOnSampler - samples all traces
- AlwaysOffSampler - samples no traces
- ParentBased - samples based on parent span
- TraceIdRatioBased - samples a configurable percentage of traces
autoInstrumentation & autoInstrumentationConfig
Enabling automatic instrumentation allows OpenTelemetry to capture telemetry data from third-party libraries without the need to modify code.
metricExportIntervalMillis
This field specifies the metrics export interval in milliseconds.
metricExportTimeoutMillis
This field specifies the timeout for the metrics export in milliseconds.
disableMetrics
Provides an override that disables metrics export while still exporting traces and logs.
disableTraces
Provides an override that disables exporting traces while still exprting metrics and logs.
disableLoggingIO
Provides an override that disables collecting input and output logs.
forceDevExport
This option will force Genkit to export telemetry and log data when running in
the dev environment (e.g. locally).
Test your integration
When configuring the plugin, use forceDevExport: true to enable telemetry
export for local runs. Navigate to the Google Cloud Logs, Metrics, or Trace
Explorer to view telemetry.
Google Cloud Observability suite
Once your code (e.g. flow) is deployed, navigate to the Cloud Monitoring dashboard and select your project. From here, you can easily navigate between the Logs, Metrics and Trace explorers for production monitoring.
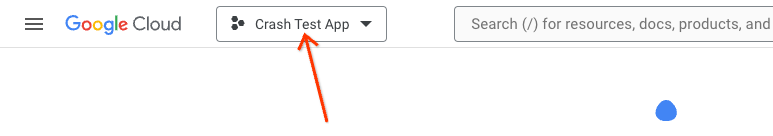
Logs and traces
From the left hand side menu, click 'Logs explorer' under the 'Explore' heading.
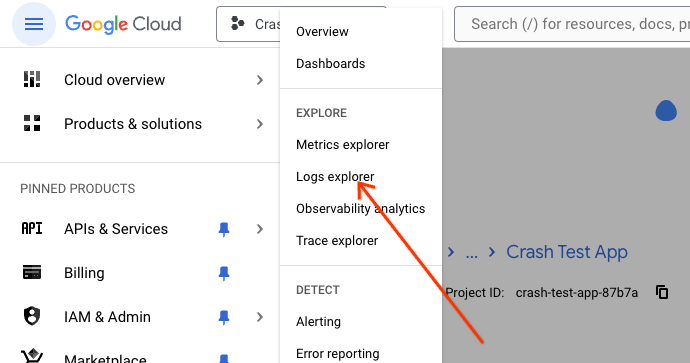
Here, you will see all logs that are associated with your deployed Genkit code,
including console.log(). Any log which has the prefix [genkit] is a
Genkit-internal log that contains information that may be interesting for
debugging purposes. For example, Genkit logs in the format Config[...] contain
metadata such as the temperature and topK values for specific LLM inferences.
Logs in the format Output[...] contain LLM responses while Input[...] logs
contain the prompts. Cloud Logging has robust ACLs that allow fine grained
control over access to sensitive logs.
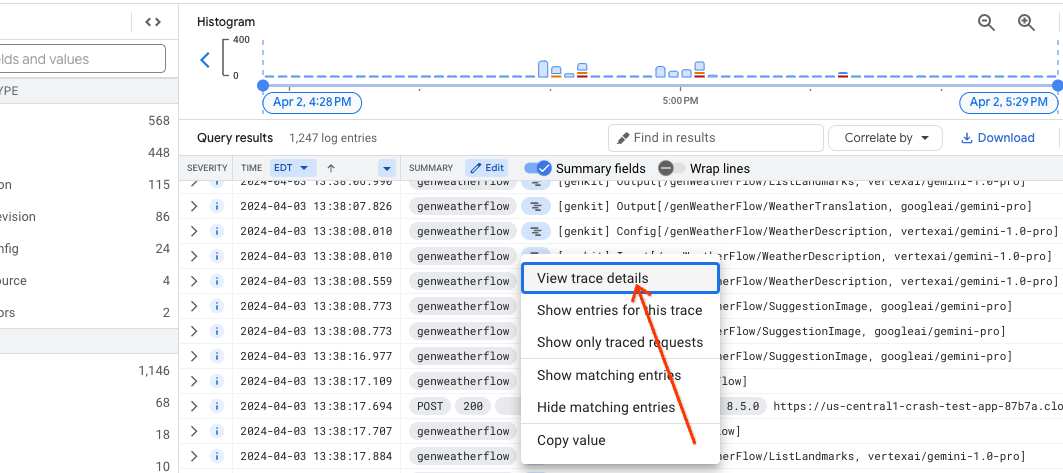
This will bring up a trace preview pane providing a quick glance of the details of the trace. To get to the full details, click the "View in Trace" link at the top right of the pane.
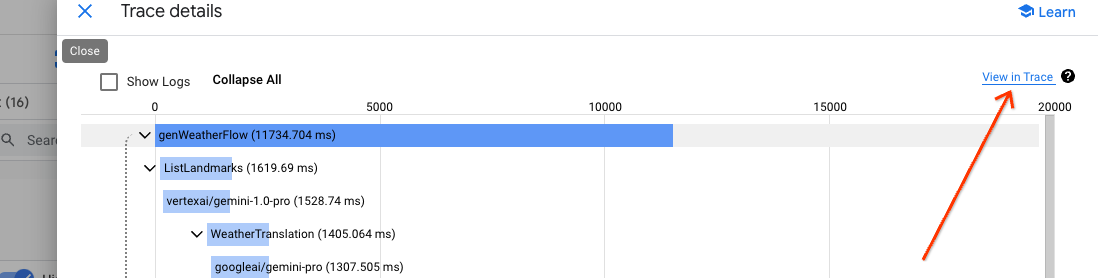
The most prominent navigation element in Cloud Trace is the trace scatter plot. It contains all collected traces in a given time span.
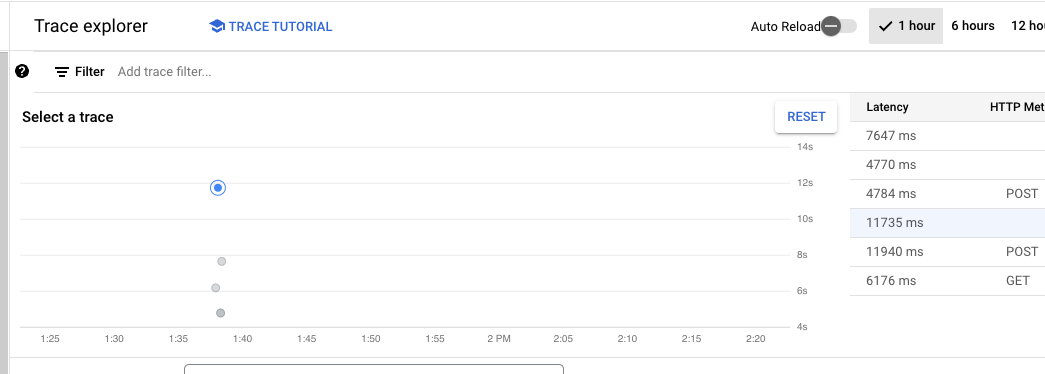
Clicking on each data point will show its details below the scatter plot.
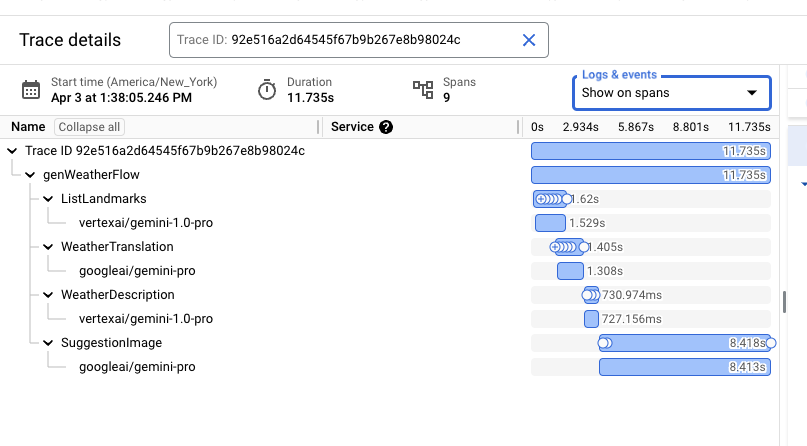
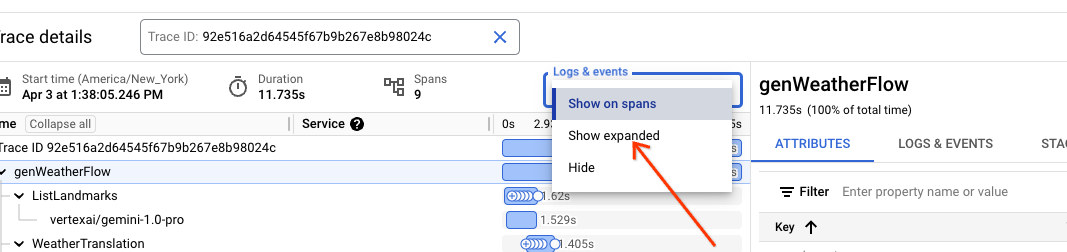
The detailed view contains the flow shape, including all steps, and important timing information. Cloud Trace has the ability to interleave all logs associated with a given trace within this view. Select the "Show expanded" option in the "Logs & events" drop down.
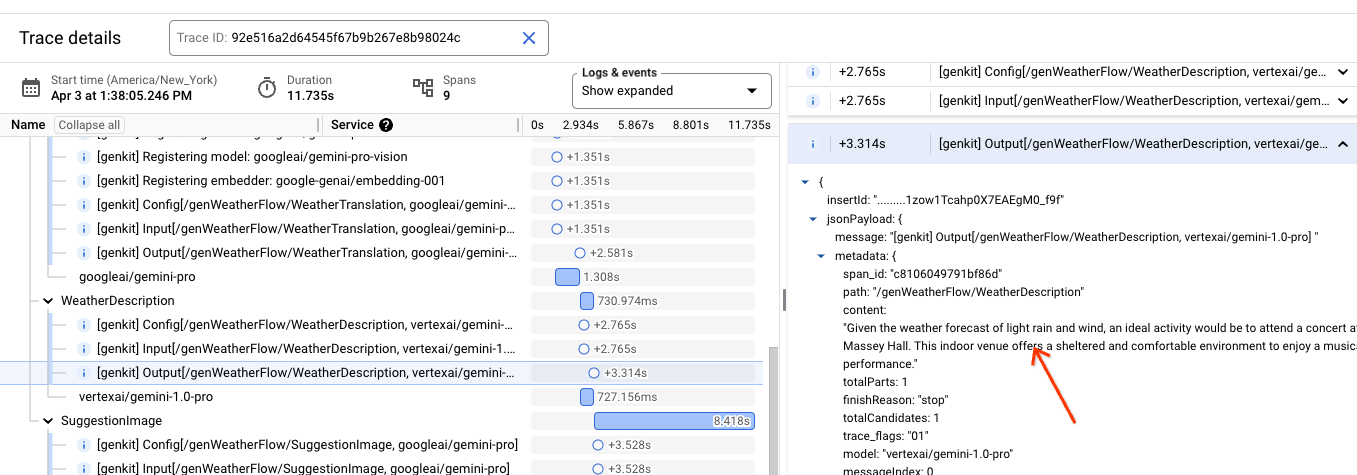
The resultant view allows detailed examination of logs in the context of the trace, including prompts and LLM responses.
Metrics
Viewing all metrics exported by Genkit can be done by clicking on 'Metrics management' under the 'Configure' heading in the left hand side menu.
The metrics management console contains a tabular view of all collected metrics,
including those that pertain to Cloud Run and its surrounding environment.
Clicking on the 'Workload' option will reveal a list that includes
Genkit-collected metrics. Any metric with the genkit prefix constitutes an
internal Genkit metric.
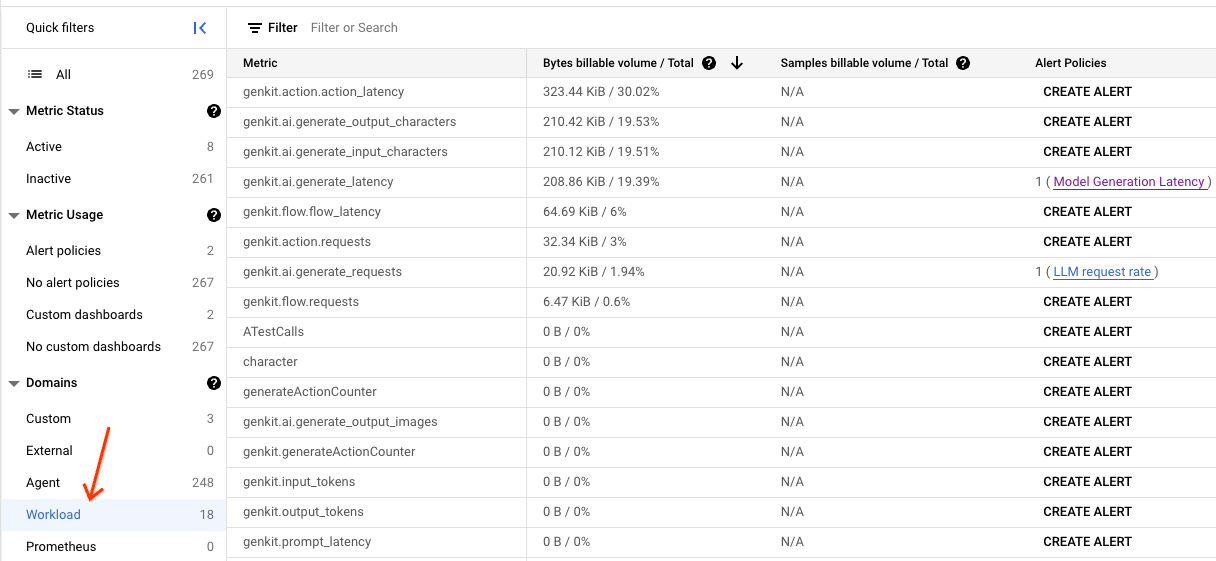
Genkit collects several categories of metrics including: feature, action, and generate. Each metric has several useful dimensions facilitating robust filtering and grouping.
Common dimensions include:
flow_name- the top-level name of the flow.flow_path- the span and its parent span chain up to the root span.error_code- in case of an error, the corresponding error code.error_message- in case of an error, the corresponding error message.model- the name of the model.
Feature metrics
Features are the top-level entry-point to your Genkit code. In most cases, this will be a flow. Otherwise, this will be the top-most span in a trace.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| genkit/feature/requests | Counter | Number of requests |
| genkit/feature/latency | Histogram | Execution latency in ms |
Each feature metric contains the following dimensions:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| name | The name of the feature. In most cases, this is the top-level Genkit flow |
| status | 'success' or 'failure' depending on whether or not the feature request succeeded |
| error | Only set when status=failure. Contains the error type that caused the failure |
| source | The Genkit source language. Eg. 'ts' |
| sourceVersion | The Genkit framework version |
Action metrics
Actions represent a generic step of execution within Genkit. Each of these steps will have the following metrics tracked:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| genkit/action/requests | Counter | Number of times this action has been executed |
| genkit/action/latency | Histogram | Execution latency in ms |
Each action metric contains the following dimensions:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| name | The name of the action |
| featureName | The name of the parent feature being executed |
| path | The path of execution from the feature root to this action. eg. '/myFeature/parentAction/thisAction' |
| status | 'success' or 'failure' depending on whether or not the action succeeded |
| error | Only set when status=failure. Contains the error type that caused the failure |
| source | The Genkit source language. Eg. 'ts' |
| sourceVersion | The Genkit framework version |
Generate metrics
These are special action metrics relating to actions that interact with a model. In addition to requests and latency, input and output are also tracked, with model specific dimensions that make debugging and configuration tuning easier.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| genkit/ai/generate/requests | Counter | Number of times this model has been called |
| genkit/ai/generate/latency | Histogram | Execution latency in ms |
| genkit/ai/generate/input/tokens | Counter | Input tokens |
| genkit/ai/generate/output/tokens | Counter | Output tokens |
| genkit/ai/generate/input/characters | Counter | Input characters |
| genkit/ai/generate/output/characters | Counter | Output characters |
| genkit/ai/generate/input/images | Counter | Input images |
| genkit/ai/generate/output/images | Counter | Output images |
| genkit/ai/generate/input/audio | Counter | Input audio files |
| genkit/ai/generate/output/audio | Counter | Output audio files |
Each generate metric contains the following dimensions:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| modelName | The name of the model |
| featureName | The name of the parent feature being executed |
| path | The path of execution from the feature root to this action. eg. '/myFeature/parentAction/thisAction' |
| latencyMs | The response time taken by the model |
| status | 'success' or 'failure' depending on whether or not the feature request succeeded |
| error | Only set when status=failure. Contains the error type that caused the failure |
| source | The Genkit source language. Eg. 'ts' |
| sourceVersion | The Genkit framework version |
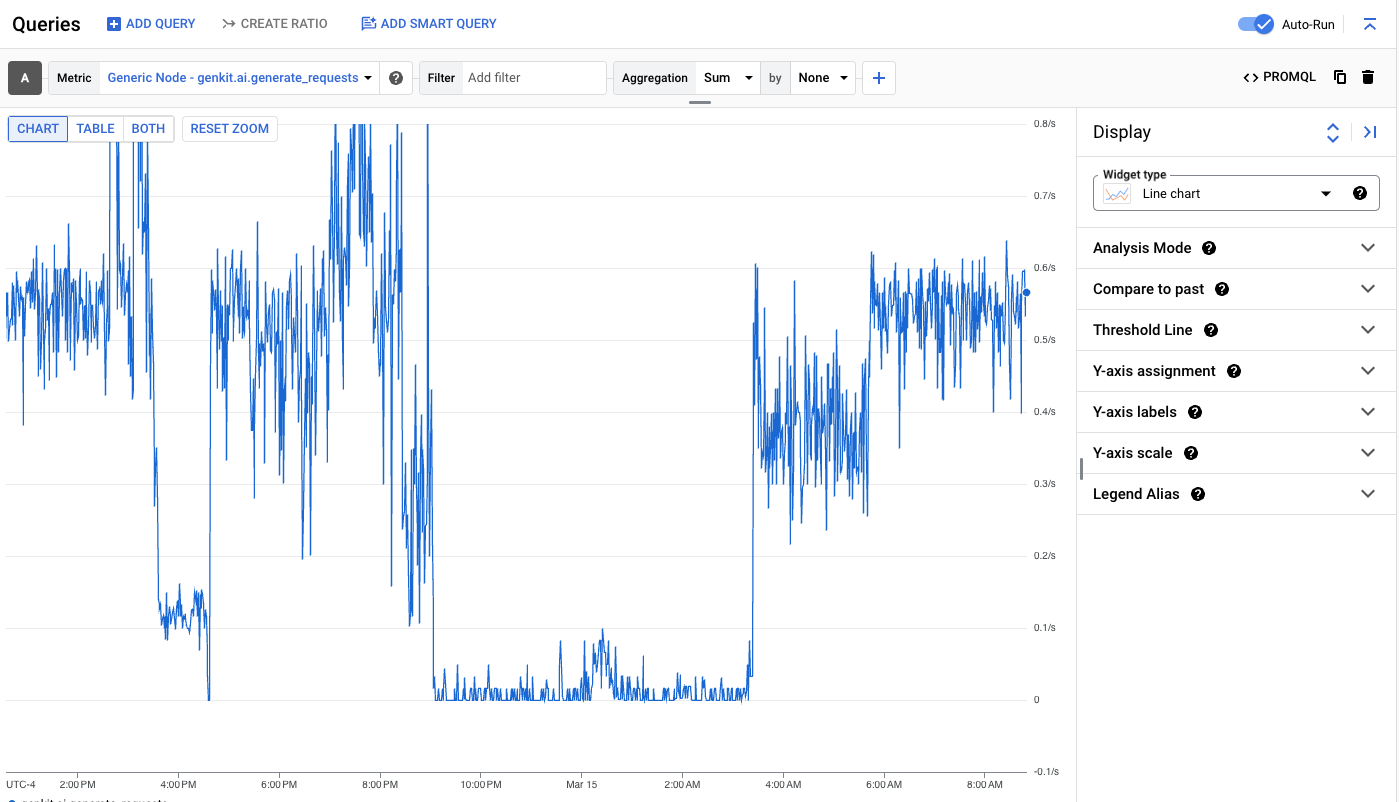
Visualizing metrics can be done through the Metrics Explorer. Using the left hand side menu, click 'Metrics explorer' under the 'Explore' heading.
Select a metrics by clicking on the 'Select a metric' dropdown, selecting 'Generic Node', 'Genkit', and a metric.
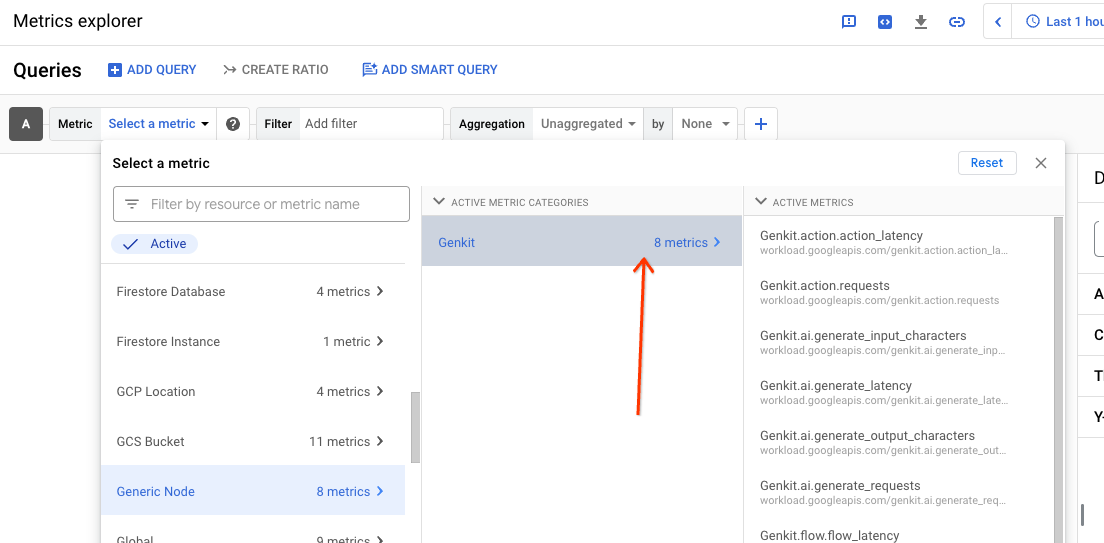
The visualization of the metric will depend on its type (counter, histogram, etc). The Metrics Explorer provides robust aggregation and querying facilities to help graph metrics by their various dimensions.
Telemetry delay
There may be a slight delay before telemetry for a particular execution of a flow is displayed in Cloud's operations suite. In most cases, this delay is under 1 minute.
Quotas and limits
There are several quotas that are important to keep in mind:
Cost
Cloud Logging, Cloud Trace, and Cloud Monitoring have generous free tiers. Specific pricing can be found at the following links:
