Sau khi thêm SDK App Check vào ứng dụng, nhưng trước khi bật chế độ thực thi App Check, bạn nên đảm bảo rằng việc này sẽ không làm gián đoạn người dùng hợp pháp hiện tại.
Một công cụ quan trọng mà bạn có thể dùng để đưa ra quyết định này cho Firebase AI Logic, Data Connect, Realtime Database, Cloud Firestore, Cloud Storage, Authentication, Google Identity cho iOS, Maps JavaScript API và Places API (Mới) là màn hình số liệu về yêu cầu App Check.
Để xem các chỉ số về yêu cầu App Check cho một sản phẩm, hãy mở phần App Check của bảng điều khiển Firebase. Ví dụ:
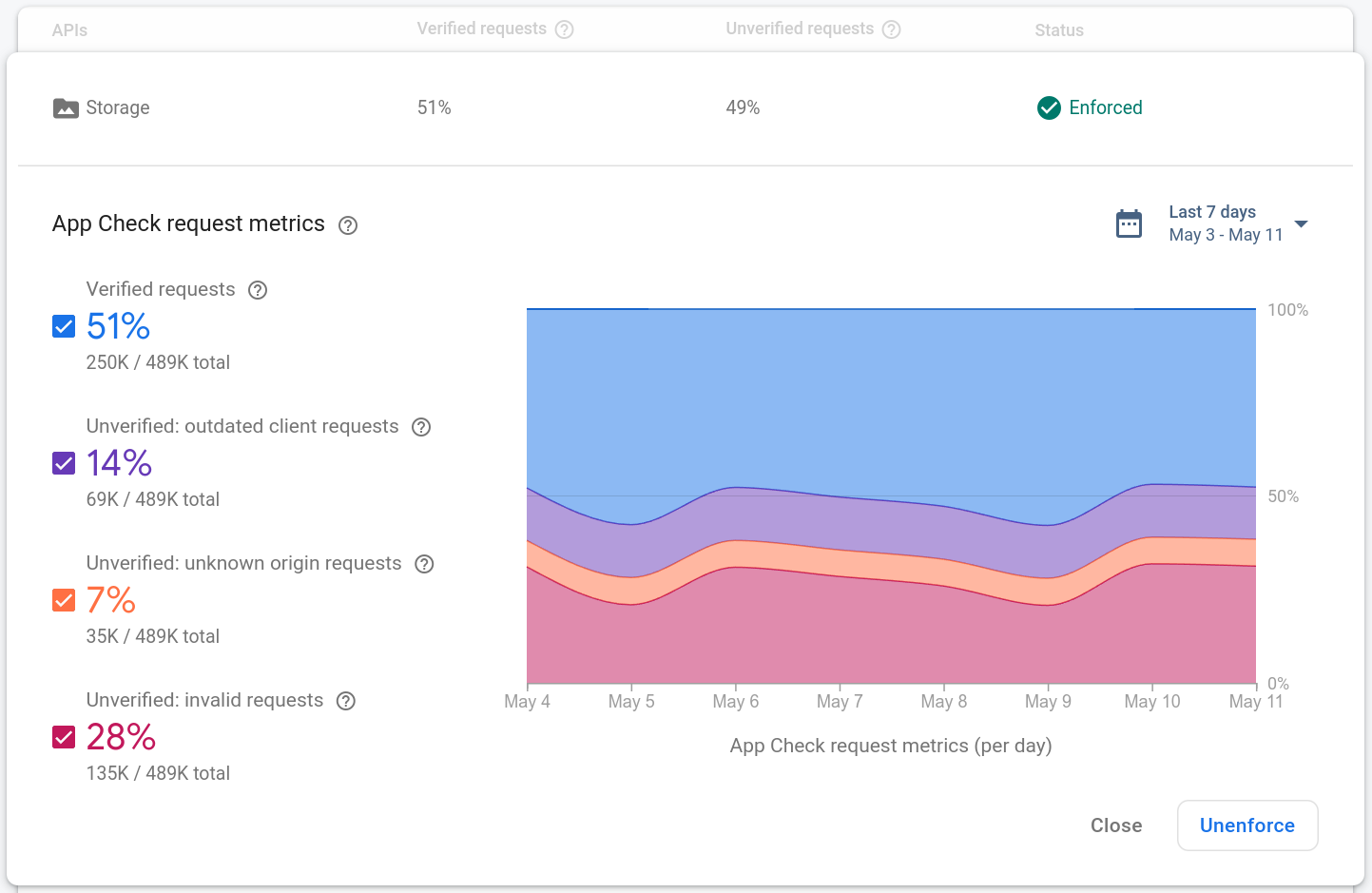
Các chỉ số yêu cầu cho từng sản phẩm được chia thành 4 danh mục:
Đã xác minh là những yêu cầu có mã thông báo App Check hợp lệ. Sau khi bạn bật chế độ thực thi App Check, chỉ những yêu cầu thuộc danh mục này mới thành công.
Yêu cầu Ứng dụng lỗi thời là những yêu cầu thiếu mã thông báo App Check. Các yêu cầu này có thể đến từ một phiên bản cũ của Firebase SDK trước khi App Check được đưa vào ứng dụng.
Yêu cầu Nguồn không xác định là những yêu cầu thiếu mã thông báo App Check và có vẻ như không đến từ SDK Firebase. Đây có thể là những yêu cầu được thực hiện bằng khoá API bị đánh cắp hoặc yêu cầu giả mạo được thực hiện mà không có Firebase SDK.
Yêu cầu không hợp lệ là những yêu cầu có mã thông báo App Check không hợp lệ. Mã thông báo này có thể đến từ một ứng dụng khách không xác thực đang cố gắng mạo danh ứng dụng của bạn hoặc từ môi trường mô phỏng.
Việc phân phối các danh mục này cho ứng dụng của bạn sẽ cho bạn biết thời điểm bạn quyết định bật chế độ thực thi. Dưới đây là một số nguyên tắc:
Nếu hầu hết các yêu cầu gần đây đều đến từ những ứng dụng khách đã được xác minh, hãy cân nhắc việc bật chế độ thực thi để bắt đầu bảo vệ các tài nguyên phụ trợ của bạn.
Nếu một phần đáng kể trong số các yêu cầu gần đây đến từ những ứng dụng có khả năng đã lỗi thời, thì để tránh làm gián đoạn người dùng, hãy cân nhắc chờ thêm nhiều người dùng cập nhật ứng dụng của bạn trước khi bật chế độ thực thi. Việc thực thi App Check trên một ứng dụng đã phát hành sẽ làm hỏng các phiên bản ứng dụng trước đó chưa được tích hợp với SDK App Check.
Nếu ứng dụng của bạn chưa ra mắt, bạn nên bật chế độ thực thi App Check ngay lập tức, vì không có ứng dụng nào lỗi thời đang được sử dụng.
Các bước tiếp theo
Khi hiểu rõ cách App Check sẽ ảnh hưởng đến người dùng và bạn đã sẵn sàng tiếp tục, bạn có thể bật chế độ thực thi App Check cho Firebase AI Logic, Data Connect, Realtime Database, Cloud Firestore, Cloud Storage, Authentication, Google Identity cho iOS, Maps JavaScript API và Places API (Mới).
