تتضمّن العديد من التطبيقات مستندات تمت فهرستها حسب المواقع الجغرافية الفعلية. على سبيل المثال، قد يسمح تطبيقك للمستخدمين بتصفُّح المتاجر بالقرب من موقعهم الجغرافي الحالي.
الحل: Geohashes
Geohash هو نظام لترميز زوج (latitude, longitude) في سلسلة Base32 واحدة. في نظام Geohash، ينقسم العالم إلى شبكة مستطيلة.
يحدد كل حرف من سلسلة Geohash أحد الأقسام الفرعية البالغ عددها 32
لتجزئة البادئة. على سبيل المثال، Geohash abcd هي واحدة من 32 علامة تجزئة مكوّنة من أربعة أحرف ومضمّنة بالكامل في Geohash abc الأكبر.
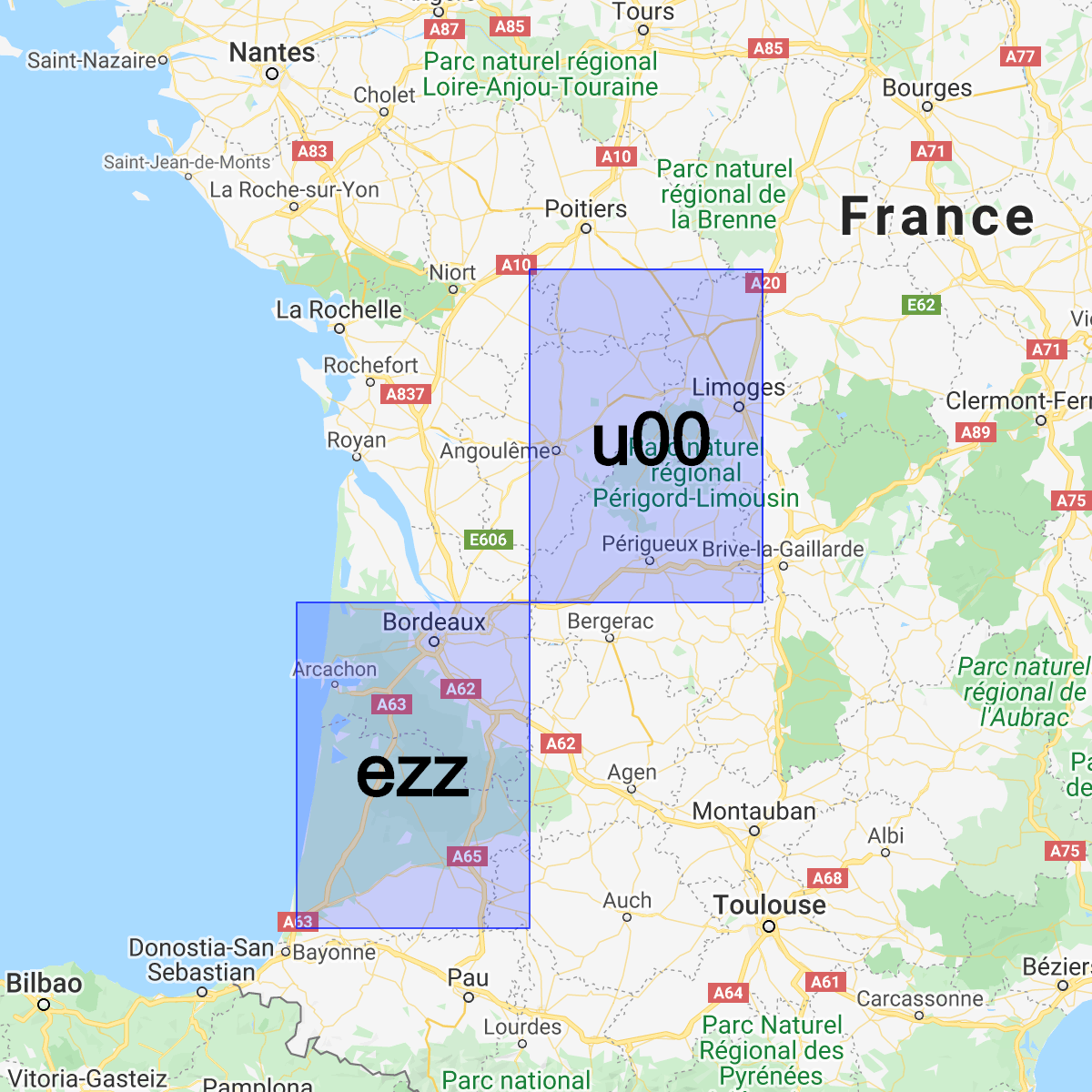
كلما زاد طول البادئة المشتركة بين جزأين، كلما اقتربتهما من بعضهما البعض. على سبيل المثال، إنّ القيمة abcdef أقرب إلى abcdeg من قيمة abcdff. ومع ذلك،
العكس ليس صحيحًا! قد تكون منطقتان قريبتين جدًا من بعضهما البعض
بينما تحتويان أشكال Geohashes مختلفة جدًا:
يمكننا استخدام عناصر Geohashes لتخزين المستندات والاستعلام عنها حسب موضعها في Cloud Firestore بكفاءة معقولة مع الحاجة إلى حقل واحد فقط مفهرس.
تثبيت مكتبة المساعدة
يتضمن إنشاء وتحليل Geohashes بعض العمليات الحسابية الصعبة، لذلك أنشأنا مكتبات مساعدة لاستخلاص أصعب الأجزاء على Android وApple وWeb:
Web
// Install from NPM. If you prefer to use a static .js file visit
// https://github.com/firebase/geofire-js/releases and download
// geofire-common.min.js from the latest version
npm install --save geofire-common
Web
// Install from NPM. If you prefer to use a static .js file visit
// https://github.com/firebase/geofire-js/releases and download
// geofire-common.min.js from the latest version
npm install --save geofire-common
Swift
Kotlin+KTX
// Add this to your app/build.gradle
implementation 'com.firebase:geofire-android-common:3.2.0'
Java
// Add this to your app/build.gradle
implementation 'com.firebase:geofire-android-common:3.1.0'
تخزين Geohashes
لكل مستند تريد فهرسته حسب الموقع، ستحتاج إلى تخزين حقل Geohash:
Web
import { doc, updateDoc } from 'firebase/firestore';
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point
const lat = 51.5074;
const lng = 0.1278;
const hash = geofire.geohashForLocation([lat, lng]);
// Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash
// for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons.
const londonRef = doc(db, 'cities', 'LON');
await updateDoc(londonRef, {
geohash: hash,
lat: lat,
lng: lng
});Web
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point
const lat = 51.5074;
const lng = 0.1278;
const hash = geofire.geohashForLocation([lat, lng]);
// Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash
// for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons.
const londonRef = db.collection('cities').doc('LON');
londonRef.update({
geohash: hash,
lat: lat,
lng: lng
}).then(() => {
// ...
});Swift
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point
let latitude = 51.5074
let longitude = 0.12780
let location = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: latitude, longitude: longitude)
let hash = GFUtils.geoHash(forLocation: location)
// Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash
// for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons.
let documentData: [String: Any] = [
"geohash": hash,
"lat": latitude,
"lng": longitude
]
let londonRef = db.collection("cities").document("LON")
londonRef.updateData(documentData) { error in
// ...
}Kotlin+KTX
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point
val lat = 51.5074
val lng = 0.1278
val hash = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashForLocation(GeoLocation(lat, lng))
// Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash
// for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons.
val updates: MutableMap<String, Any> = mutableMapOf(
"geohash" to hash,
"lat" to lat,
"lng" to lng,
)
val londonRef = db.collection("cities").document("LON")
londonRef.update(updates)
.addOnCompleteListener {
// ...
}Java
// Compute the GeoHash for a lat/lng point
double lat = 51.5074;
double lng = 0.1278;
String hash = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashForLocation(new GeoLocation(lat, lng));
// Add the hash and the lat/lng to the document. We will use the hash
// for queries and the lat/lng for distance comparisons.
Map<String, Object> updates = new HashMap<>();
updates.put("geohash", hash);
updates.put("lat", lat);
updates.put("lng", lng);
DocumentReference londonRef = db.collection("cities").document("LON");
londonRef.update(updates)
.addOnCompleteListener(new OnCompleteListener<Void>() {
@Override
public void onComplete(@NonNull Task<Void> task) {
// ...
}
});طلب بحث عن Geohashes
تسمح لنا العناصر الجغرافية بالتقريب من استعلامات المنطقة من خلال ضم مجموعة من الاستعلامات في حقل Geohash ثم تصفية بعض النتائج الموجبة الخاطئة:
Web
import { collection, query, orderBy, startAt, endAt, getDocs } from 'firebase/firestore';
// Find cities within 50km of London
const center = [51.5074, 0.1278];
const radiusInM = 50 * 1000;
// Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue
// a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds
// depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4.
const bounds = geofire.geohashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM);
const promises = [];
for (const b of bounds) {
const q = query(
collection(db, 'cities'),
orderBy('geohash'),
startAt(b[0]),
endAt(b[1]));
promises.push(getDocs(q));
}
// Collect all the query results together into a single list
const snapshots = await Promise.all(promises);
const matchingDocs = [];
for (const snap of snapshots) {
for (const doc of snap.docs) {
const lat = doc.get('lat');
const lng = doc.get('lng');
// We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash
// accuracy, but most will match
const distanceInKm = geofire.distanceBetween([lat, lng], center);
const distanceInM = distanceInKm * 1000;
if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) {
matchingDocs.push(doc);
}
}
}Web
// Find cities within 50km of London
const center = [51.5074, 0.1278];
const radiusInM = 50 * 1000;
// Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue
// a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds
// depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4.
const bounds = geofire.geohashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM);
const promises = [];
for (const b of bounds) {
const q = db.collection('cities')
.orderBy('geohash')
.startAt(b[0])
.endAt(b[1]);
promises.push(q.get());
}
// Collect all the query results together into a single list
Promise.all(promises).then((snapshots) => {
const matchingDocs = [];
for (const snap of snapshots) {
for (const doc of snap.docs) {
const lat = doc.get('lat');
const lng = doc.get('lng');
// We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash
// accuracy, but most will match
const distanceInKm = geofire.distanceBetween([lat, lng], center);
const distanceInM = distanceInKm * 1000;
if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) {
matchingDocs.push(doc);
}
}
}
return matchingDocs;
}).then((matchingDocs) => {
// Process the matching documents
// ...
});
Swift
// Find cities within 50km of London
let center = CLLocationCoordinate2D(latitude: 51.5074, longitude: 0.1278)
let radiusInM: Double = 50 * 1000
// Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue
// a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds
// depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4.
let queryBounds = GFUtils.queryBounds(forLocation: center,
withRadius: radiusInM)
let queries = queryBounds.map { bound -> Query in
return db.collection("cities")
.order(by: "geohash")
.start(at: [bound.startValue])
.end(at: [bound.endValue])
}
@Sendable func fetchMatchingDocs(from query: Query,
center: CLLocationCoordinate2D,
radiusInMeters: Double) async throws -> [QueryDocumentSnapshot] {
let snapshot = try await query.getDocuments()
// Collect all the query results together into a single list
return snapshot.documents.filter { document in
let lat = document.data()["lat"] as? Double ?? 0
let lng = document.data()["lng"] as? Double ?? 0
let coordinates = CLLocation(latitude: lat, longitude: lng)
let centerPoint = CLLocation(latitude: center.latitude, longitude: center.longitude)
// We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash accuracy, but
// most will match
let distance = GFUtils.distance(from: centerPoint, to: coordinates)
return distance <= radiusInM
}
}
// After all callbacks have executed, matchingDocs contains the result. Note that this code
// executes all queries serially, which may not be optimal for performance.
do {
let matchingDocs = try await withThrowingTaskGroup(of: [QueryDocumentSnapshot].self) { group -> [QueryDocumentSnapshot] in
for query in queries {
group.addTask {
try await fetchMatchingDocs(from: query, center: center, radiusInMeters: radiusInM)
}
}
var matchingDocs = [QueryDocumentSnapshot]()
for try await documents in group {
matchingDocs.append(contentsOf: documents)
}
return matchingDocs
}
print("Docs matching geoquery: \(matchingDocs)")
} catch {
print("Unable to fetch snapshot data. \(error)")
}Kotlin+KTX
// Find cities within 50km of London
val center = GeoLocation(51.5074, 0.1278)
val radiusInM = 50.0 * 1000.0
// Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue
// a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds
// depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4.
val bounds = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM)
val tasks: MutableList<Task<QuerySnapshot>> = ArrayList()
for (b in bounds) {
val q = db.collection("cities")
.orderBy("geohash")
.startAt(b.startHash)
.endAt(b.endHash)
tasks.add(q.get())
}
// Collect all the query results together into a single list
Tasks.whenAllComplete(tasks)
.addOnCompleteListener {
val matchingDocs: MutableList<DocumentSnapshot> = ArrayList()
for (task in tasks) {
val snap = task.result
for (doc in snap!!.documents) {
val lat = doc.getDouble("lat")!!
val lng = doc.getDouble("lng")!!
// We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash
// accuracy, but most will match
val docLocation = GeoLocation(lat, lng)
val distanceInM = GeoFireUtils.getDistanceBetween(docLocation, center)
if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) {
matchingDocs.add(doc)
}
}
}
// matchingDocs contains the results
// ...
}Java
// Find cities within 50km of London
final GeoLocation center = new GeoLocation(51.5074, 0.1278);
final double radiusInM = 50 * 1000;
// Each item in 'bounds' represents a startAt/endAt pair. We have to issue
// a separate query for each pair. There can be up to 9 pairs of bounds
// depending on overlap, but in most cases there are 4.
List<GeoQueryBounds> bounds = GeoFireUtils.getGeoHashQueryBounds(center, radiusInM);
final List<Task<QuerySnapshot>> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
for (GeoQueryBounds b : bounds) {
Query q = db.collection("cities")
.orderBy("geohash")
.startAt(b.startHash)
.endAt(b.endHash);
tasks.add(q.get());
}
// Collect all the query results together into a single list
Tasks.whenAllComplete(tasks)
.addOnCompleteListener(new OnCompleteListener<List<Task<?>>>() {
@Override
public void onComplete(@NonNull Task<List<Task<?>>> t) {
List<DocumentSnapshot> matchingDocs = new ArrayList<>();
for (Task<QuerySnapshot> task : tasks) {
QuerySnapshot snap = task.getResult();
for (DocumentSnapshot doc : snap.getDocuments()) {
double lat = doc.getDouble("lat");
double lng = doc.getDouble("lng");
// We have to filter out a few false positives due to GeoHash
// accuracy, but most will match
GeoLocation docLocation = new GeoLocation(lat, lng);
double distanceInM = GeoFireUtils.getDistanceBetween(docLocation, center);
if (distanceInM <= radiusInM) {
matchingDocs.add(doc);
}
}
}
// matchingDocs contains the results
// ...
}
});القيود
يمنحنا استخدام Geohashes للاستعلام عن المواقع إمكانات جديدة، ولكن يأتي مع مجموعة القيود الخاصة به:
- الإيجابيات الخاطئة - لا يُعد طلب البحث باستخدام Geohash دقيقًا، ويجب تصفية النتائج الإيجابية الخاطئة من جانب العميل. تضيف هذه القراءات الإضافية التكلفة ووقت الاستجابة إلى تطبيقك.
- حالات الحافة - تعتمد طريقة طلب البحث هذه على تقدير المسافة بين سطور خطوط الطول/العرض. تقل دقة هذا التقدير كلما اقتربت النقاط من القطب الشمالي أو الجنوبي مما يعني أن استعلامات Geohash تكون أكثر إيجابية خاطئة في خطوط العرض القصوى.

